55 Maps
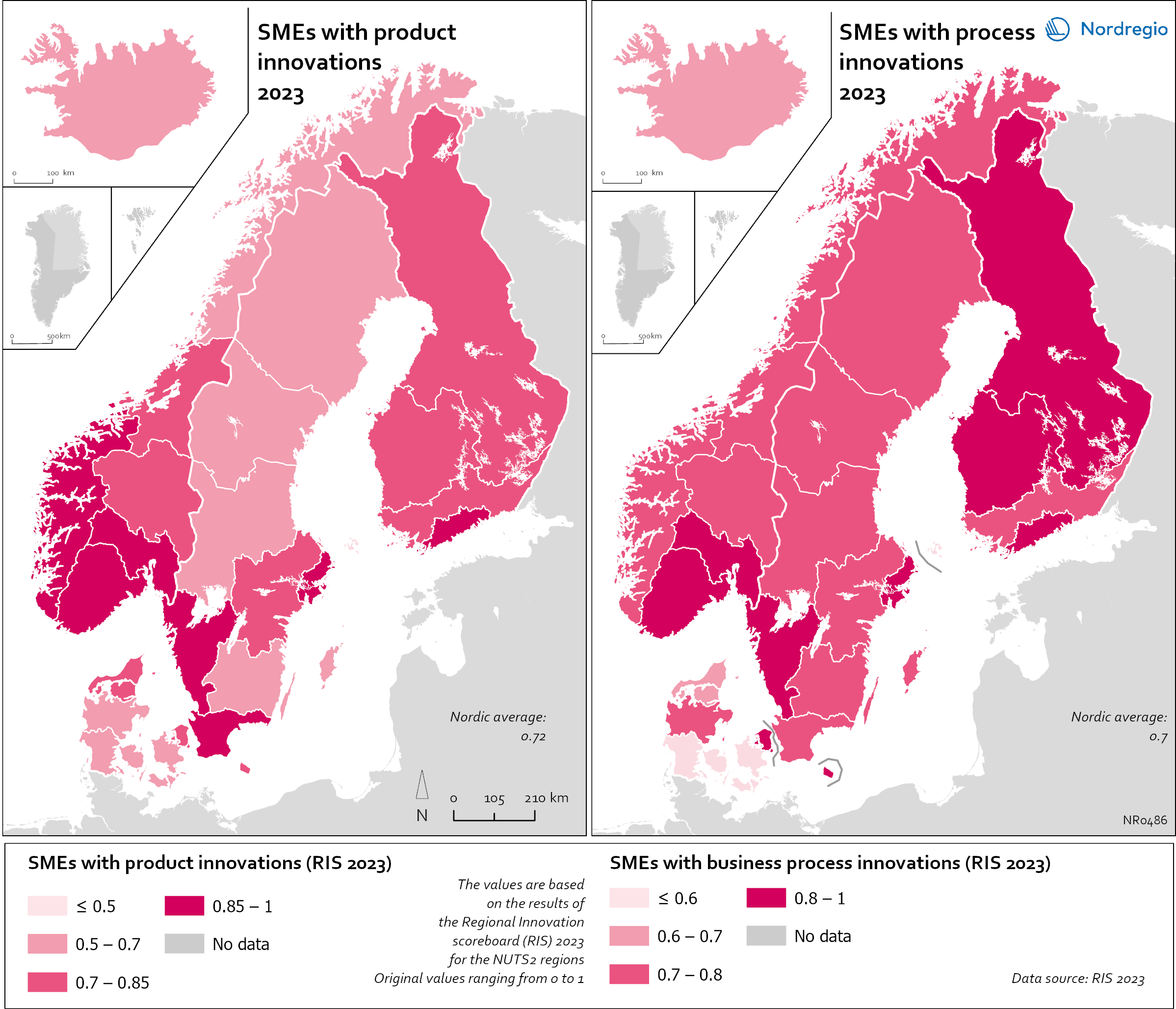
Small and Medium Sized Enterprises (SMEs) with product and business process innovation in 2023
These maps depicts Small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs) with product innovation (left map) and process innovation (right map) in 2023. The data is displayed at the NUTS2 level and the data comes from the Regional Innovation Scoreboard 2023. The left map depicts SMEs introducing product innovations as a percentage of SMEs in the Nordic regions, calculated as the share of SMEs who introduced at least one product innovation. The values for the map are normalised from 0–10. In this context, a product innovation is defined as the market introduction of a good or service that is new or significantly improved with respect to its capabilities, user-friendliness, components, or sub-systems. Rural regions tend to have lower levels of SMEs with product innovations, while urban regions have the highest levels. In 2023, Åland (0.235) had the lowest number of SMEs with product innovations in the Nordic Region, while Oslo had the highest (1.0). Etelä-Suomi and Stockholm regions were slightly behind, with 0.954 and 0.948, respectively. In Denmark, the leading regions were the Capital Region (Hovedstaden) and Northern Jutland (Nordjylland), with 0.719 and 0.715, respectively. Southern Denmark (Syddanmark) had the lowest level in Denmark, at 0.545. In Norway, the lowest value was in Northern Norway (Nord-Norge), 0.67, while in Sweden it was Middle Norrland (Mellersta Norrland), with 0.53. Taken as an average across the Nordic countries, Norway has a significantly higher number of SMEs with product innovations than the other countries. The right map shows the share of SMEs introducing at least one business-process innovation, which includes process, marketing, and organisational innovations. In general, Nordic SMEs are more likely to innovate in products rather than processes. The highest shares of process-innovating SMEs are found in most of the Finnish regions ranging from 0,79 in Länsi-Suomi to 0,91 in Etelä-Suomi, except of Åland…
2025 April
- Economy
- Nordic Region
- Research and innovation
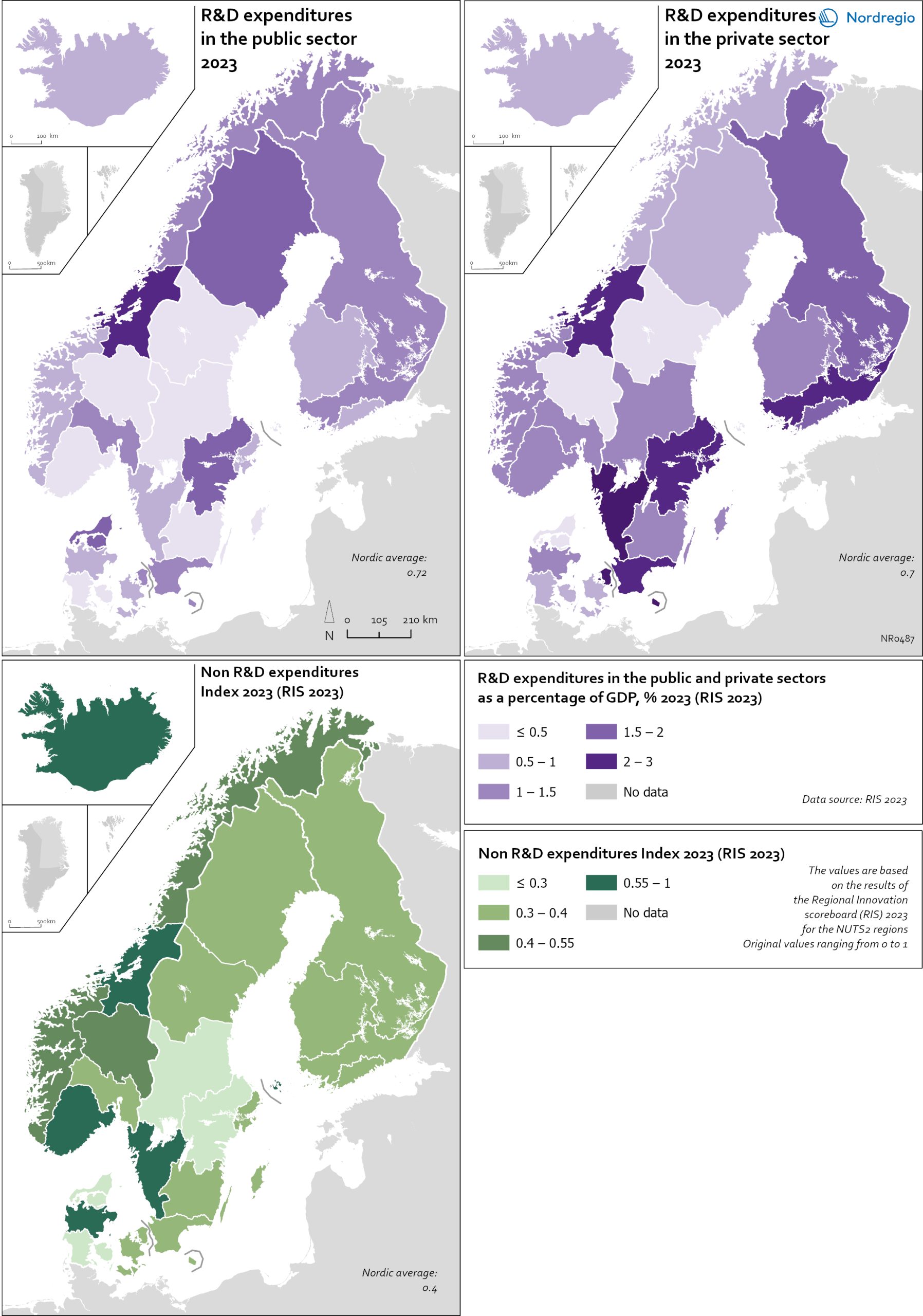
R&D and non-R&D expenditures in the public and private sector
These maps shows the expenditure on Research and Development (R&D) in the public and business sectors as a percentage of regional GDP, along with non-R&D innovation expenditure in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) as a percentage of turnover. Together, these metrics offer a comprehensive understanding of the innovation landscape and provide insights into governments’ and higher education institutions’ commitment to foundational research, as well as the competitiveness and dynamism of the business environment and SMEs’ innovation capacity. By considering investment in both R&D and non-R&D activities, these indicators illustrate a broad spectrum of innovation drivers, from basic research to market-driven initiatives, and underscore the diverse pathways through which innovation fosters economic growth and social progress First, the top left map showcases R&D expenditure in the public sector as a percentage of GDP in the Nordic countries in 2023. In that year, the European level of R&D expenditure in the public sector, as a percentage of GDP, was 0.78%. By comparison, the Nordic average was 0.9%. While the more urban regions, in general, lead the Nordic regions, this is not always the case, as shown by the variation between the frontrunners. The leading region is Trøndelag (including Norway’s third-largest city, Trondheim), with 2.30% of regional GDP. It is in third place in the EU as a whole. The next regions are Övre Norrland with 1.77%, Northern Jutland with 1.54%, Östra Mellansverige with 1.52%, and Hovedstaden with 1.49%. A common feature of most of the top-ranking regions is that they host universities and other higher education institutions known for innovation practices. Most Nordic regions have not seen significant increases or decreases in public R&D spending between 2016 and 2023. The top right map focuses on the private sector’s investment in research and development activities and depicts R&D expenditure in the business sector…
2025 April
- Economy
- Nordic Region
- Research and innovation

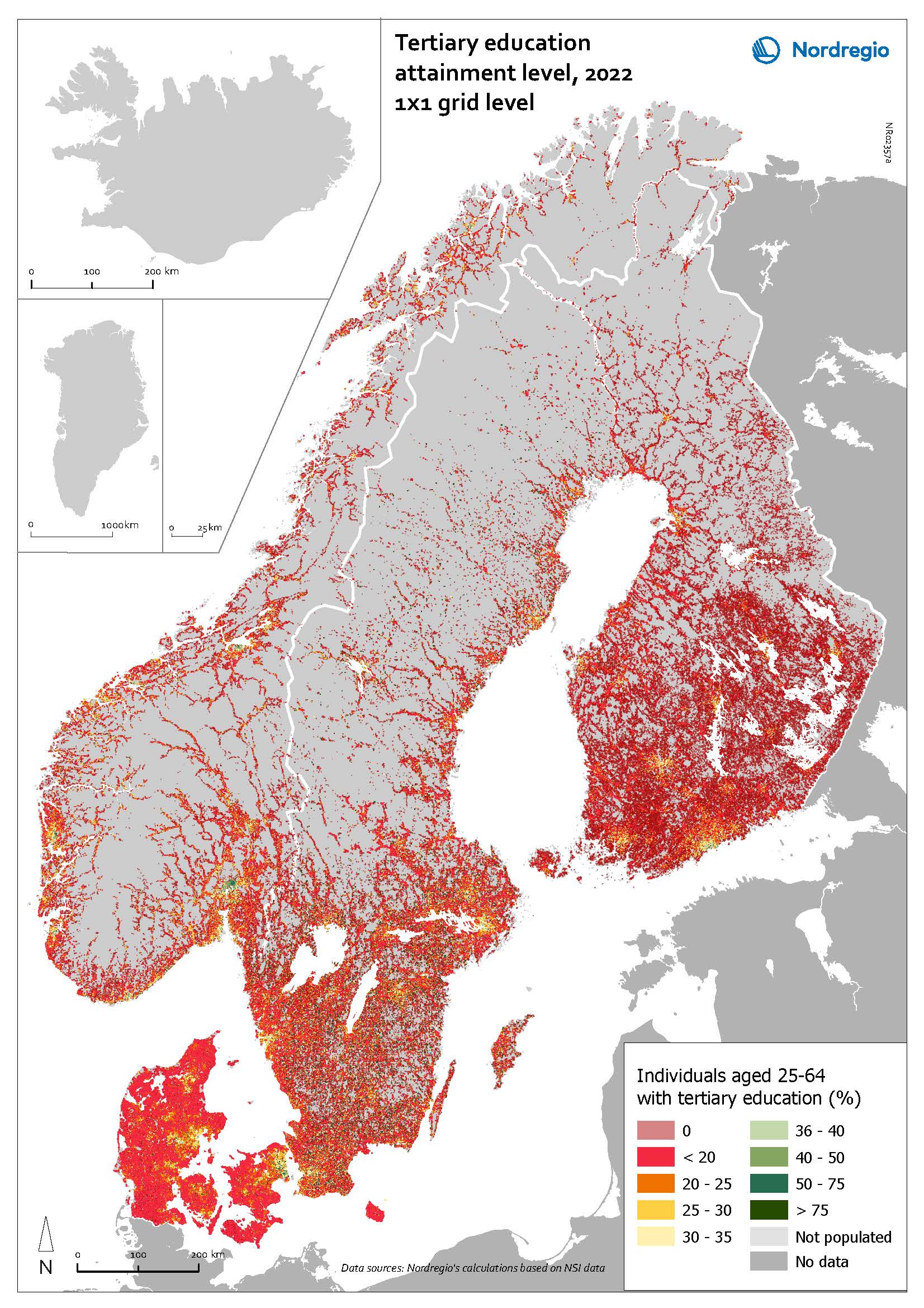
Employment in high-skilled occupations 2022
This map displays the share of high-skilled workers as a share of the total number of workers in Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map). “High-skilled workers” is here defined as group 1-3 (Managers, Professionals and Techinicians/associated professionals) of the International Standard Classification of Occupations (ISCO). For Iceland national data is used. The EU average of high-skilled workers is 43%, and the Nordic countries are at the top of the rankings – 49.5% in Finland, 51.1% in Denmark, 54.2% in Norway, 54.5% in Iceland and 58.9% in Sweden. On a regional level, the highest share is in the capitals and bigger cities, such as Stockholm (72%), Oslo (71%), Hovedstaden (Copenhagen) (60%), Uppsala (60%) and Uusima (Helsinki) (59%). The lowest shares are in the Finnish regions of EteläPohjanmaa, Keski-Pohjanmaa, Satakunta and Etelä-Savo (less than 40%). However, this does not necessarily mean that employers will have a greater chance of successfully recruiting high-skilled workers in the future, partly because those in this group already have jobs and partly due to generally lower investments in education.
2025 April
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
- Research and innovation
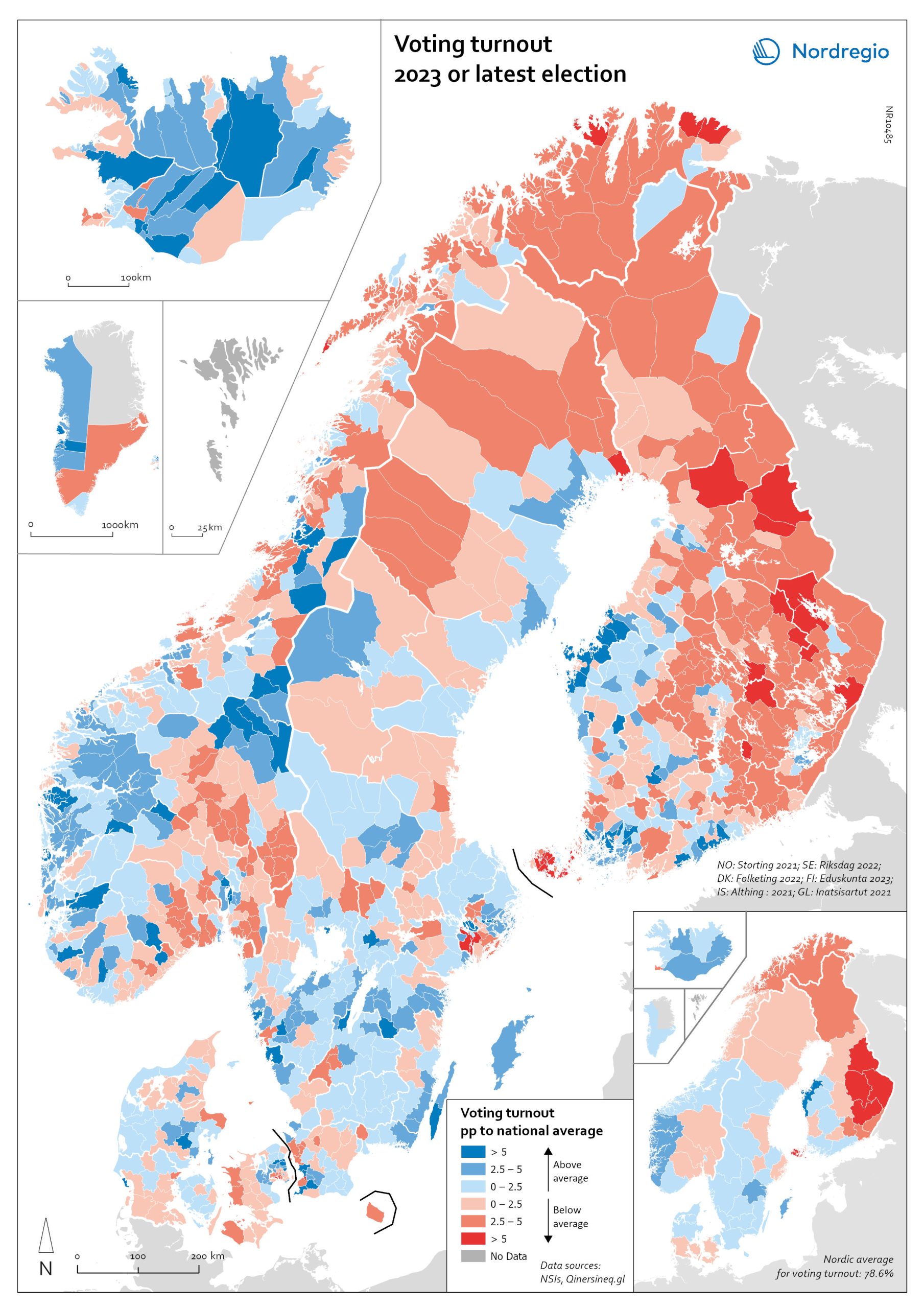
Voting turnout in national elections
Voting turnout in 2023 (or latest national election). The map illustrates voter turnout as a percentage point relative to national averages, highlighting differences in participation levels between countries. This method removes inter-country differences in participation levels, providing a clearer view of the urban-rural divide. Lower turnout is observed in eastern Finland, northern Sweden, and the more rural parts of Denmark. In Norway, the lowest turnout occurs in the north and in municipalities outside Oslo. Nationally, the highest voter turnouts are in the Faroe Islands (88%), Sweden (84.2%), and Denmark (84.16%). Lower participation rates are found in Iceland (80.1%), Norway (77.2%), Finland (68.5%), and Greenland (65.9%).
2024 May
- Nordic Region
- Others
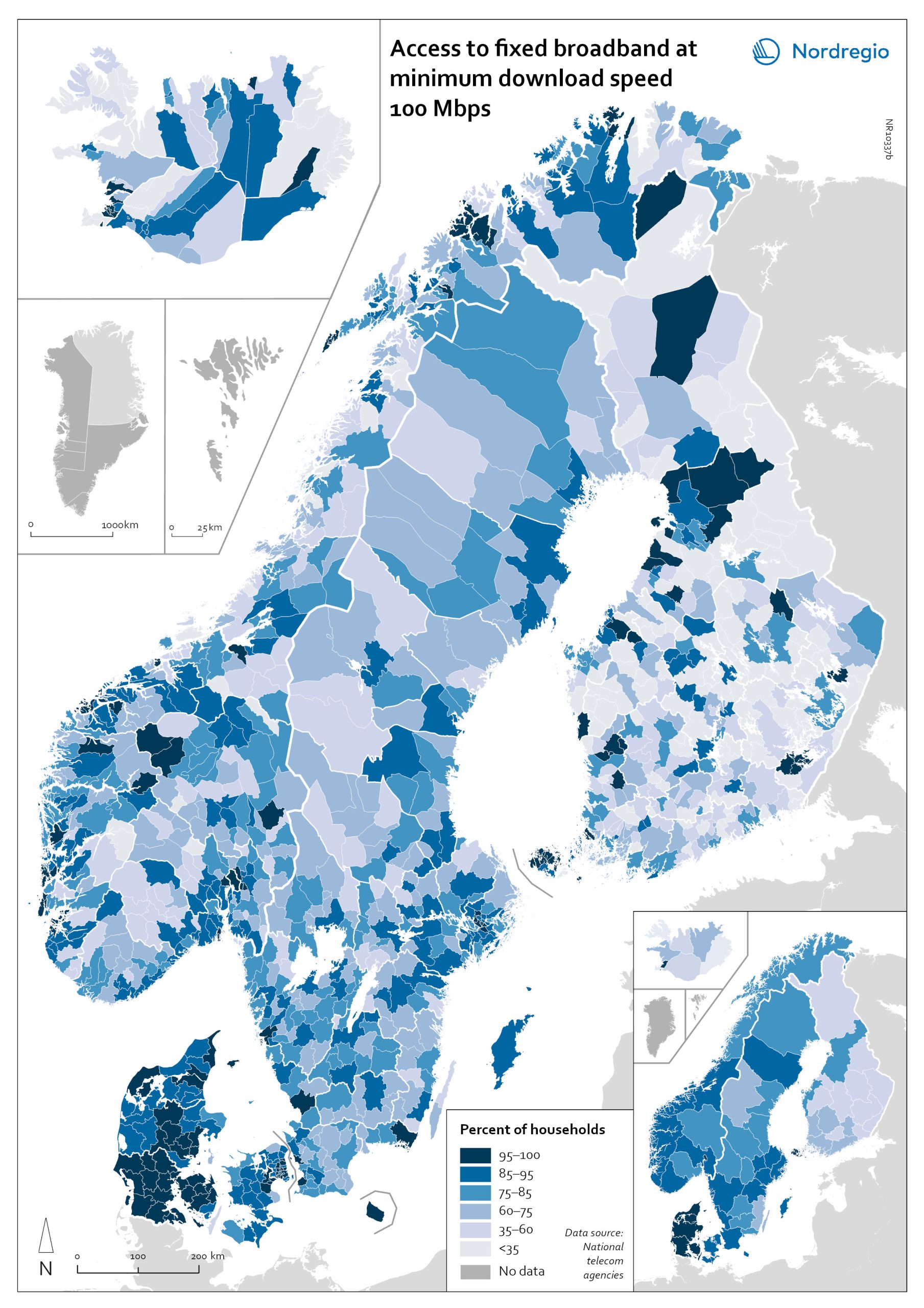
Access to fixed broadband at minimum download speed 100 Mpbs
The map shows the proportion of households that had access to fixed-line broadband with download speeds >100 Mbps (superfast broadband) at the municipal level, with darker colours indicating higher coverage. Overall, Denmark has the highest levels of connectivity, with 92% of municipalities providing superfast broadband to at least 85% of households. In over half (59%) of all Danish municipalities, almost all (>95%) of households have access to this connection speed. The lowest levels of connectivity are found in Finland. This is particularly evident in rural municipalities where, on average, less than half of households (48%) have access to superfast broadband. Connectivity levels are also rather low in some parts of Iceland, for example, the Westfjords and several municipalities in the east. Households in urban municipalities are still more likely to have access to superfast broadband than households in rural or intermediate municipalities, but the gap appears to be closing in most. This is most evident in Norway, where the average household coverage for rural municipalities increased by 31% between 2018 and 2020. By comparison, average household coverage for urban municipalities in Norway increased by only 0.7%. In the archipelago (Åland Islands, Stockholm and Helsinki), general broadband connectivity is good; however, some islands with many second homes still have poor coverage.
2022 March
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
- Others
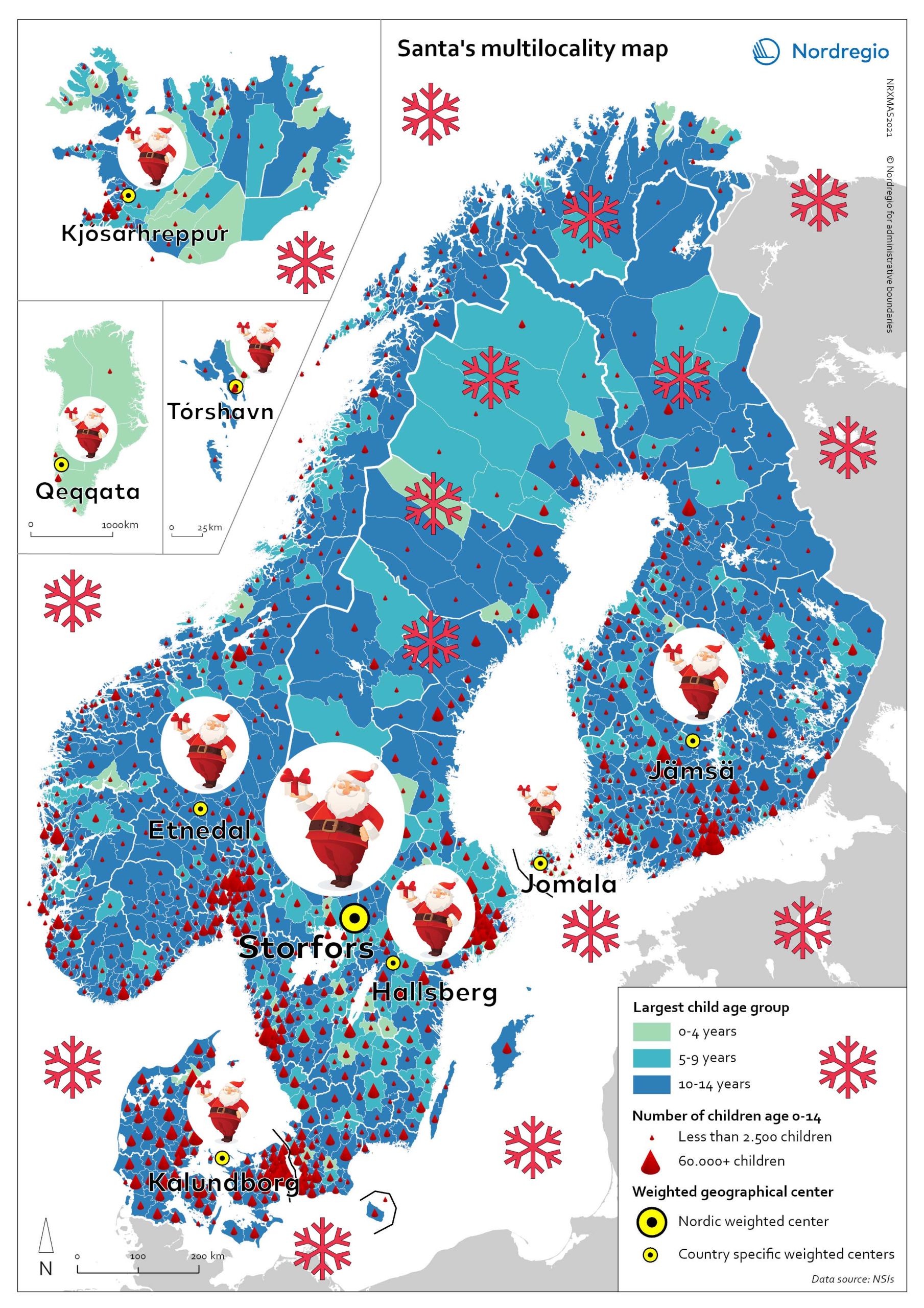
Help Santa to work remotely – where to locate in 2021?
Help Santa! To reduce his transit times and emissions – reindeers burn a lot of (green) fuel – and find an optimal remote workplace from where to deliver gifts to all the children in the Nordic Region! Santa has heard about this new trend “multilocational lifestyle” and he would like to know if this would suit him as well. But where to move? Santa’s little researchers have worked hard this year and done some mapping for him – and discovered places you have never even heard of! If Santa is to serve all children (0-14 years old) throughout the Nordic Region from a single address, the solution lies in Storfors Municipality. WHERE? – you might think. It is a real place, in Central-Southern Sweden. Here Santa has an average distance of 425 km distance to each child from his own backyard. This still sounds like awfully many kilometers. Could he be even more multilocal – with a home in each of the Nordic countries? This would help him to reduce his overall commuting to work significantly. Let’s try it! If he serves all 4.974 children in Åland from a residence (like a luxury hotel with all-inclusive and pets allowed) in Jomala Municipality, he will only have to travel 11 km to work on average. In Greenland, the distances are somewhat larger, and Santa, even with the most optimal location from a residence (a cabin) in Qeqqata Municipality would have to travel 288 km to each of the 11,748 children in the country. Can you guess what the other optimal locations would be in the Nordics? I bet you can’t so I will tell you: it’s the municipalities of Hallsberg in Sweden, Jämsä in Finland, Etnedal in Norway, Kalundborg in Denmark, Kjósarhreppur in Iceland and Tórshavn in Faroe Islands. Well, Santa…
2021 December
- Nordic Region
- Others
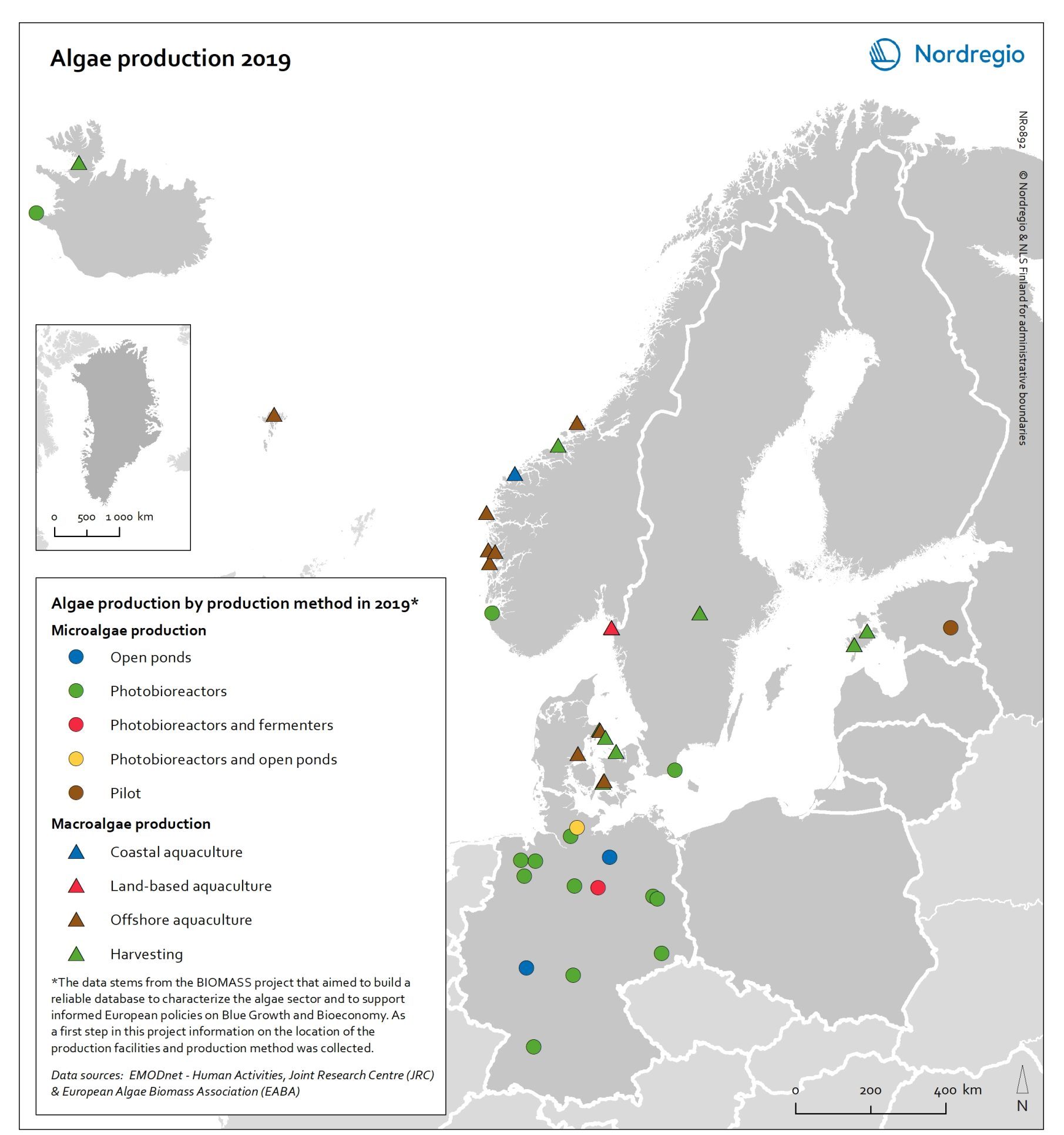
Algae production in 2019
This map shows location of algae production by production method in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea Region in 2019 Algae and seaweeds are gaining attention as useful inputs for industries as diverse as energy and human food production. Aquatic vegetation – both in the seas and in freshwater – can grow at several times the pace of terrestrial plants, and the high natural oil content of some algae makes them ideal for producing a variety of products, from cosmetic oils to biofuels. At the same time, algae farming has added value in potential synergies with farming on land, as algae farms utilise nutrient run-off and reduce eutrophication. In addition, aquatic vegetation is a highly versatile feedstock. Algae and seaweed thrive in challenging and varied conditions and can be transformed into products ranging from fuel, feeds, fertiliser, and chemicals, to third-generation sugar and biomass. These benefits are the basis for seaweed and algae emerging as one of the most important bioeconomy trends in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea region. The production of algae for food and industrial uses has hence significant potential, particularly in terms of environmental impact, but it is still at an early stage. The production of algae (both micro- and macroalgae) can take numerous forms, as shown by this map. At least nine different production methods were identified in the region covered in this analysis. A total of 41 production sites were operating in Denmark, Estonia, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Norway, Germany, and Sweden. Germany has by far the most sites for microalgae production, whereas Denmark and Norway have the most macroalgae sites.
2021 December
- Arctic
- Baltic Sea Region
- Nordic Region
- Others
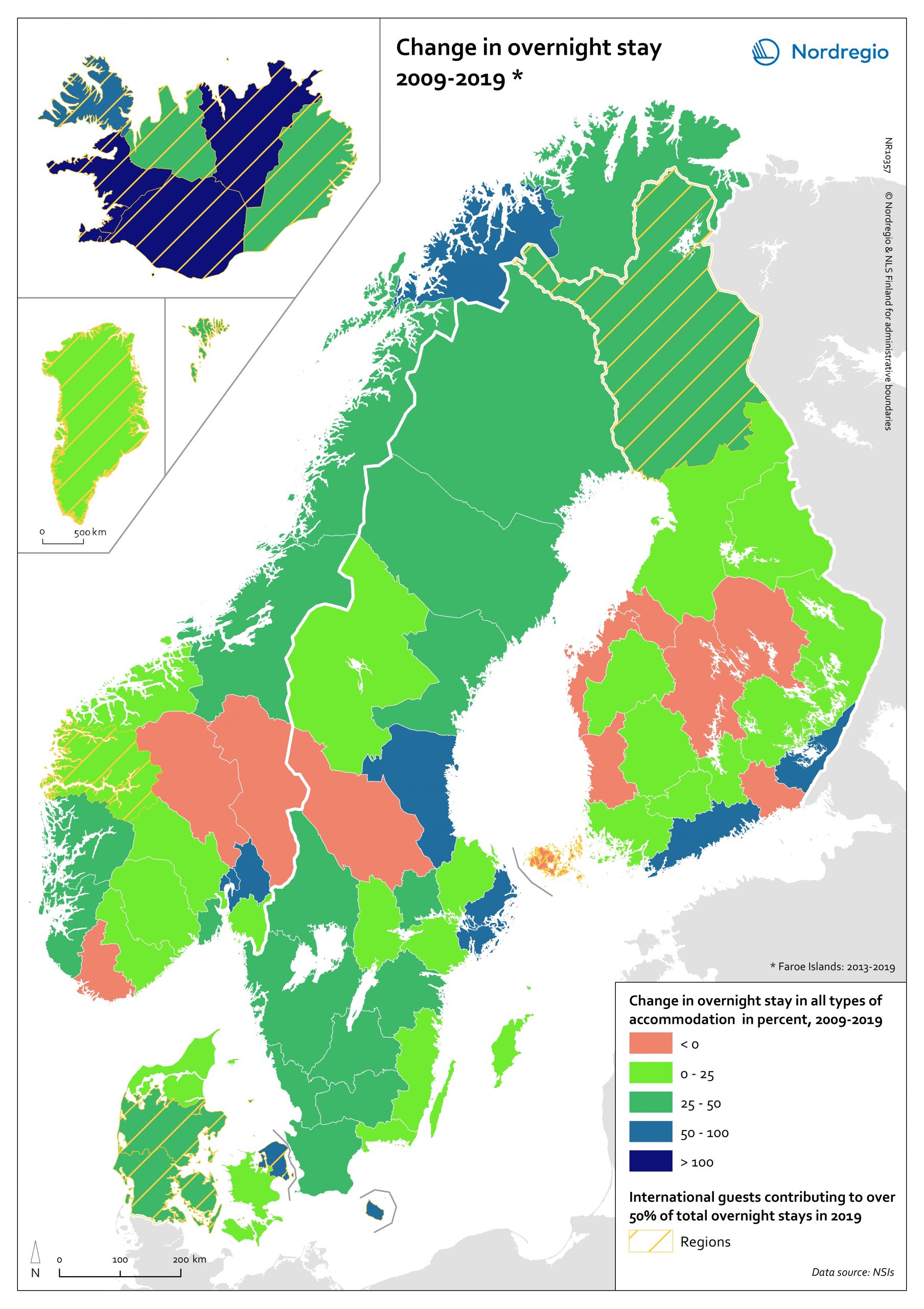
Change in overnight stay 2009-2019
The indicator measures the total overnight stays by guests in all types of accommodation, i.e., hotels and holiday resorts, camping sites, youth hostels, marinas, and holiday cottages. The map shows the change in percent from 2009 and 2019 (Faroe Island: 2013-2019 due to limited data availability). The orange colour indicates a shrink, while bluish colours indicate an increase. Bluer the colour is, larger is the increase. The shaded colour in yellow highlights the regions where international guests contributed to more than half of the total overnight stays in 2019. Most Nordic regions and territories have experienced an increase in the number of overnight stays during the last decade. The most dramatic increase can be observed in Iceland, with 5 of its 8 regions witnessing an increase in overnight stays over 100% between 2009-2019. The overnight stays in Suðurnes have increased by 451% during 2009-2019, being the largest increase in the Nordic Region. It’s also worth noting that the nearly all the regions and territories with more international guests have an increase in the total number of overnight stays, indicating that international tourism is playing a more important role in the Nordic tourism industry. The only exception is Åland, whose overnight stays dropped by 5% during 2009-2019. The traditional skiing destinations in Norway and Sweden have also witnessed a decrease in their total overnight stays, i.e., Hedmark, Oppland and Dalarna. Hedmark, among all the Nordic regions and territories, experienced the largest decline of overnight stays of 15% between 2009-2019. The number of overnight stays in some regions in eastern and central Finland also decreased from 2009 to 2019, e.g., Central Ostrobothnia and Satakunta, with domestic guests as the main tourists.
2021 February
- Nordic Region
- Others
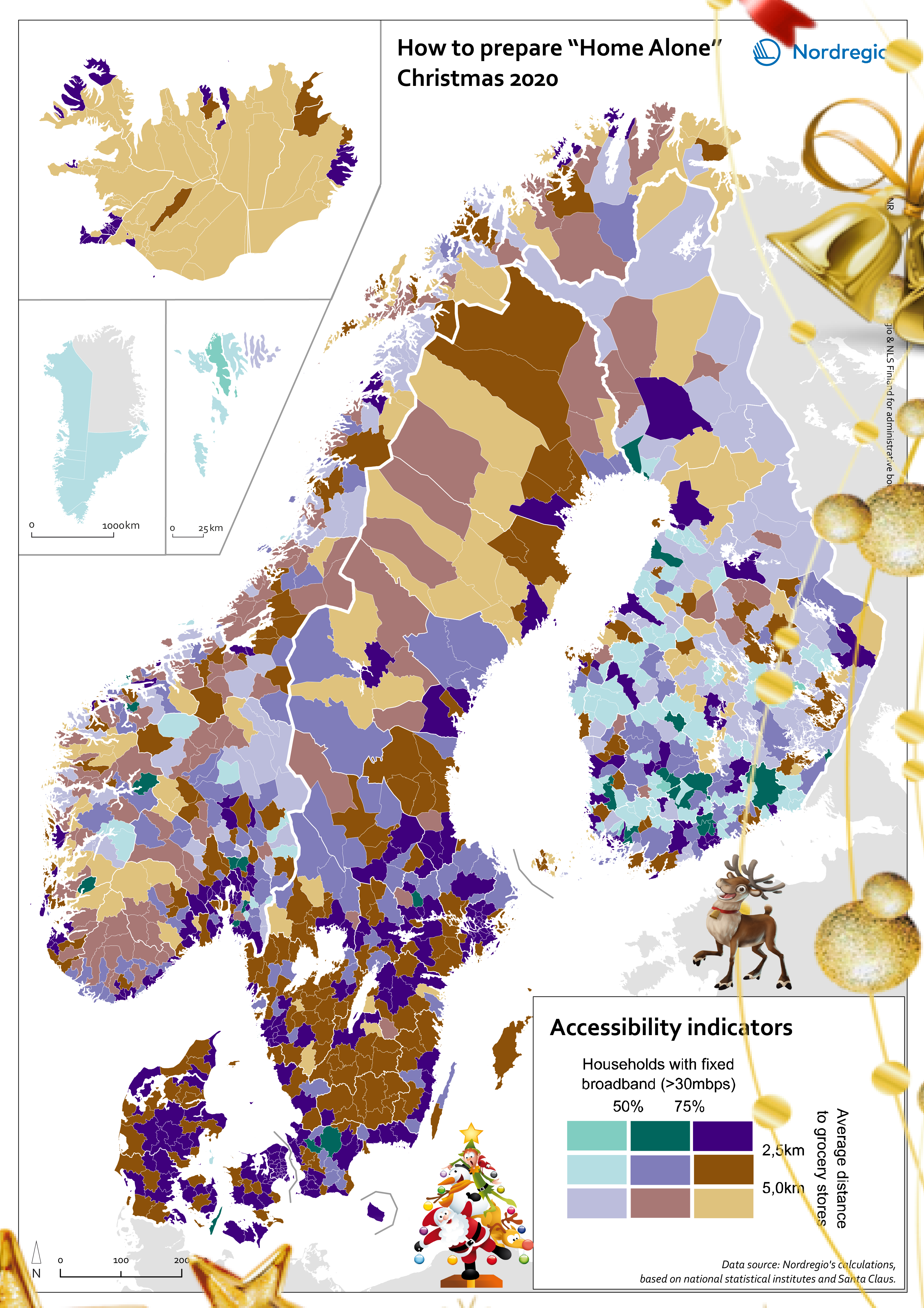
How to prepare for Home Alone Christmas 2020?
The conditions for a Home Alone Christmas vary greatly across the Nordic Region. The combination of the selected two accessibility indicators is visualised on Nordregio’s Christmas Map 2020. It classifies the Nordic municipalities into nine categories, based on: – The share of households with fixed broadband of at least 30mbps is used to measure the quality and distribution of internet connection. The higher the percentage, the bigger chance you will have an uninterrupted online celebration! – The average distance to grocery stores is used to estimate the time required to get your Christmas food: the closer to a grocery store, the more spontaneous you can be. On one side of the spectrum are about a fourth of the municipalities having a high share of households (>75%) with a decent broadband connection and a short average distance to the closest grocery store (<2,5 km). This enhances last-minute Christmas preparation and high-quality online celebrations. These municipalities are colored in dark purple on the map and are mostly, but not exclusively, located in urban areas in Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden. On the other side of the spectrum, about 10% of Nordic municipalities have rather weak fixed broadband coverage (<50%) and relatively long travel distances to the closest grocery store (> 5km), requiring more planning for celebrating Christmas. These municipalities are colored in light purple on the map and are mostly found in sparsely population municipalities in Finland and mountainous municipalities in Norway.
2020 December
- Nordic Region
- Others
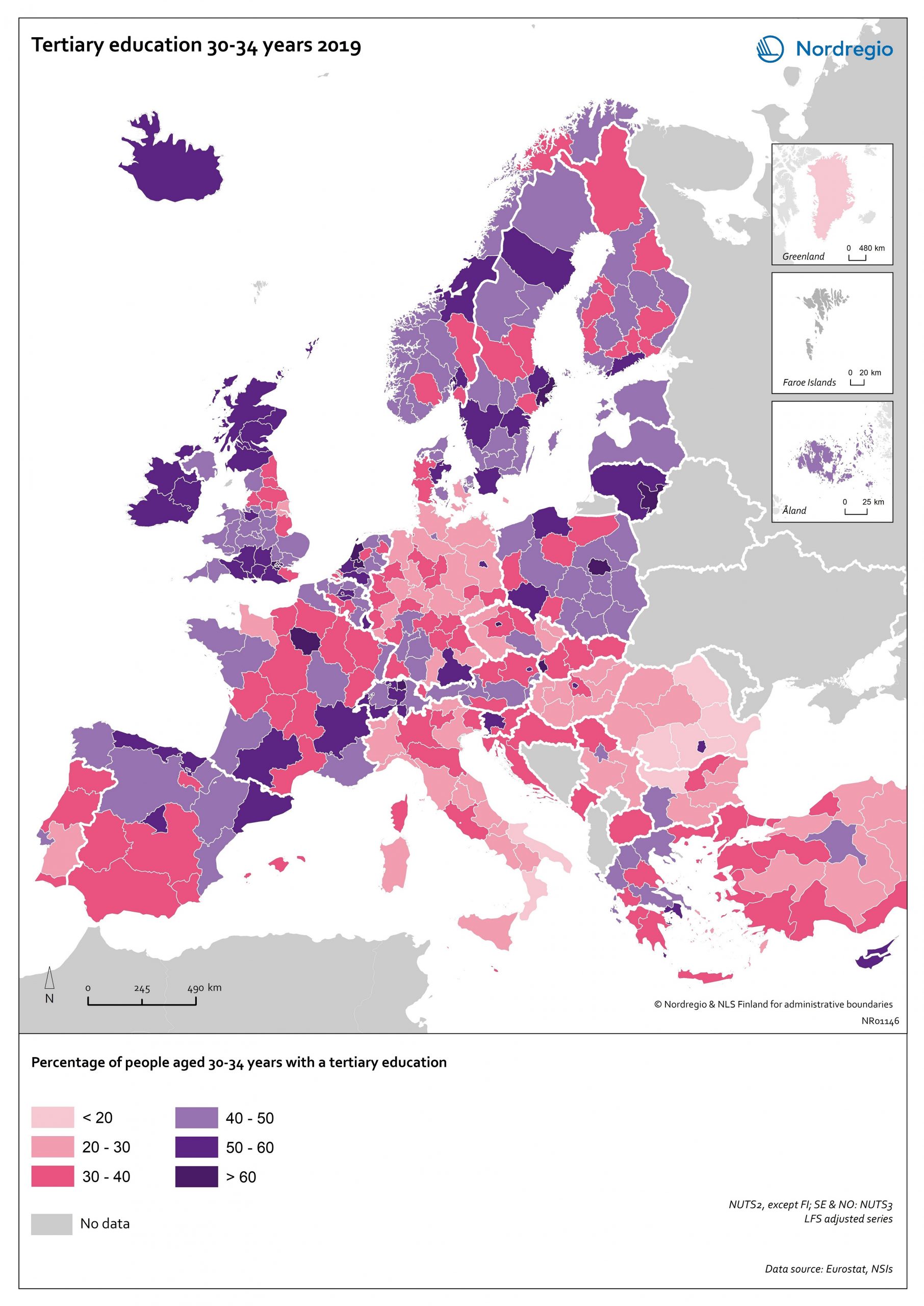
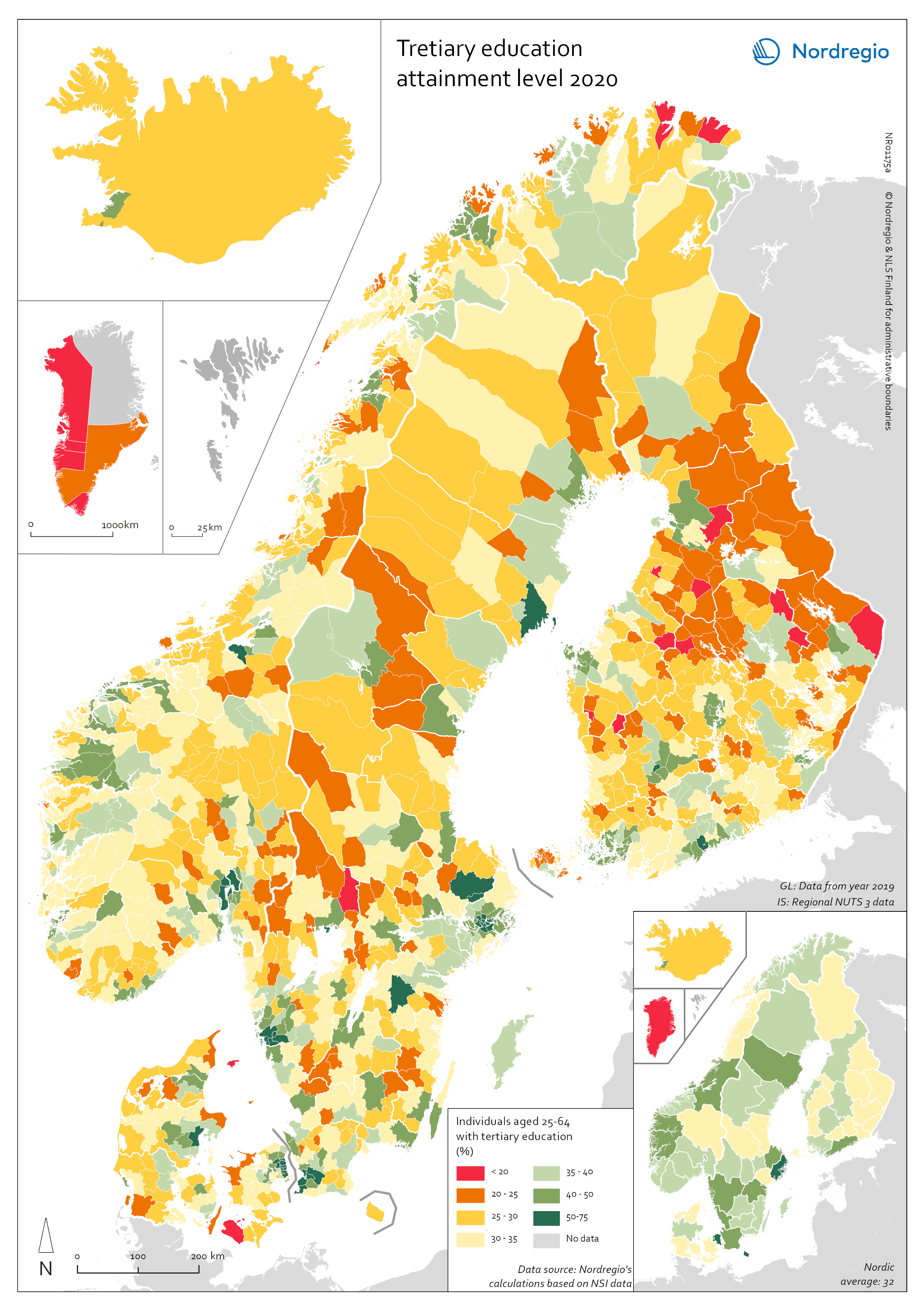
Tertiary education attainment level of 30- to 34-year-olds 2019
The map shows the proportion of the population aged 30-34 years old, who had a tertiary education at the European level in 2019. Purple shades indicate higher proportions, and pinkish shades reflect lower proportions. It is common to show the education attainment for the age group 30-34 since it is an age group where most people have finalised their studies. The focus on this age group makes it easier to see recent trends and outcomes of policies. Overall, over 40% of Europeans aged 30-34 years old had a tertiary education in 2019. Young people in the Nordic countries are among the most educated, with approximately half of 30 to 34-year-olds achieving a tertiary education across all Nordic countries. The highest proportions can be found in the capital regions. Stockholm is particularly noteworthy, with over 60% of 30 to 34-year-olds having had a tertiary education. Regions with prominent universities also stand out – for example, Skåne, Uppsala, Västerbotten and Västra Götaland (Sweden), Trøndelag (Norway) and Østjylland (Denmark).
2020 October
- Baltic Sea Region
- Demography
- Europe
- Nordic Region
- Others
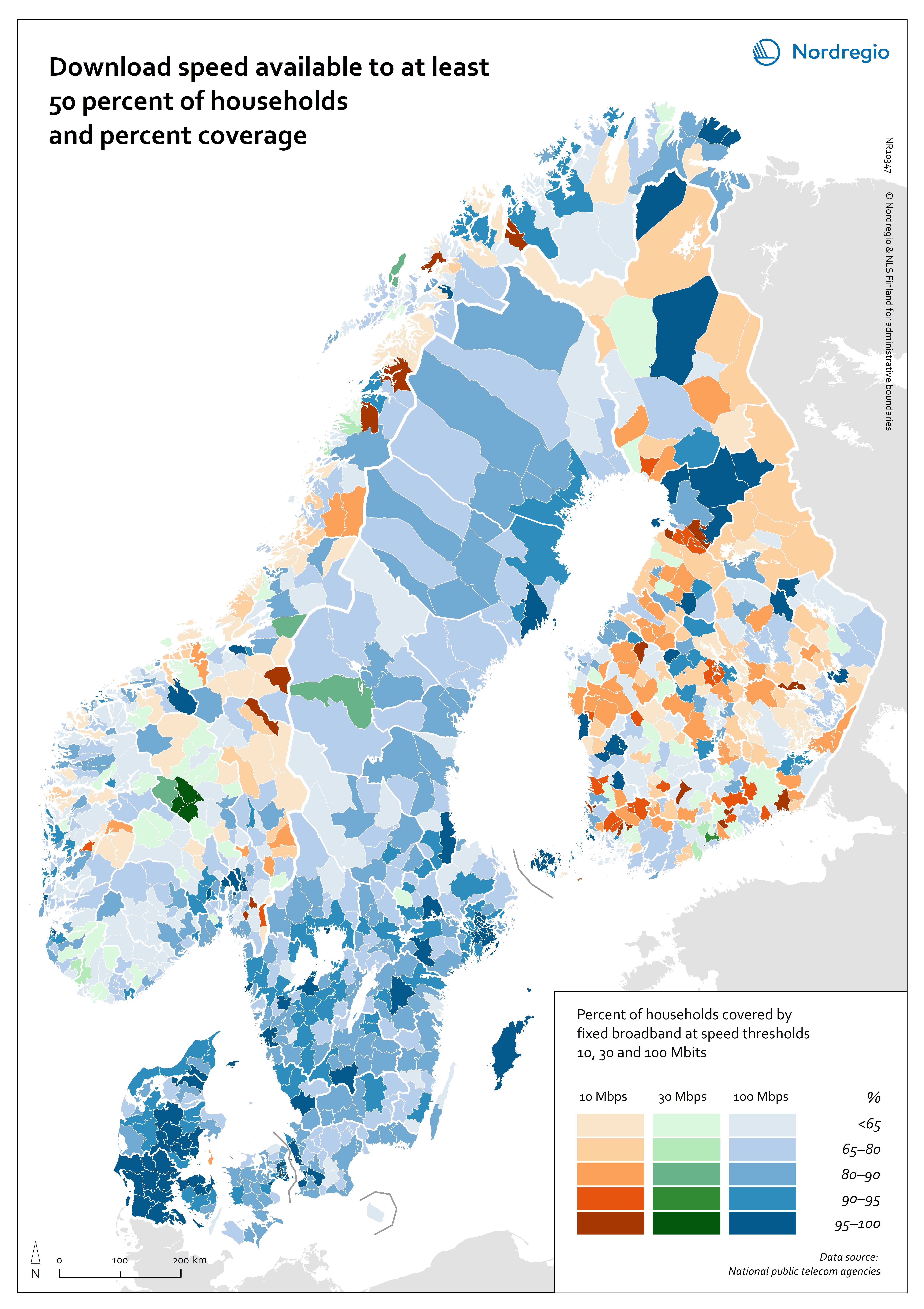
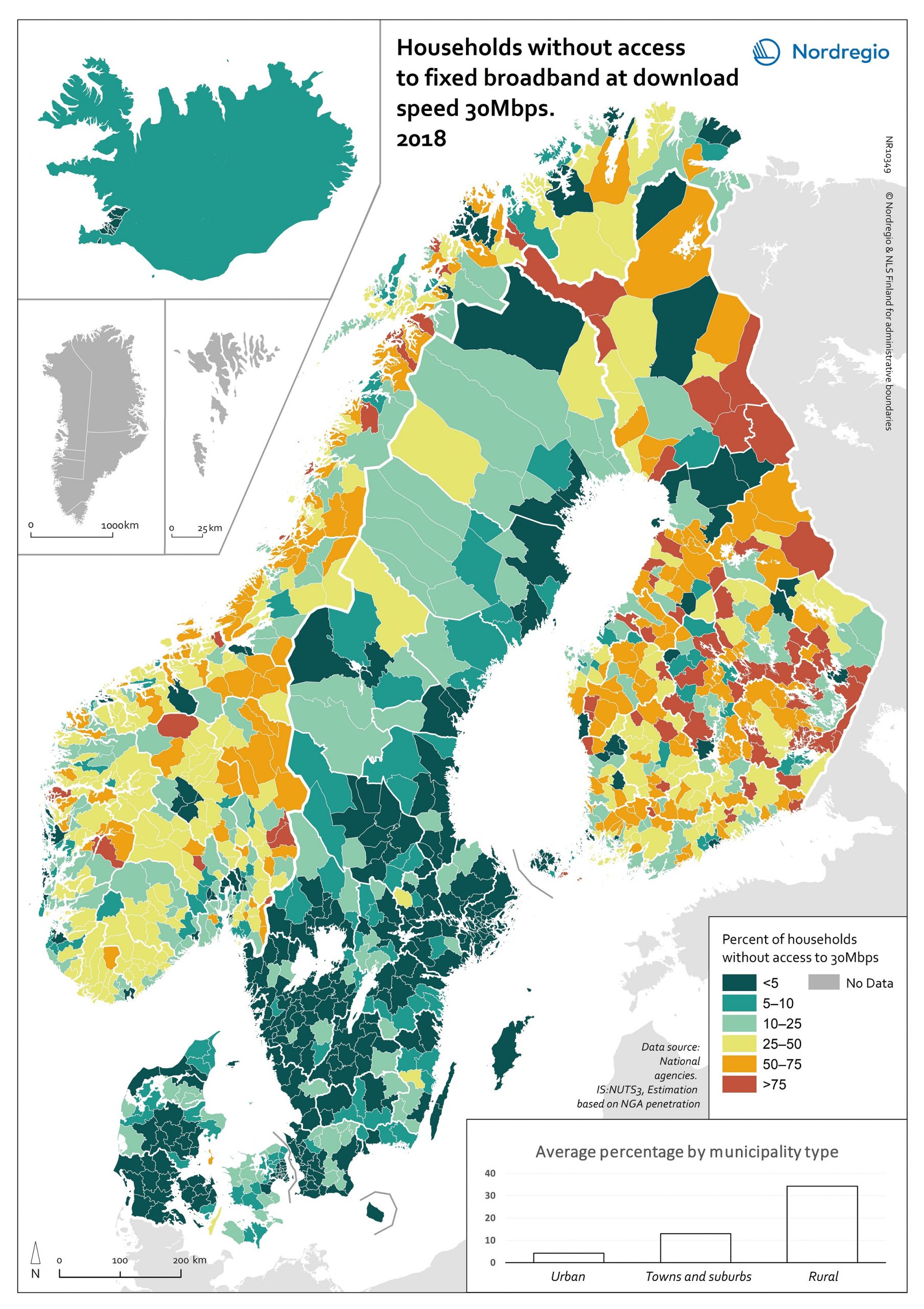
Broadband speed availability and coverage
Ambitious broadband connectivity targets have been set across the Nordic Region, with most countries working towards universal access to download speeds of >100 Mbps for all households. The deadline for reaching this target varies between countries, from 2020 (Denmark) to 2023 (Iceland) to 2025 (Finland & Sweden). Norway aims to provide access to download speeds of >100 Mbps for 90% of households by 2020. The map measures progress towards these targets, showing the minimum download speed that was available to at least 50% of households in each municipality through a fixed-line connection in 2018, along with the proportion of households which had access this speed. The blue shading shows municipalities where over 50% of households had access to fixed broadband with download speeds >100 Mbps. The green shading indicates municipalities where less than 50% had access to fixed broadband with download speeds >100 Mbps but where at least 50% of the population had access to fixed broadband with download speeds >30 Mbps. The orange shading shows the percentage of households who have access to fixed broadband with download speeds >10 Mbps for municipalities where less than 50% of households have access to fixed broadband with download speeds >30 Mbps.
2020 May
- Nordic Region
- Others
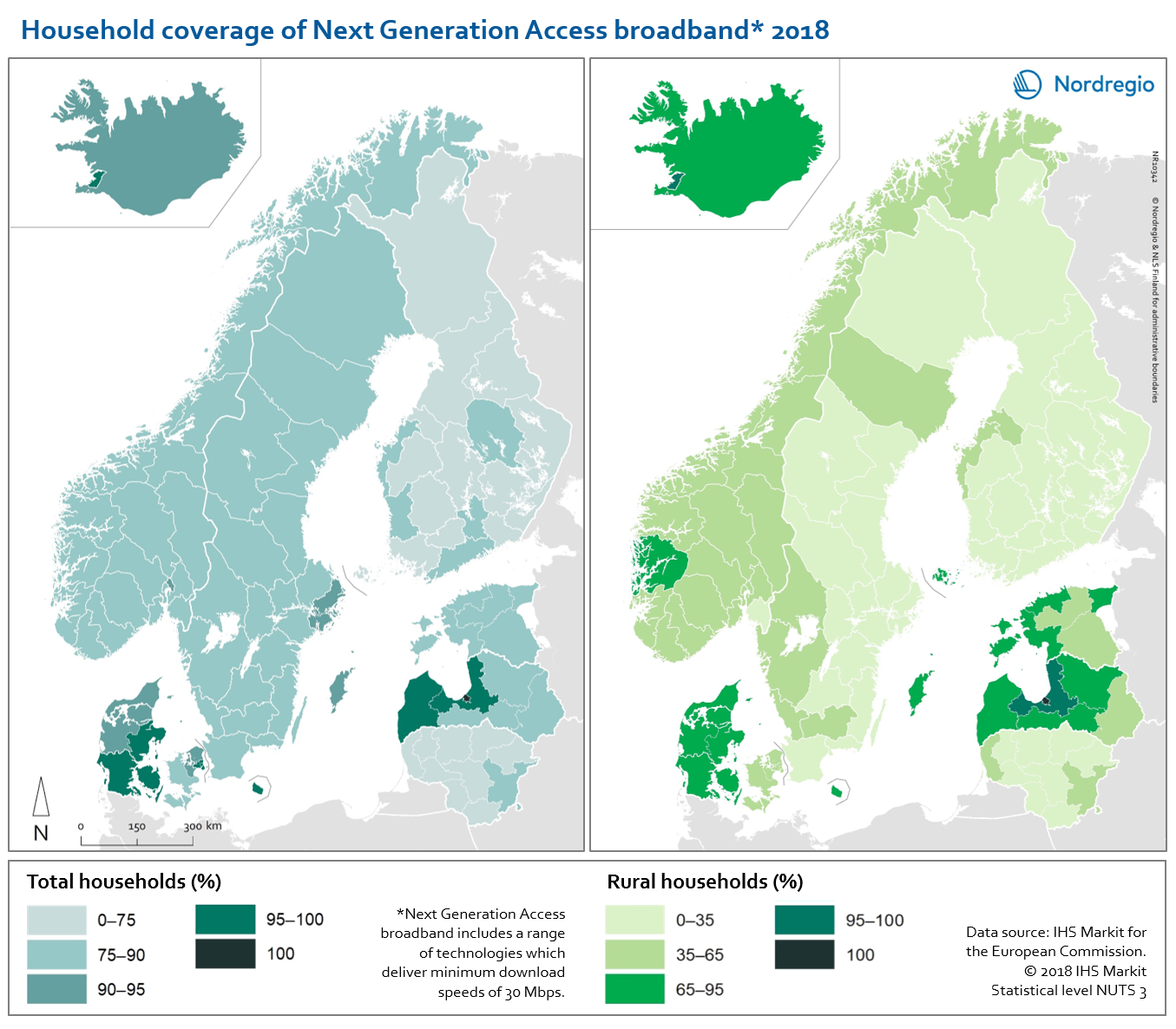
Household coverage of NGA broadband 2018
These maps highlight the urban-rural divide with respect to household coverage of Next Generation Access (NGA) broadband in the Nordic-Baltic Region in 2018. NGA includes a range of technologies, all of which deliver minimum download speeds of 30 Mbps. The map on the left-hand side shows NGA coverage for “all households”, with darker shading representing higher levels of coverage. Here we see that over 75% of households have access to NGA coverage in most regions for most countries, with the exception of Finland and Lithuania. The highest levels of household coverage can be found in regions in Denmark, Iceland and Latvia. The map on the right-hand side shows the same indicator but includes only rural households. Here we see a quite different picture. In most of Finland and Lithuania, as well as many regions in Sweden, less than 35% of rural households have NGA coverage. Norway performs somewhat better, with NGA access for 35-65% of rural households in most regions. Again, regions in Denmark, Iceland and Latvia have the best coverage. Estonia also performs relatively well, with 65-95% of rural households covered in three of its five regions.
2020 May
- Nordic Region
- Others
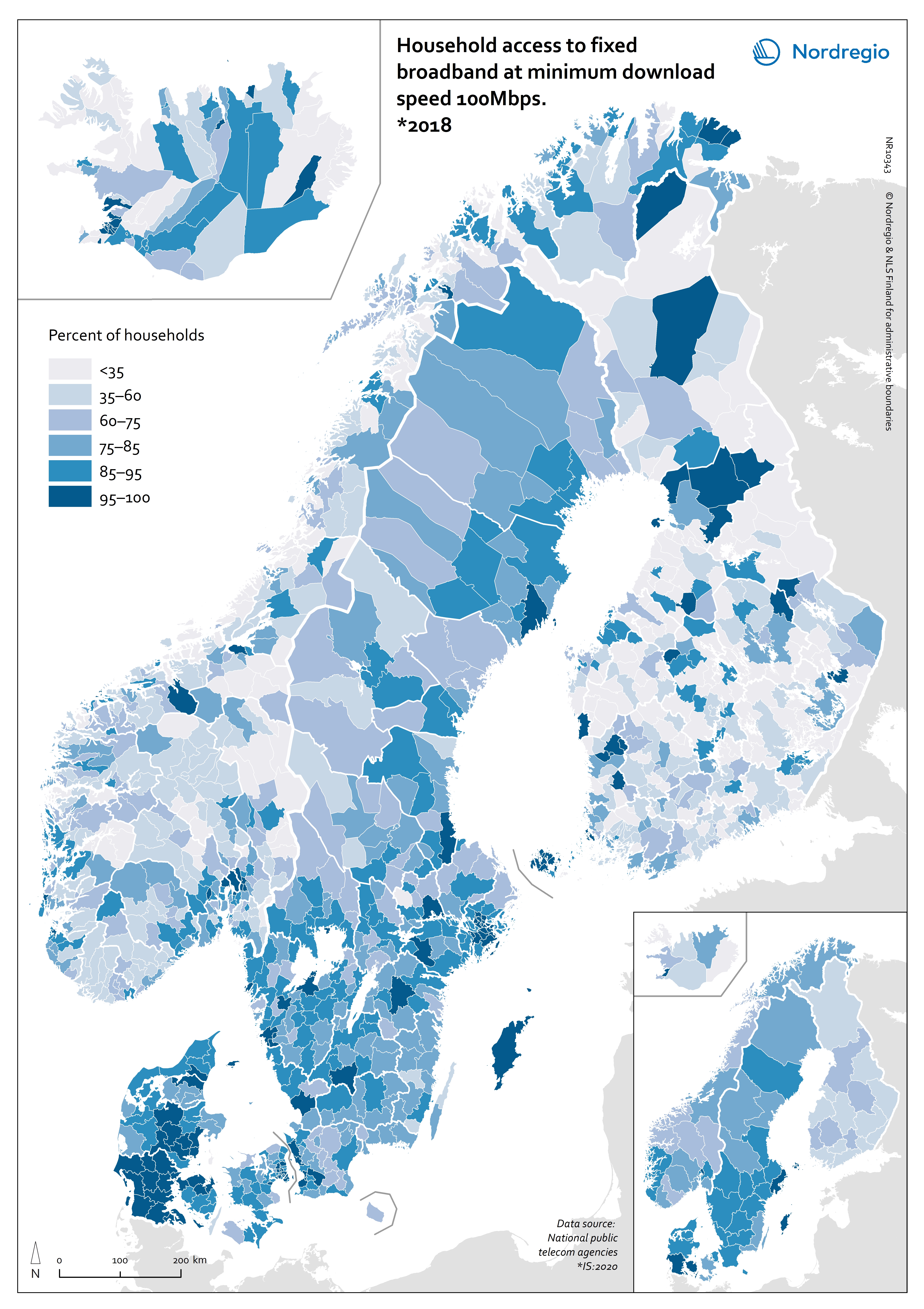
Household access to broadband 100Mbps
Ambitious broadband connectivity targets have been set across the Nordic Region, with most countries working towards universal access to download speeds of >100 Mbps for all households. The deadline for reaching this target varies between countries, from 2020 (Denmark) to 2023 (Iceland) to 2025 (Finland & Sweden). Norway aims to provide access to download speeds of >100 Mbps for 90% of households by 2020. The map measures progress towards these targets, showing the percentage of households with access to a fixed-line broadband connection with a minimum download speed of 100 Mbps in 2018.* Darker shading represents proportionally higher levels of coverage. According to the map, a substantial proportion of households (>75%) had access to 100 Mbps in most Danish municipalities in 2018. Sweden also has relatively good fixed broadband coverage across most of the country, though there are several municipalities where coverage drops below 60% of households. The most limited coverage can be found in Finland, parts of Norway and the Westfjords and easternmost municipalities of Iceland. *Municipal level data was not available for the Faroe Islands or Greenland. Due to municipal level data availability, Icelandic figures are from 2020.
2020 May
- Nordic Region
- Others
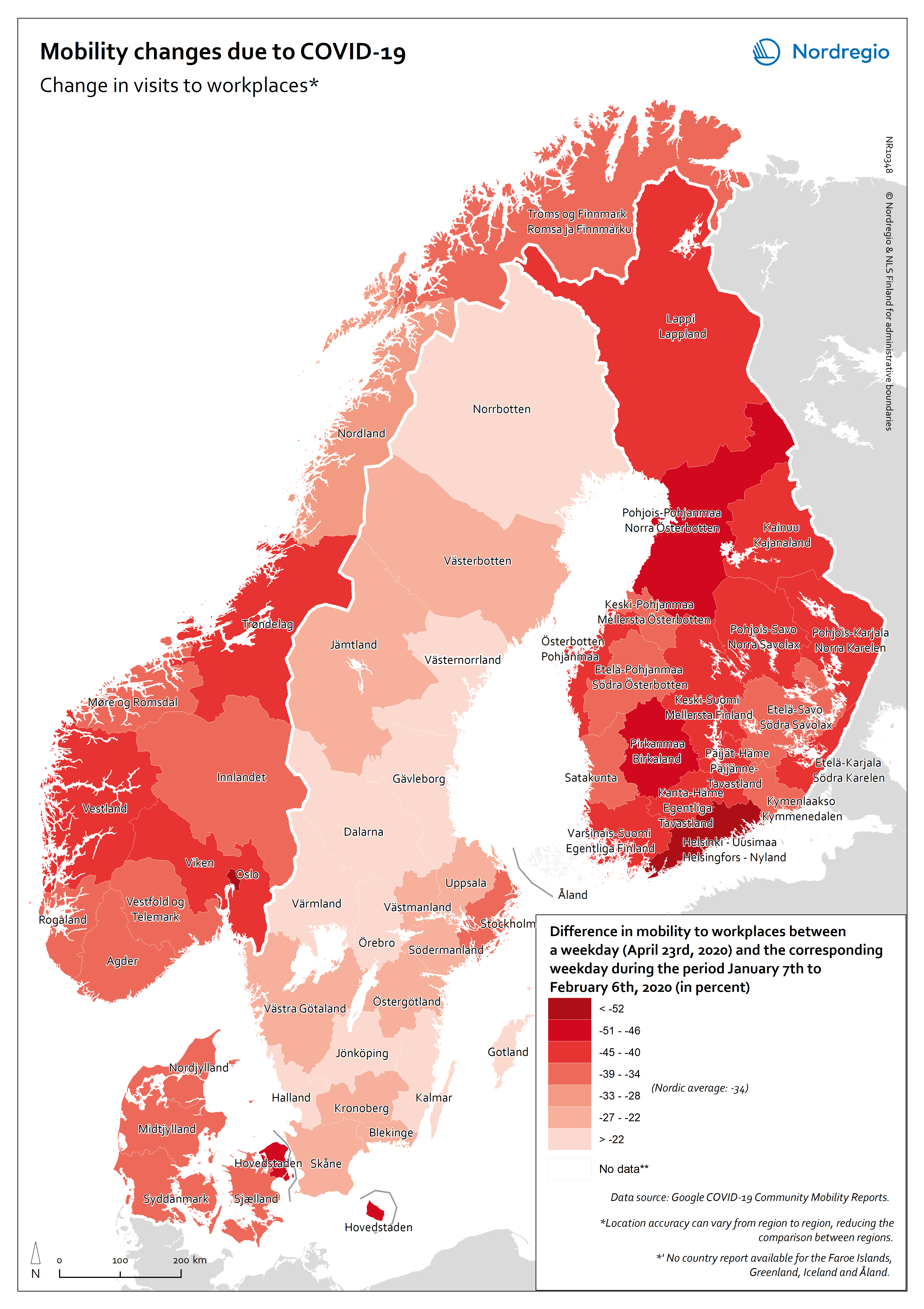
Mobility changes due to COVID-19
This map shows the difference in mobility to workplaces between a weekday (April 23rd, 2020) and the corresponding weekday during the period January 7th to February 6th, 2020 (in percent). The data highlights the percent change in visits to workplaces within each administrative region in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden. Data is not available for the Faroe Islands, Greenland, Iceland and Åland. Read more about the data here. The average value of the Nordic regions included in the map is a reduction by 34% of the number of visits to workplaces on April 23rd (in comparison to a baseline). This average value hides large variations within the Nordic Region with the most modest change occurring in Gotland (-12%) and the most severe change in Oslo (-57%). More generally, variations can be identified both between and within countries. The variations between countries reveal differences in recommendations and restrictions from published by the different national governments. Details for each country have been gathered by Info Norden and can be found here. As a result, the change in visits to workplaces decreased by 26% in Sweden, 39% in Denmark, 41% in Norway and 47% in Finland. The variations within countries also reveal differences in government´s decisions (e.g. lockdown of the Helsinki-Uusimaa region reducing the mobility to workplaces by 53%), but not only. There are indeed a number of local characteristics of the labour markets that contribute at explaining that the largest changes in mobility to workplaces are found in capital city regions. These local characteristics are a greater dependency on public transport for commuters, who are adviced to avoid using such means of transportation under the COVID-19 context; and having a higher share of jobs that can be done by teleworking, among others.
2020 May
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
- Others
- Transport
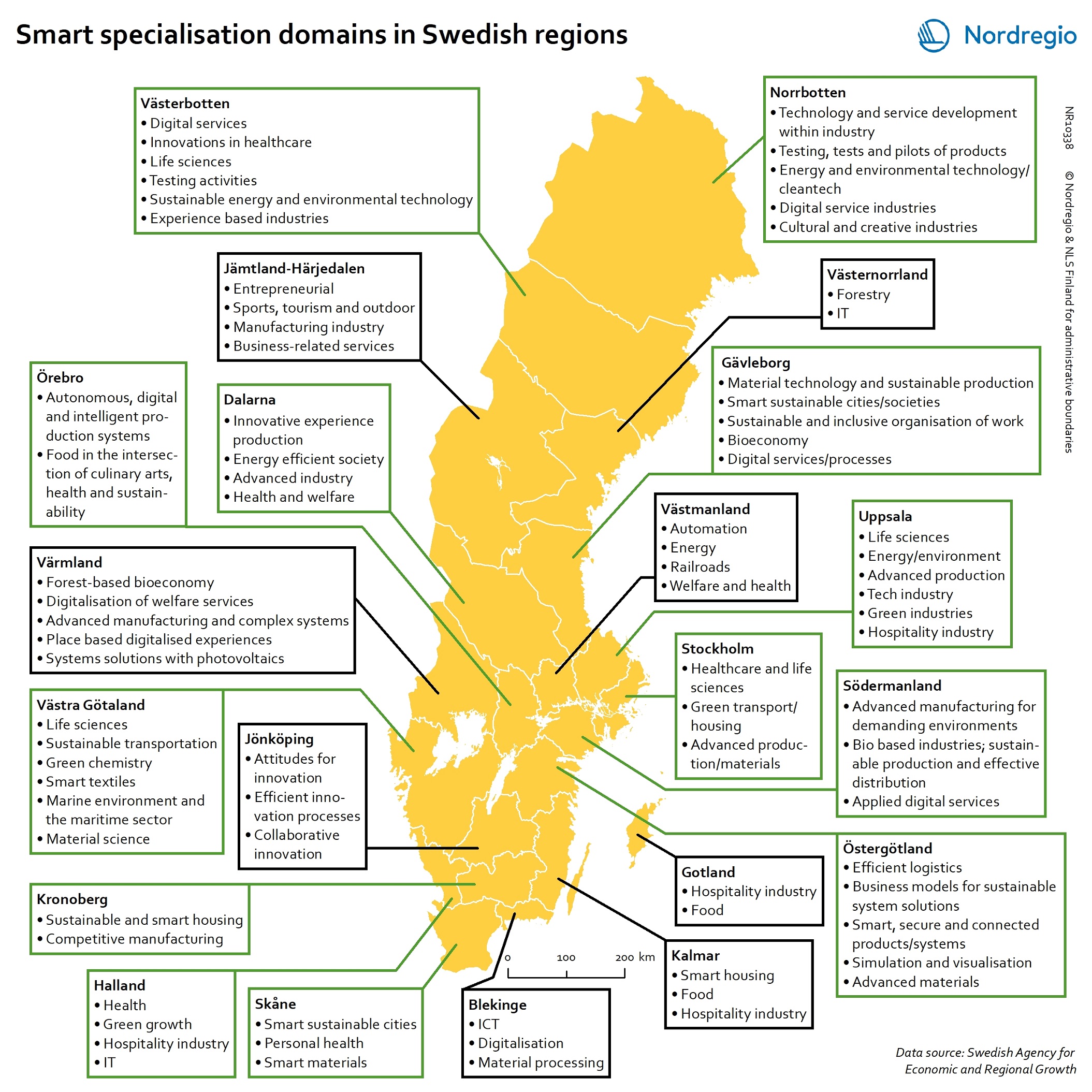
Smart specialisation domains in Swedish regions
This map gives an overview of the S3 focus areas in the Swedish regions in 2019. The major S3 domains in Sweden shown in the map provide a good overview of the key specialisation areas in Sweden. It is possible, for example, to check which Swedish regions have “green”, “sustainable”, “environment” at their smart specialisation domains (marked in green in their respective infoboxes for the domains in the figure). The information illustrated in the map can assist Swedish regions when they are considering opportunities for S3 synergy and co-operation with each other. In Sweden, the Swedish Agency for Economic and Regional Growth (Tillväxtverket) is a central actor in assisting regions in their work with smart specialisation. Tillväxtverket promotes opportunities for cooperation between the Swedish regional S3 processes and provides relevant information and learning seminars related to S3. Read the digital publication here.
2020 February
- Economy
- Research and innovation
- Sweden
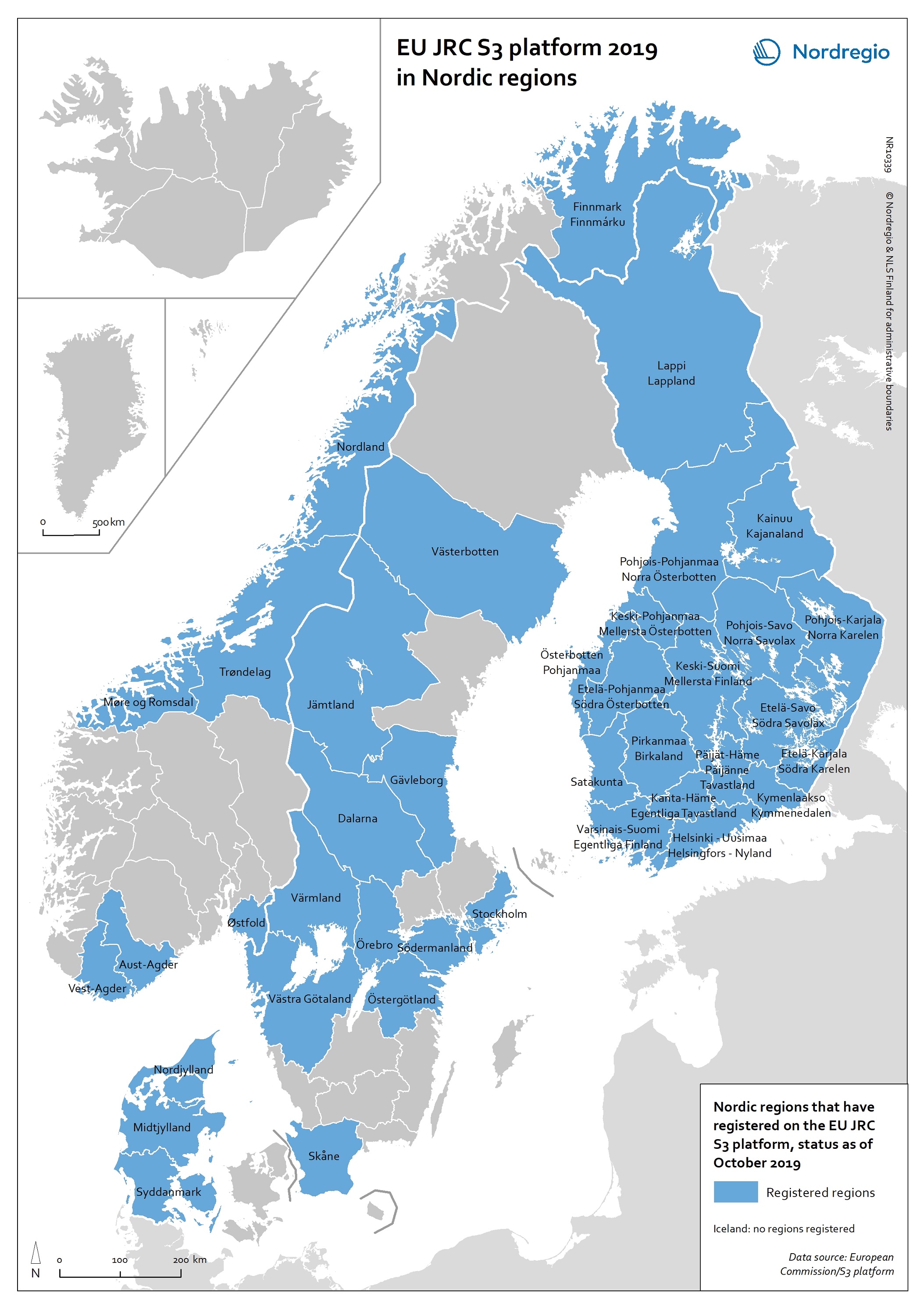
EU JRC S3 Platform 2019 in Nordic regions
This map shows the Nordic Regions that have registered on the EU JRC S3 platform, status as of October 2019. The regions that have registered on the S3 platform receive practical advice and broadened opportunities for international networking. In October 2019, there were 182 EU regions registered on the S3 platform, as well as 18 non-EU Member State regions. Of these regions, 38 are Nordic. It is worth noting that, as a non-EU member state, Norway has seven registered regions on the platform. Registration on the S3 platform is by no means a guarantee of success of a regional smart specialisation process, but it indicates the willingness of the region to learn more about S3 and to participate in international and interregional S3 cooperation through the possibilities provided by the S3 platform. The smart specialisation concept has been diffusing rapidly across Europe in the 2010s, as an increasing number of regions adopt it and design strategies departing from their own preconditions. The S3 platform in Seville, Spain, hosted by the Institute for Prospective Technological Studies (IPTS), was established in 2011 to assist EU countries and regions to develop, implement and review their smart specialisation strategies. The S3 platform provides information, methodologies, expertise and advice to national and regional policymakers, promotes mutual learning and transnational co-operation, and contributes to academic debates around the concept of smart specialisation. Read the digital publication here.
2020 February
- Economy
- Nordic Region
- Research and innovation
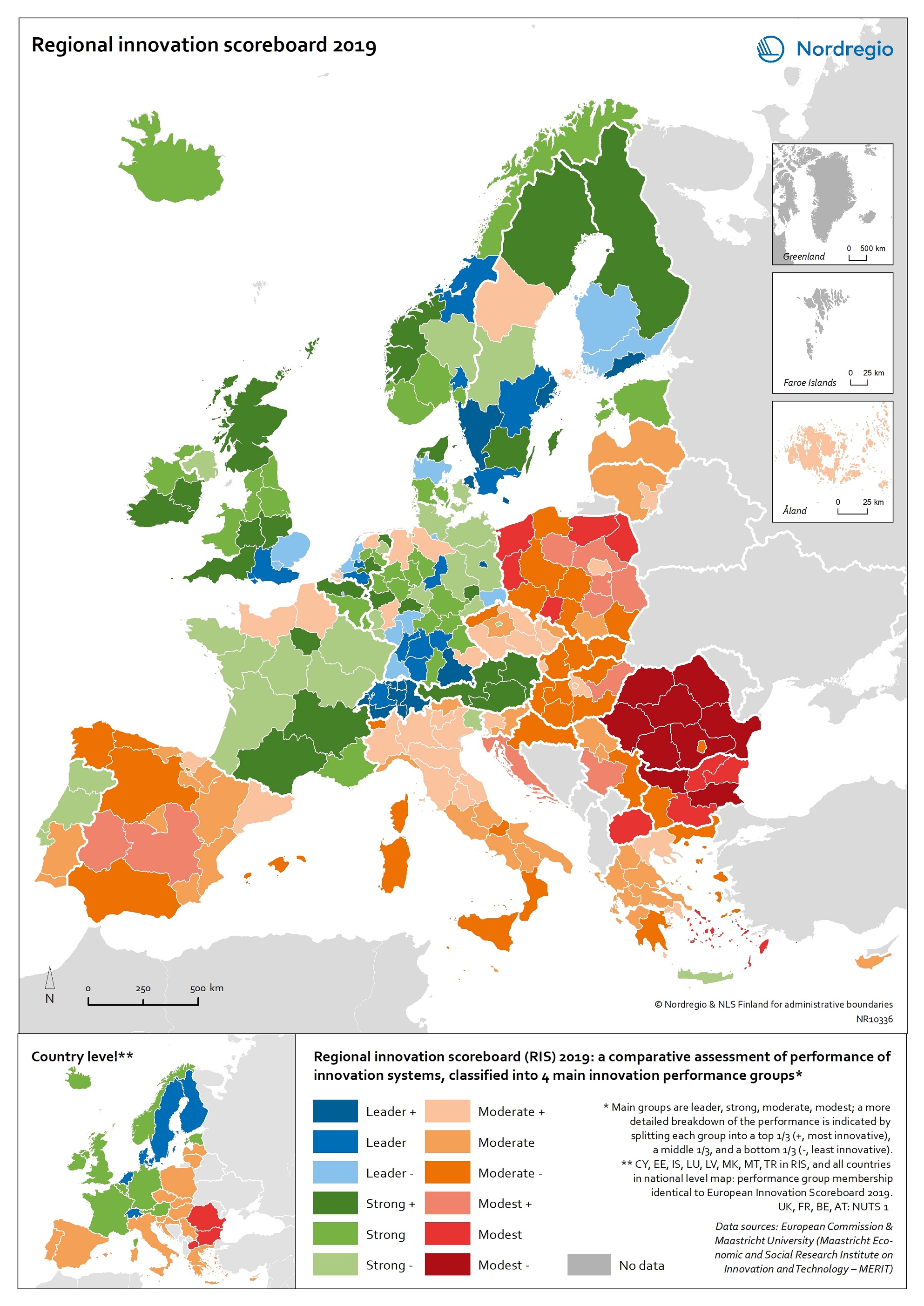
Regional innovation scoreboard 2019
This map shows the regional innovation scoreboard (RIS) in the European regions in 2019. The small map shows the innovation scoreboard at national level. The index shows the performance of innovation systems, classified into four main performance groups (leader, strong, moderate and modest). The European innovation scoreboard provides a comparative assessment of the research and innovation performance in European countries. It assesses the relative strengths and weaknesses of national innovation systems and helps countries identify areas they need to address. The Regional innovation scoreboard (RIS), a regional extension of the European innovation scoreboard, assesses the innovation performance of European regions on a limited number of indicators. The RIS 2019 covers 238 regions across 23 EU countries, as well as Norway, Serbia and Switzerland. Cyprus, Estonia, Latvia, Luxembourg and Malta are also included at country level. The RIS 2019 is a comparative assessment of regional innovation based on the European innovation scoreboard methodology, using 18 of the latter’s 27 indicators. It provides a more detailed breakdown of the performance groups with contextual data that can be used to analyse and compare structural economic, business and socio-demographic differences between regions. The Nordic regions are doing well in an overall RIS comparison regarding innovation performance. There are, however, considerable differences in innovation performance between the Nordic regions. For example, the capital regions have higher levels of innovation performance than more rural and peripheral regions, according to RIS 2019. This is often due to the critical mass of companies and the spatial significance of the proximity of firms and entrepreneurs, enabling knowledge-sharing and spill-over effects. Read the digital publication here.
2020 February
- Economy
- Europe
- Research and innovation