218 Maps
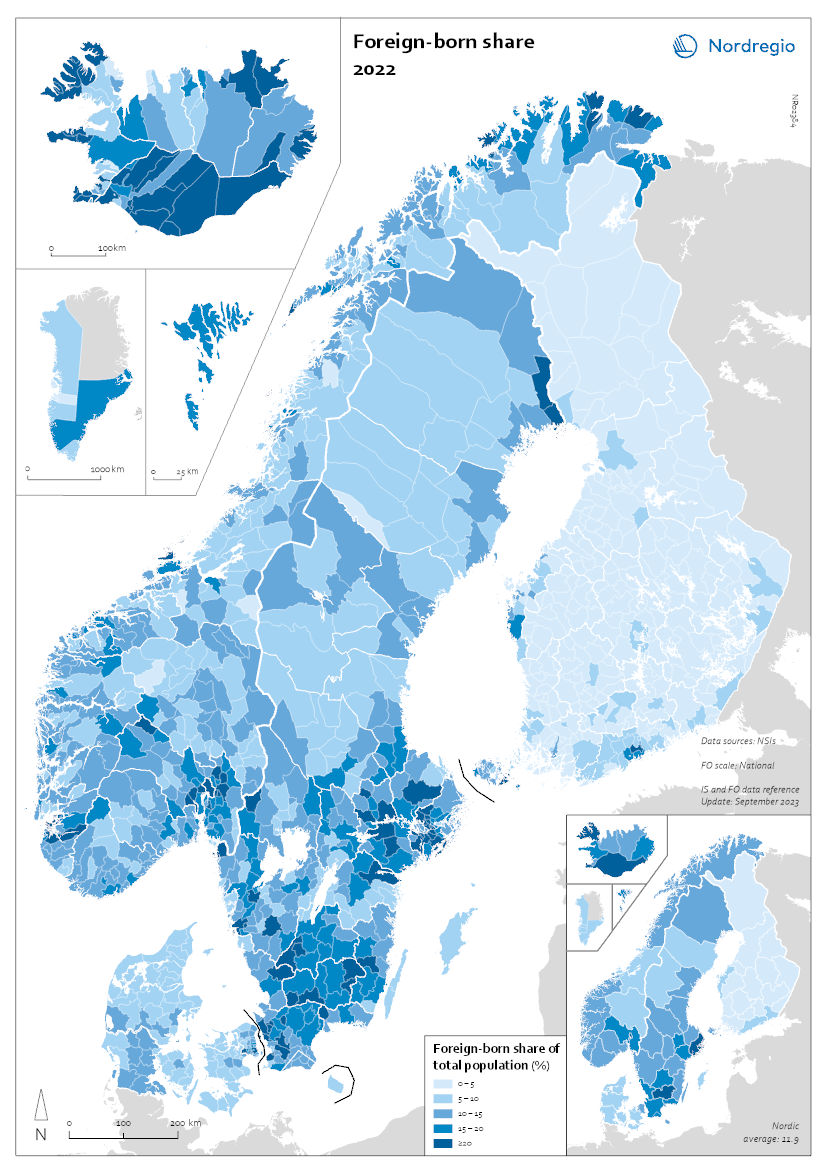
Foreign-born share 2022
This map shows the share of foreign-born of the total population in the Nordic countries. This map shows the share of foreign-born of the total population in Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map), and municipalities (big map) in 2022. Iceland has the highest share of foreign-born residents in the Nordic Region, at 22%. Mýrdalshreppur, the municipality in the south containing the village of Vik, has the largest foreign-born population, at 58%. It is also the only municipality in the Nordic Region with a majority non-native population. Other municipalities in the south, some of which are quite small, also have significant foreign-born populations. Reykjanesbær, near Keflavik airport, is the largest municipality with a sizeable foreign-born population, at 29%. In Reykjavíkurborg, 20% of the population is foreign-born, about the same as the national average. Many municipalities with tiny populations in the Westfjords and the north also have small shares of foreign-born persons. In 2022, 17% of the population of Norway was foreign-born. Municipalities with high shares of foreign-born include Oslo (28%), several suburban municipalities near Oslo, and a few in the north – which have small overall populations but large numbers of foreign workers employed in the fishing industry. In Sweden, 20% of residents are foreign-born, with large differences in distribution by region and municipality. At the regional level, Stockholm has the highest share of foreign-born persons (27%), followed by Skåne, including the city of Malmö (24%). The percentage of foreign-born persons in Västra Götaland, which encompasses Gothenburg, is the same as that of Sweden as a whole. The regions with low shares of foreign-born persons are in the north of the country – Dalarna, Gävleborg, Västernorrland, Jämtland, Västerbotten, and Norrbotten – plus the island of Gotland, which has the lowest share (9%). There are no municipalities in which foreign-born…
2025 April
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
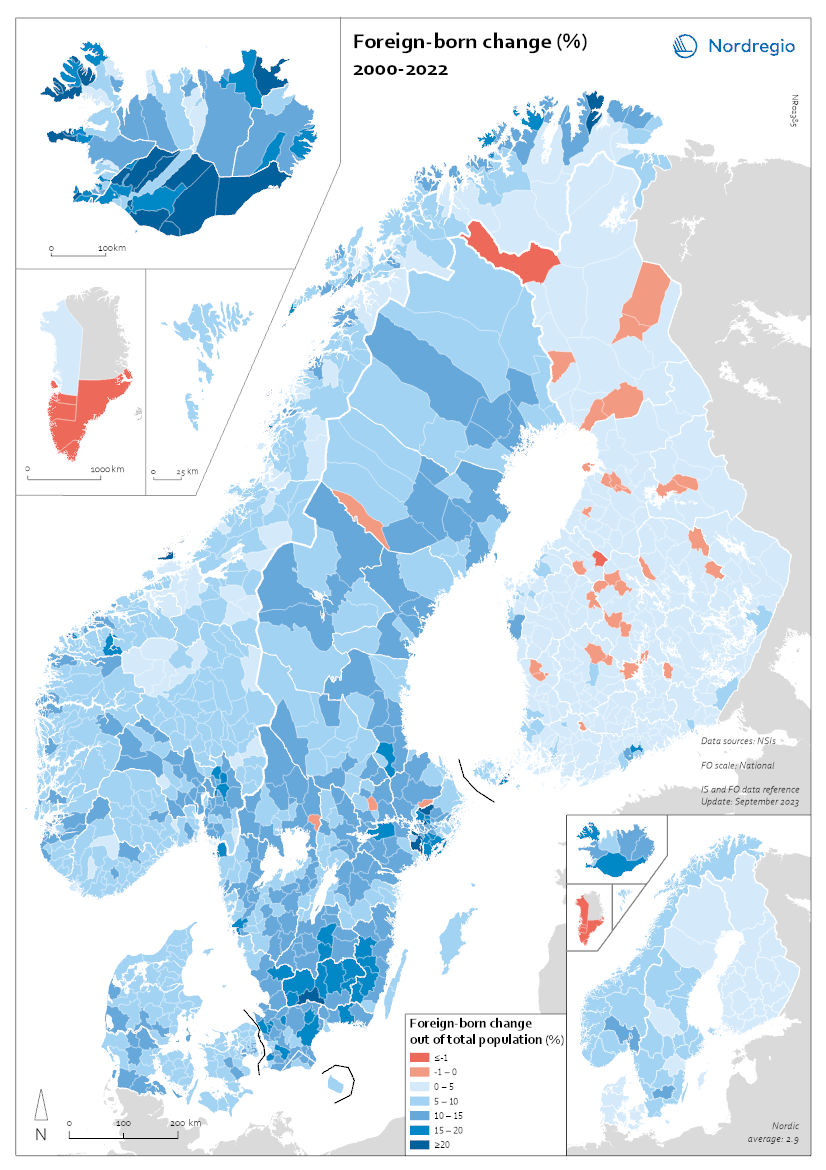
Foreign-born change (%) 2000-2022
This map shows the percentage-point change in foreign-born populations in the Nordic countries. This map shows the percentage-point change in foreign-born populations by region (small map) and municipality (big map) between 2000 and 2022. The blue shades indicate an increase in the number of foreign-born while the red shades indicate a decrease. The recent growth in foreign-born populations differs among the Nordic countries, regions, and municipalities. During the period 2000-2022, much of both the absolute and percentage-point increases in the foreign-born populations took place in suburbs around the capital cities and other large urban centres. However, with few exceptions, every municipality across the Nordic Region saw increases in foreign-born populations. In Iceland, the foreign-born population increased from 5% to 20%. The largest percentage-point increases in the foreign-born populations were in municipalities in the southwest, which had small populations and small foreign-born shares. Of the larger municipalities, Reykjanesbaer and the Capital Region had the largest absolute and percentage point increases. The foreign-born population in Norway grew from 7% to 17%. The municipalities with significant increases in foreign-born populations include several suburban areas near Oslo, as well as scattered municipalities elsewhere that had small foreign-born shares in 2000. The percentage of foreign-born residents in Oslo increased from 16% to 28% between 2000 and 2022. No municipalities experienced a decline in foreign-born population during this period.
2025 April
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
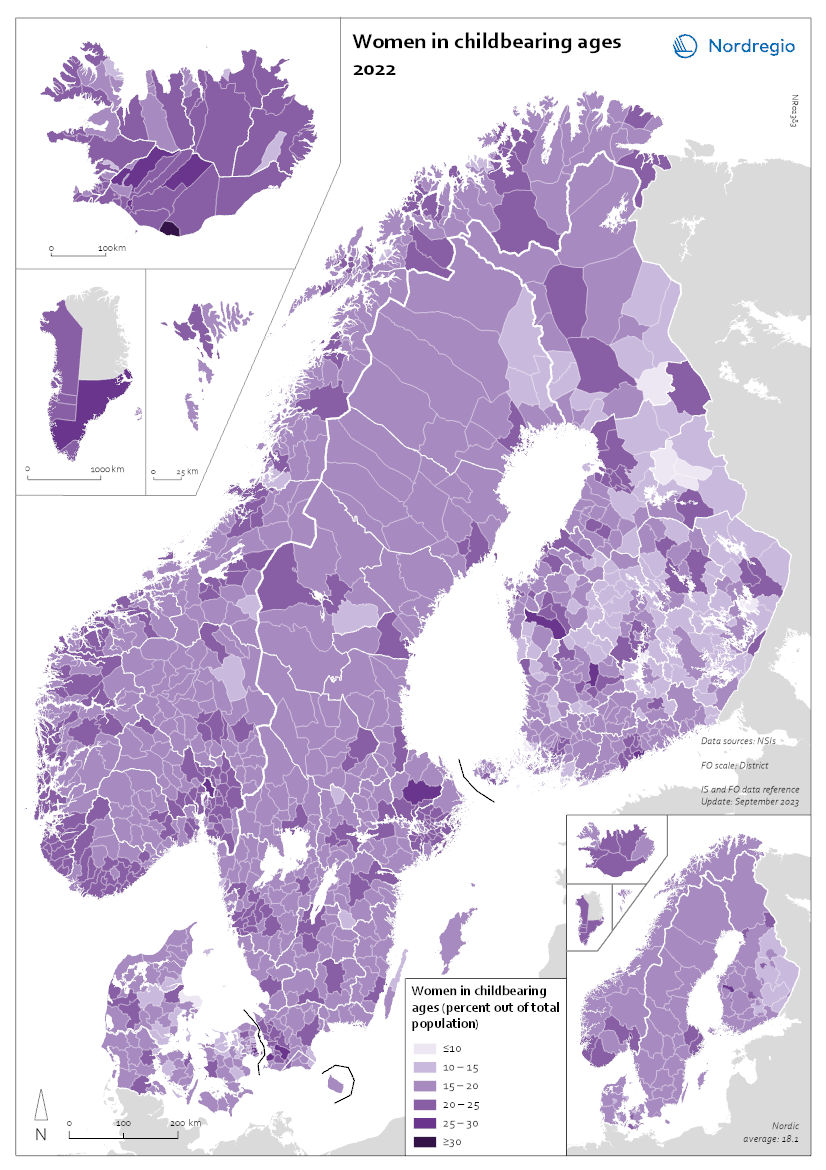
Women in childbearing ages 2022
This map shows the number of women in childbearing age as a percentage of the total population in the Nordic countries. This map shows the number of women in childbearing ages as percent of total population in the Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map) in 2022. At the national level, Greenland and Iceland have the largest shares of women of childbearing age (15–45 years), more than 20%. Next are Norway, Denmark and Sweden, with somewhat lower shares, 18–19%. The lowest share, less than 18%, is in Finland, where there have been more deaths than births since 2016. The Faroes and Åland both have shares of less than 17%. Municipalities in Greenland and Iceland follow the national trends, mostly with shares of women of childbearing age of 20–25%, although some are higher than 25%. In the other countries, municipalities in and around the capitals and other large cities have larger shares, 20% or higher. Most regions outside of the large cities have smaller shares, between 15 and 20%. Many regions in Finland have older populations, and these have shares of less than 10%. The lack of women of childbearing age, combined with those of childbearing age having so few children, means that there will be fewer births in these municipalities in the future, leading to further population decline.
2025 April
- Demography
- Nordic Region
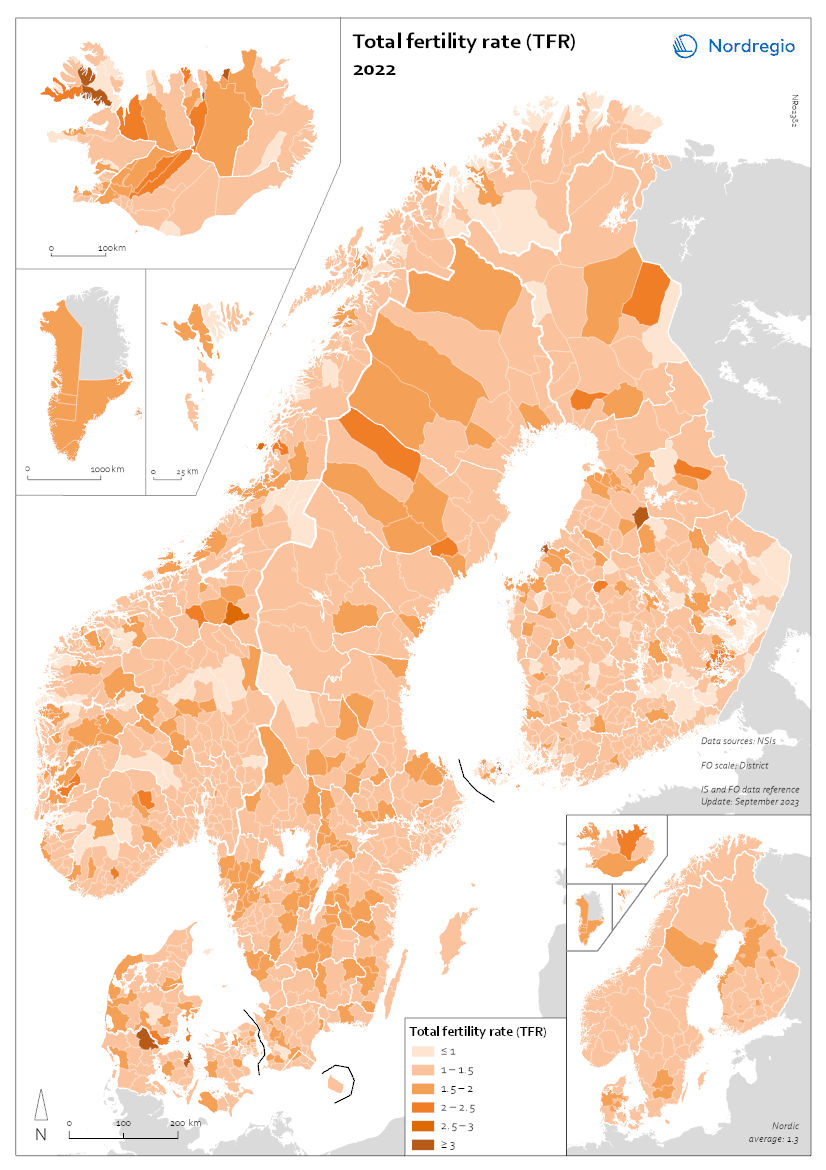
Total fertility rate (TFR) 2022
This map shows the total fertility rate (TFR) in 2022. The total fertility rate is the number of children a hypothetical cohort of women would have in one year. Data on total fertility rates is not available at the regional or municipal levels for all of the Nordic countries. The figures are estimated based on multiplying the general fertility rate by 30 (representing the typical number of reproductive years, between 15 and 45), assuming the general fertility rate is constant throughout this period. The general fertility rate is the number of births per woman during the childbearing years. At the regional level, age and gender composition are indicative of past trends but also harbingers of future population change. In 2018, prior to the pandemic, most Nordic municipalities had fertility levels in line with their respective national levels (see map Total fertility rate (TFR) 2018 in Nordregio’s Map Gallery). Most municipalities within Greenland and the Faroes had fertility rates above 1.5 children per woman, consistent with national rates of about 1.9 (2018 map). Municipalities in Sweden and Denmark typically had fertility rates of 1.5 or higher, consistent with their national rates of 1.7. By contrast, many municipalities in Norway and Finland had fertility rates of 1.5 or lower. In 2022, fertility in most municipalities across the Nordic Region fell, reflecting the declines at the national levels, but the spatial pattern had become slightly more varied (2022 map). In several municipalities in Norway, Finland, and Sweden, fertility rates fell to less than 1.0 children per woman. The drops in fertility resulted in declines in the number of births across most municipalities in 2022. Combined with increases in the number of deaths, this resulted in more deaths than births in many municipalities, consistent with trends at the national level. Most municipalities in Greenland,…
2025 April
- Demography
- Nordic Region
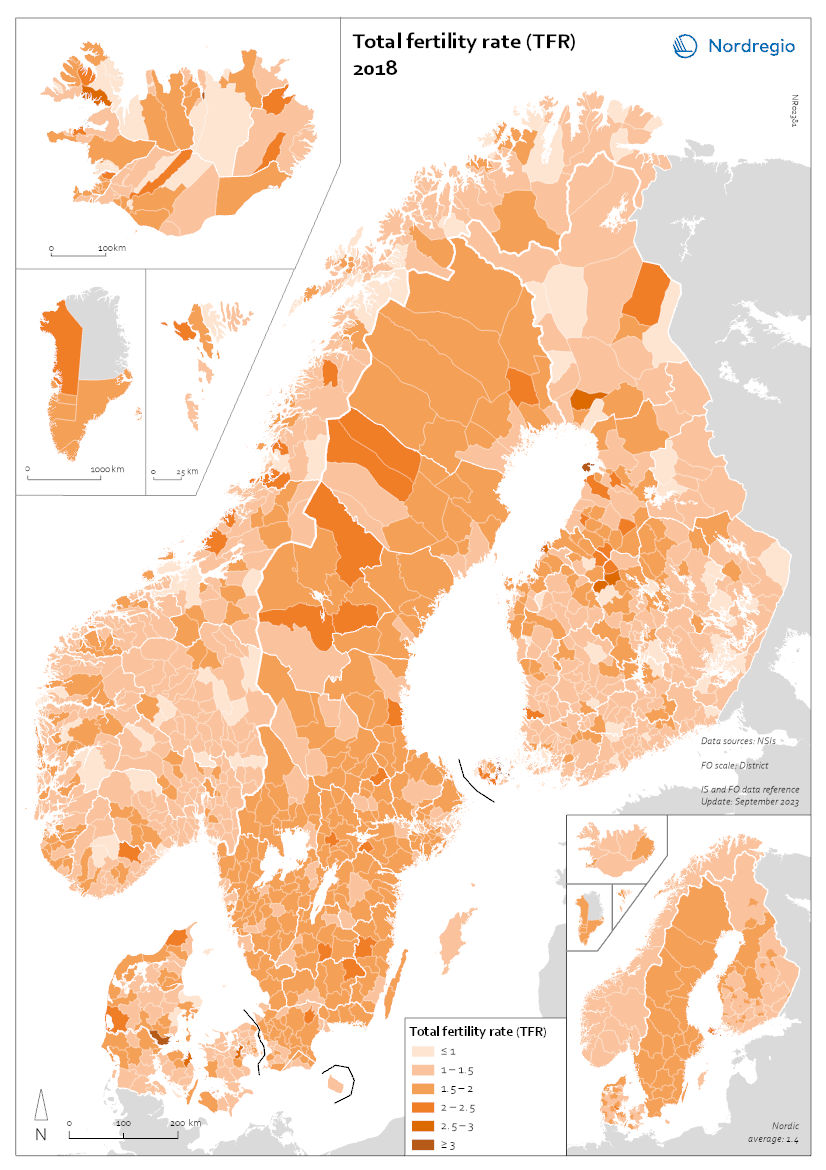
Total fertility rate (TFR) 2018
This map shows the total fertility rate (TFR) in 2018. The total fertility rate is the number of children a hypothetical cohort of women would have in one year. Data on total fertility rates is not available at the regional or municipal levels for all of the Nordic countries. The figures are estimated based on multiplying the general fertility rate by 30 (representing the typical number of reproductive years, between 15 and 45), assuming the general fertility rate is constant throughout this period. The general fertility rate is the number of births per woman during the childbearing years. At the regional level, age and gender composition are indicative of past trends but also harbingers of future population change. In 2018, prior to the pandemic, most Nordic municipalities had fertility levels in line with their respective national levels. Most municipalities within Greenland and the Faroes had fertility rates above 1.5 children per woman, consistent with national rates of about 1.9. Municipalities in Sweden and Denmark typically had fertility rates of 1.5 or higher, consistent with their national rates of 1.7. By contrast, many municipalities in Norway and Finland had fertility rates of 1.5 or lower. Iceland and Åland also showed varying rates across municipalities, ranging from 1 to over 1.5.
2025 April
- Demography
- Nordic Region
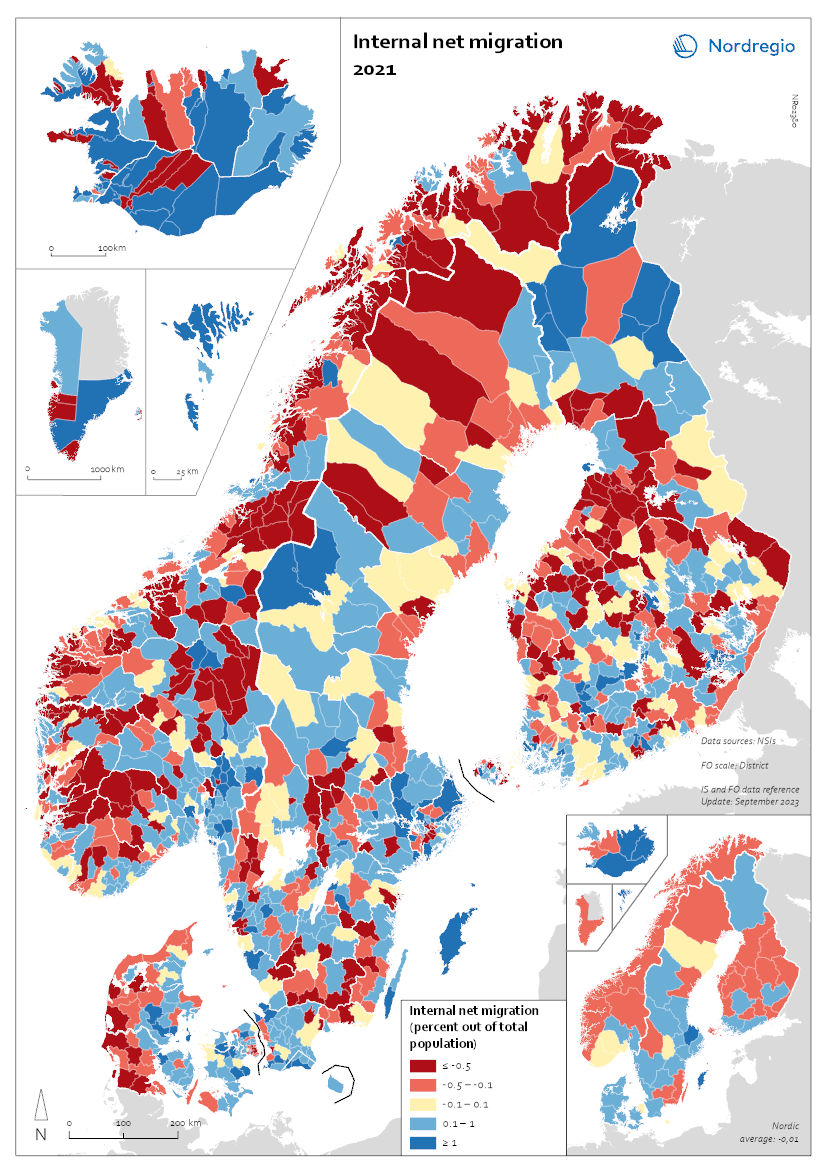
Internal Migration 2021
This map shows the internal net migration in 2021 as a percentage of the total population. This map shows the internal net migration in 2021 as a percentage of the total population. The small map shows the result on a regional level, and the big map on the municipal level. Internal (sometimes referred to as domestic) net migration refers to migration between municipalities and regions within the same country. International migration is excluded. In 2021, internal net migration was positive (indicated by shades of blue) or at least balanced (shown in yellow) in many of the municipalities in central and northern Sweden and in central and eastern Finland – areas that traditionally were more likely to lose population due to internal migration. Conversely, several municipalities in the capital regions – such as Stockholm, Oslo, and Copenhagen – exhibited negative internal net migration. Iceland, Greenland, and Åland exhibited mixed internal migration flows, with some municipalities experiencing positive net migration while others faced negative net migration. The Faroe Islands stand as an exception, maintaining only positive internal migration at the municipal level for this year.
2025 April
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
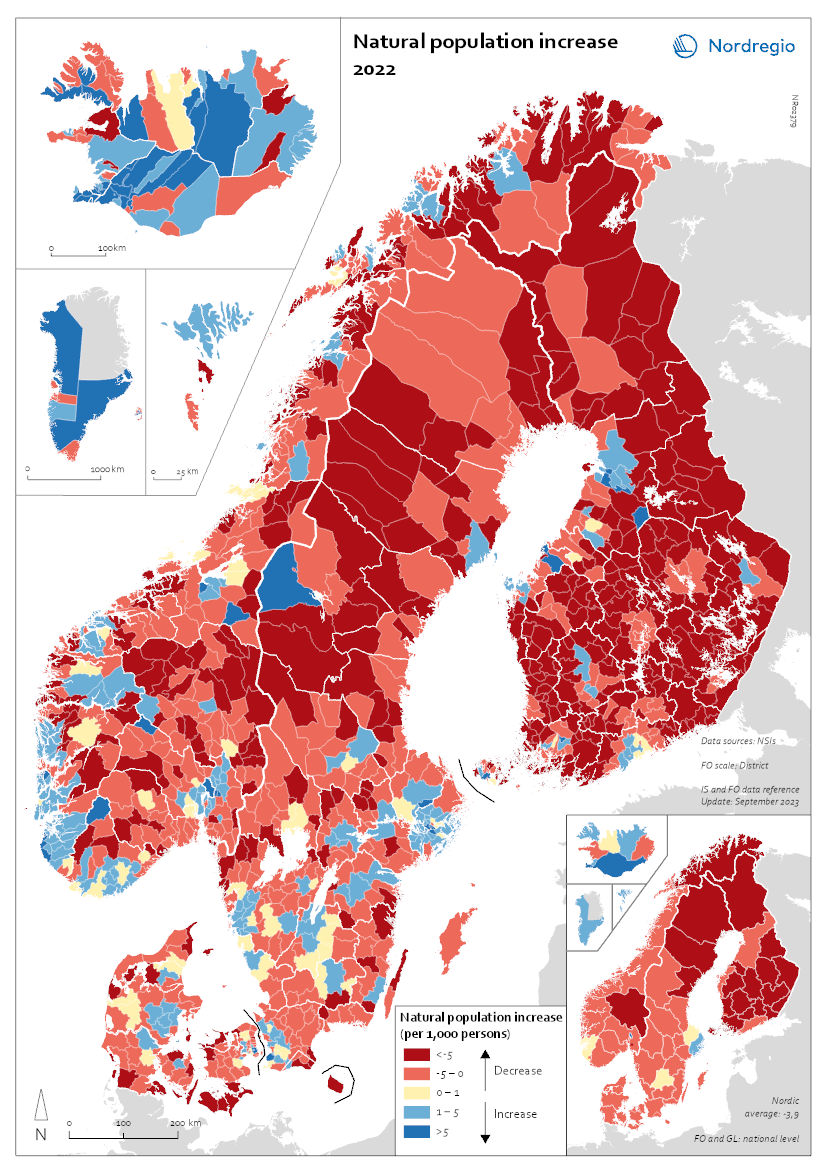
Natural population increase 2022
This map shows the natural population change per 1,000 persons in 2022. This map shows the natural population change per 1,000 persons in 2022 (i.e. between 1 Jan and 31 Dec 2022). Natural population change refers to births minus deaths (i.e. population change disregarding migration). The small map shows the result on a regional level, and the big map shows changes on the municipal level. Red shades refer to population decrease, blue shades to population increase, and yellow shades to balanced development. The map shows that levels of natural population change do not only vary across but also within the Nordic countries. Urban areas such as Stockholm and Gothenburg in Sweden; Oslo and Bergen in Norway; Copenhagen and Aarhus in Denmark; as well as Helsinki and Turku in Finland all experienced positive natural population change. This can be attributed to the comparatively young population age structure of these urban centres. Young people of child-bearing age often cluster in cities for study and work, and many start families there. By contrast, rural and remote areas often have a higher proportion of older people and, as such, tend to register more deaths than births, resulting in negative natural population change. These patterns are particularly pronounced in Finland but also in the northern parts of Sweden and Norway. Nonetheless, there are exceptions. In Iceland, Greenland, and the Faroe Islands, which had comparatively high levels of natural population growth at national level, a majority of municipalities, including many in rural areas, still registered more births than deaths in 2022 (77% of municipalities in Iceland, 60% in Greenland, 67% on the Faroe Islands). In the other Nordic countries, only a minority of municipalities, mostly in urban centres, recorded natural population increase in 2022 (30% in Norway and Sweden, 26% in Denmark, 12% in Finland).
2025 April
- Demography
- Nordic Region
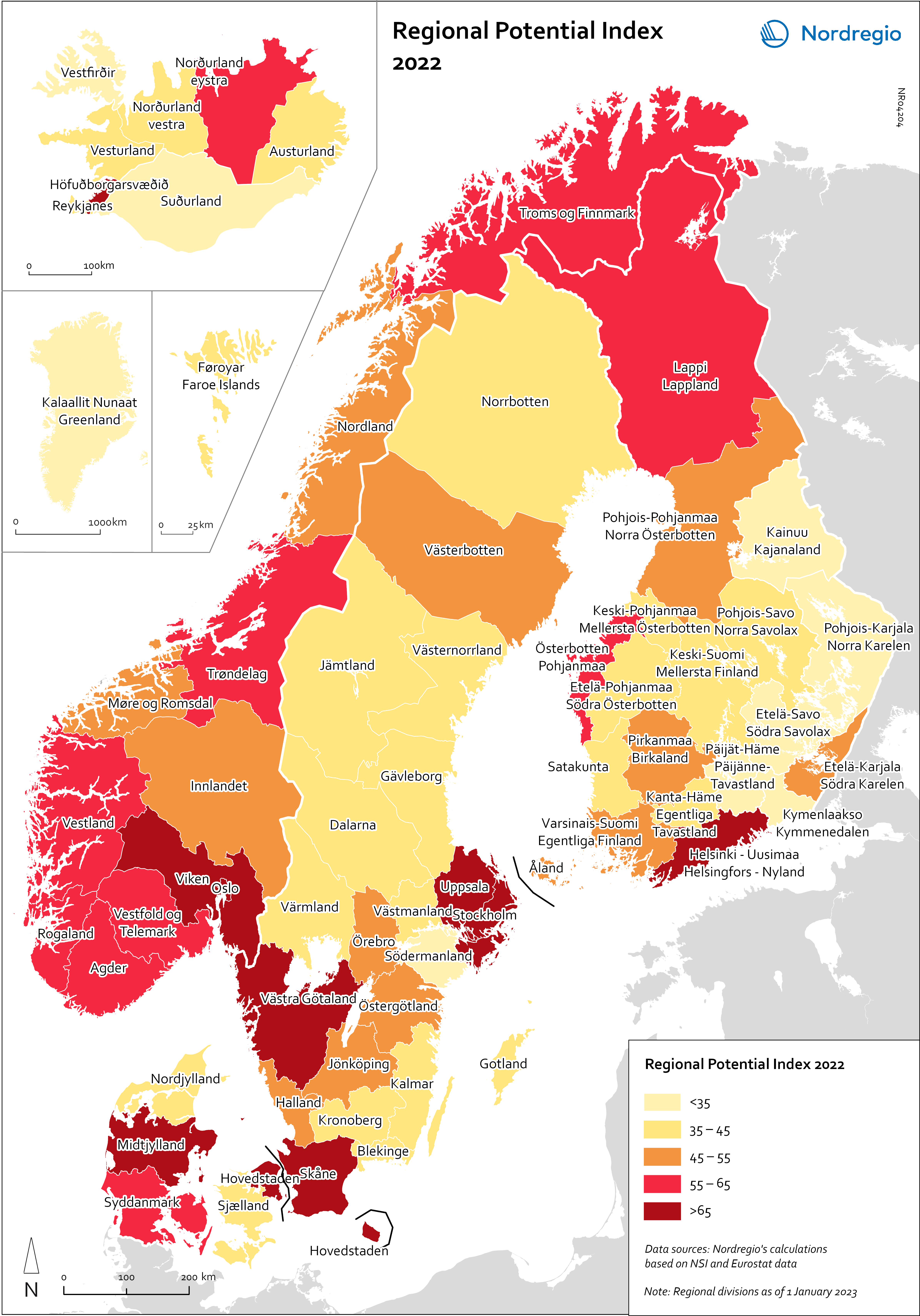
Regional Potential Index 2022
This map shows the result of Nordregio’s Regional Potential Index in 2024 (data from 2022). Nordregio’s Regional Potential Index (RPI) enables cross-regional comparison of development potential and illustrates the regional balance between the Nordic countries and has been part of the State of the Nordic Region report since 2018. The purpose of this multidimensional index is to summarise the current and past performance of the Nordic regions across major policy domains. The index helps to identify regions that have high potential and those in need of further support to boost their potential and meet existing challenges. It provides policy-makers with a comparative learning tool that informs the design of effective regional development strategies at Nordic level. Nordregio’s RPI is a multi-item measurement scale that incorporates information about the demographics, labour market and economic output of the Nordic countries’ 66 administrative regions. It consists of eight indicators classified into four main groups and eight subgroups. These components and indicators were originally selected on the basis of their relevance for regional development. The 2024 RPI is based on a new refined method that maintains a similar set of indicators but applies a more robust statistical process to the construction of the RPI. In brief, the new methodology consists of a pre-processing stage, in which the input data is prepared for analysis, and a processing stage, in which the indicators are weighted and aggregated. More information about the method can be found in the State of the Nordic Region 2024 report. The RPI was calculated retroactively for the 2015–2023 period. However, the focus in this section is on 2022 – the most recent year in our time series with full data coverage. The map shows the redesigned RPI for that period. In line with the principles of accumulation and agglomeration that drive the…
2025 April
- Demography
- Economy
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
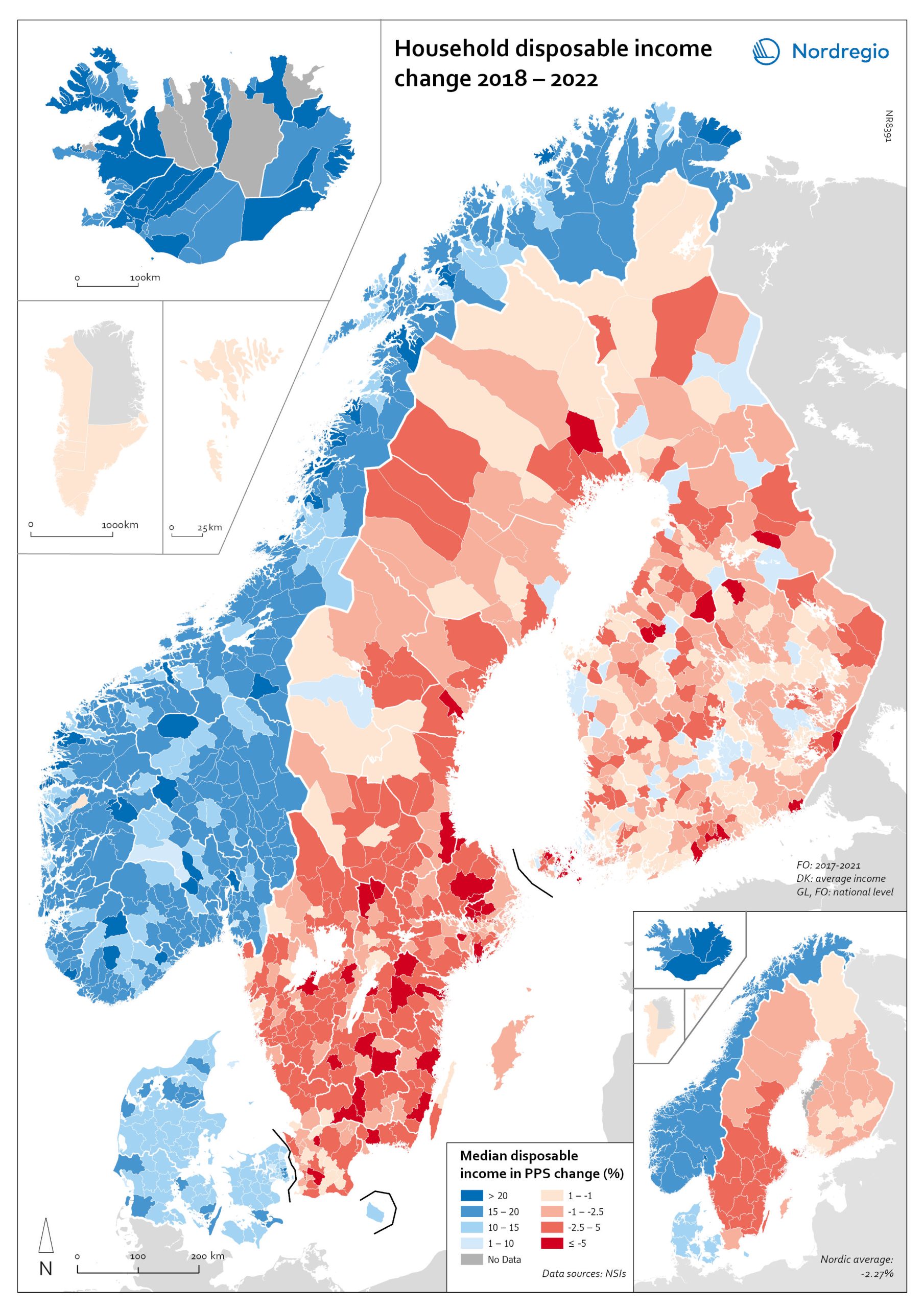
Household disposable income change 2018-2022
This map shows the percentage change in household disposable income between 2018 and 2022 in Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map). Household disposable income per capita is a common indicator of the affluence of households and, therefore, of the material quality of life. It reflects the income generated by production, measured as GDP that remains in the regions and is financially available to households, excluding those parts of GDP retained by corporations and government. In sum, household disposable income is what households have available for spending and saving after taxes and transfers. It is ‘equivalised’ – adjusted for household size and composition – to enable comparison across all households. Purchasing Power Standards (PPS) is used to compare the countries’ economies and the cost of living for households. As shown in the map, between 2018 and 2022, household disposable income increased for all Danish, Icelandic, and Norwegian municipalities and decreased for Finnish and Swedish municipalities. On average, the city municipalities have higher incomes and increased most in Finland and Sweden in 2018–2022. In Sweden, a tendency towards larger falls in income was observed in several southern municipalities. In summary, absolute household income increased in all Nordic countries but not when measured in purchasing power. Based on this metric, on average, Norwegian households are the most well-off and Iceland the worst off, while Danish households benefited from a stronger currency in 2022. Single-parent households have had lower increases in household income than other families in Norway and parts of Sweden. Municipalities show a similar trend in Norway and Denmark, although Norwegian coastal municipalities fared slightly better in 2022. Disposable income is falling in all Swedish and Finnish municipalities.
2025 April
- Economy
- Nordic Region
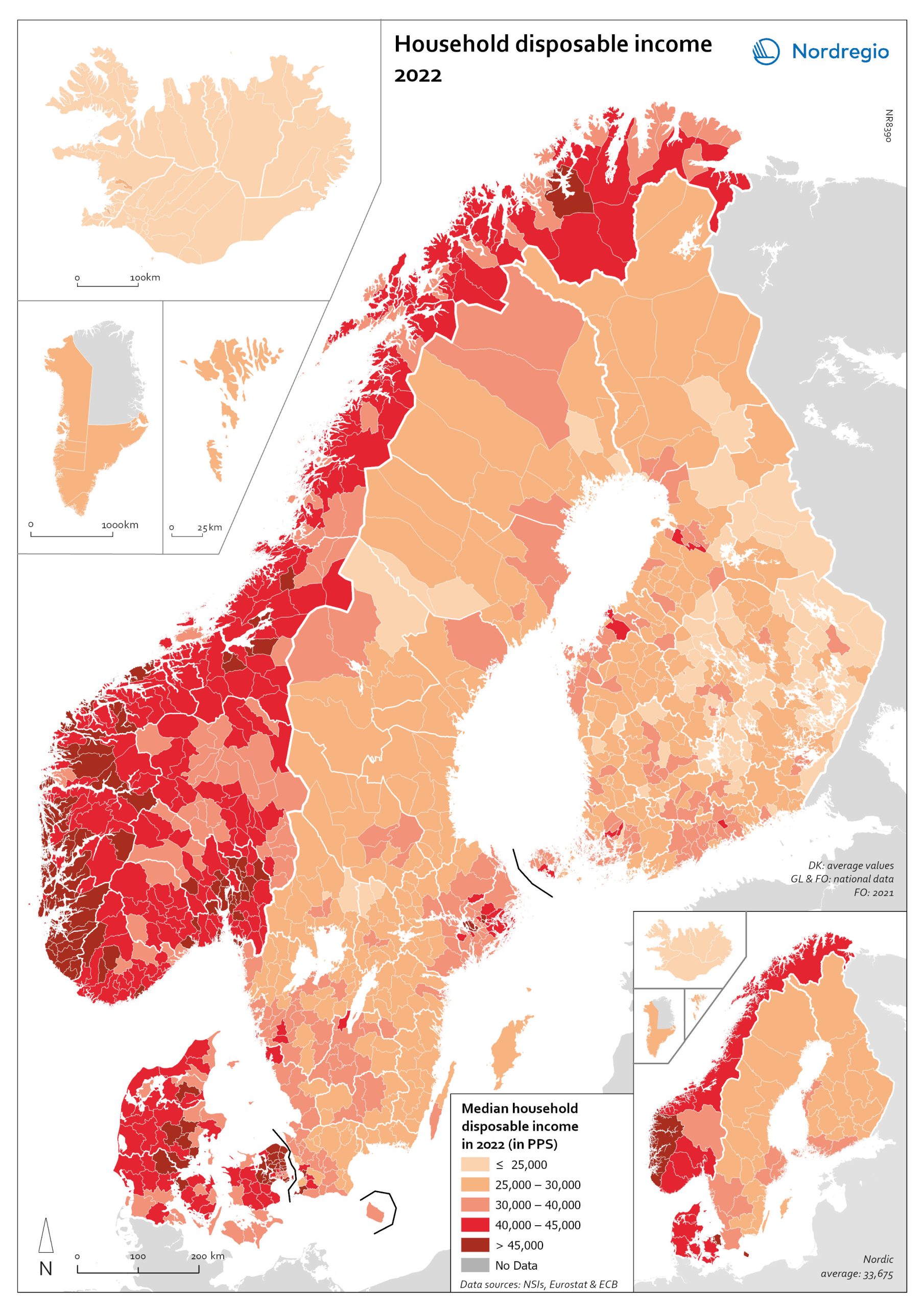
Household disposable income 2022
This map shows the median household disposiable income measured in purchasing power standard (PPS) in Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map) in 2022. Household disposable income per capita is a common indicator of the affluence of households and, therefore, of the material quality of life. It reflects the income generated by production, measured as GDP that remains in the regions and is financially available to households, excluding those parts of GDP retained by corporations and government. In sum, household disposable income is what households have available for spending and saving after taxes and transfers. It is ‘equivalised’ – adjusted for household size and composition – to enable comparison across all households. Purchasing Power Standards (PPS) is used to compare the countries’ economies and the cost of living for households. The map shows the intra-municipal differences in household disposable income in PPS, which reveals the different patterns in the Nordic countries. Norwegian coastal municipalities have slightly higher household disposable income than inland municipalities, with some exceptions. Finnish, Icelandic, and Swedish municipalities generally have much lower household disposable income compared to Norwegian and Danish municipalities, except for the larger urban areas. In Denmark, most municipalities are at a similarly high level, except for remote islands in the south. The differences between the Icelandic municipalities are rather small, at a medium to lower level.
2025 April
- Economy
- Nordic Region
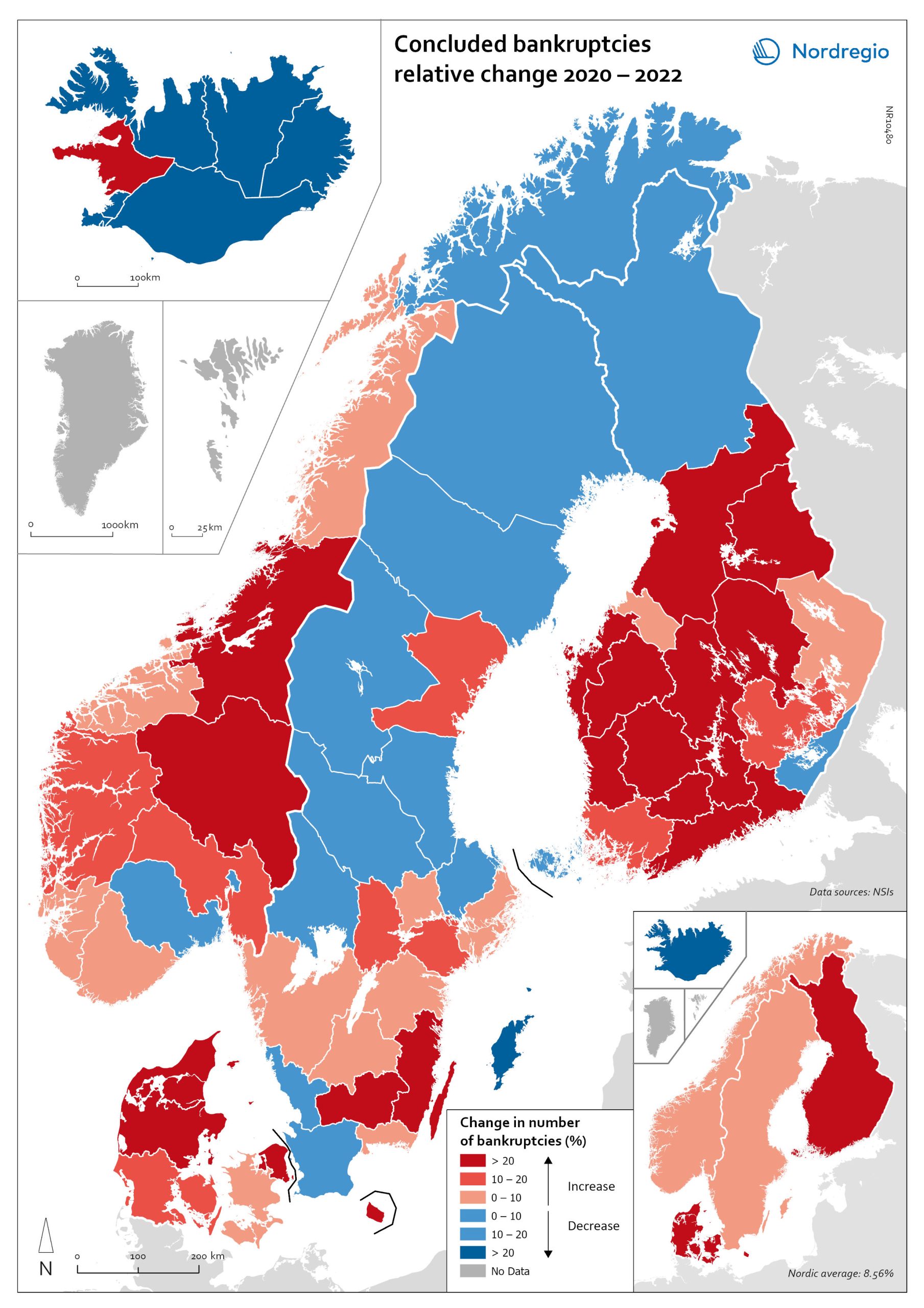
Change in the number of business bankruptcies (2020–2022)
This map depicts the change in total number of bankruptcies in the Nordic regions between 2020 and 2022. The red shades indicates an increase in numbers of bunkruptcies and blue shades a decrease. The big map shows the regional level and the small map the national level. The rate of business bankruptcies is a core indicator of the robustness of the economy from the business perspective. Nordic and international businesses have been impacted by both the COVID-19 pandemic and rising inflation in recent years. In terms of the level of bankruptcies, data from Eurostat (2024) shows that the Nordic countries fared relatively well compared to other high-income countries between 2020 – 2022. In the years during and after the COVID-19 pandemic, the most densely populated regions saw the highest levels of bankruptcies. This finding is partly to be expected, as these regions also tend to be those with the highest number of companies. However, some variation can be seen across the countries. Overall, Iceland and Finland experienced the lowest rate of bankruptcies in 2020 and 2022. Denmark had the highest level of bankruptcies during COVID-19. Potential explanations for the national variations may include the countries’ varying strategic approaches to the pandemic. Denmark enforced more restrictive lockdowns compared to, for example, Sweden, where the less restrictive approach has been linked to the more limited impact on business bankruptcies in the early part of the pandemic. Furthermore, there is a large consensus that the many jobretention schemes across the Nordic Region also served to limit the number of bankruptcies. However, new data from early 2024 shows that after the job-retention schemes ended, and while high inflation and interest rates were increasing the pressure on Nordic companies, the level of bankruptcies increased. In 2023, 8,868 companies went bankrupt in Sweden the highest number…
2025 April
- Economy
- Nordic Region
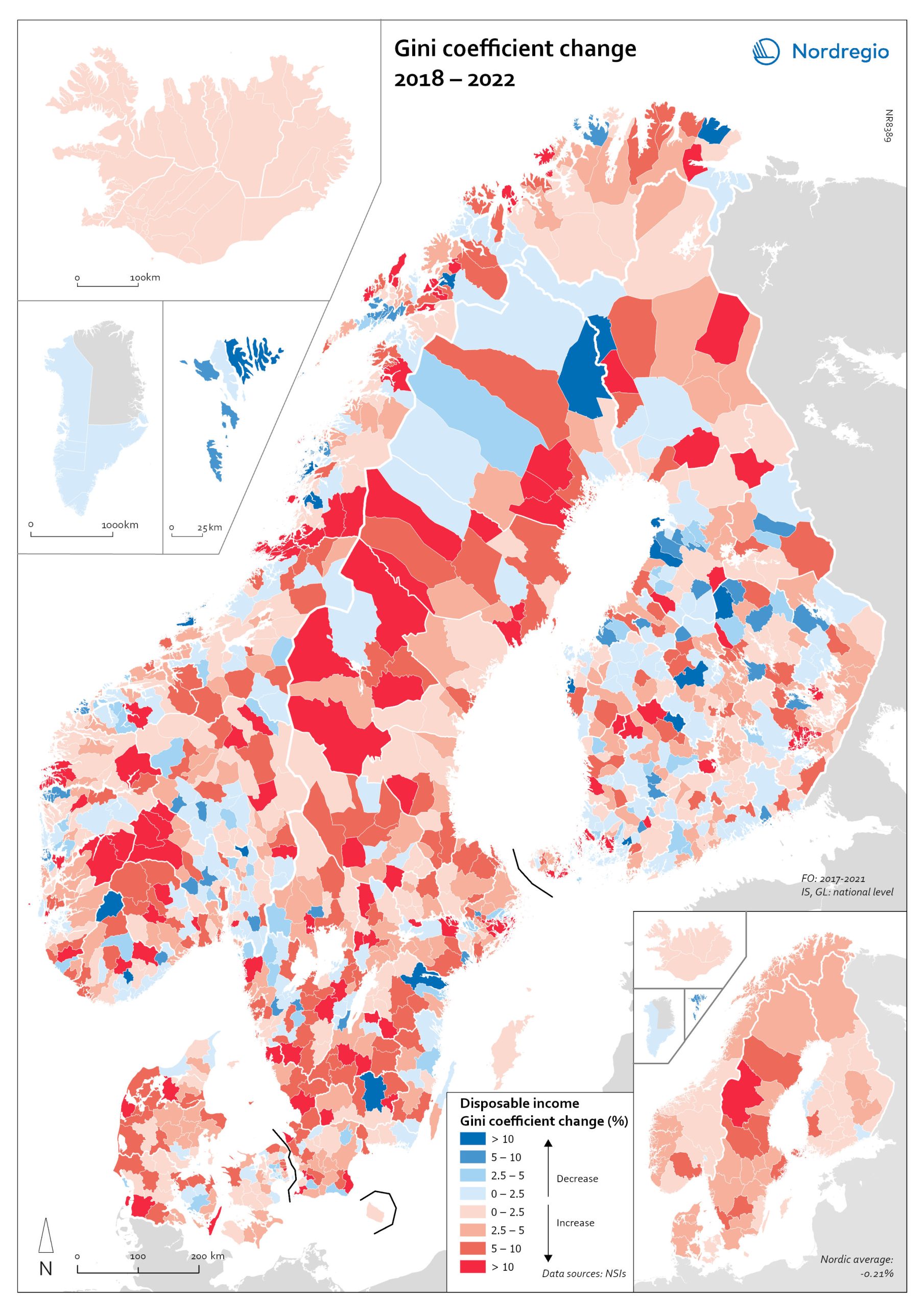
Gini coefficient change 2018-2022
This map shows the percentage change in the Gini coefficient between 2018 and 2022. The big map shows the change on municipal level and the big map at regional level. Blue shades indicate a decrease in income inequality, while red areas indicate an increase in income inequality The Gini coefficient index is one of the most widely used inequality measures. The index ranges from 0–1, where 0 indicates a society where everyone receives the same income, and 1 is the highest level of inequality, where one individual or group possesses all the resources in the society, and the rest of the population has nothing. The map illustrates significant variations in the change in income inequality across Nordic municipalities and regions. Between 2018 and 2022, income inequality increased in predominantly rural municipalities, notably in Jämtland, Gävleborg, Dalarna and Västerbotten in Sweden, as well as Telemark in Norway. For Denmark, the rise in inequality is mainly for the municipalities in Western Jutland. At the same time, approximately one third of municipalities in the Nordic Region experienced a decrease in income inequality during the same period, primarily in Finland and Åland. For example, in Finland, the distribution of inequality was more varied. This trend aligns with the ongoing narrowing of the household income gap observed in many Finnish municipalities since 2011, which is mainly attributed to the economic downturn of the early 2010s, as well as demographic shifts such as outmigration and ageing.
2025 April
- Economy
- Nordic Region
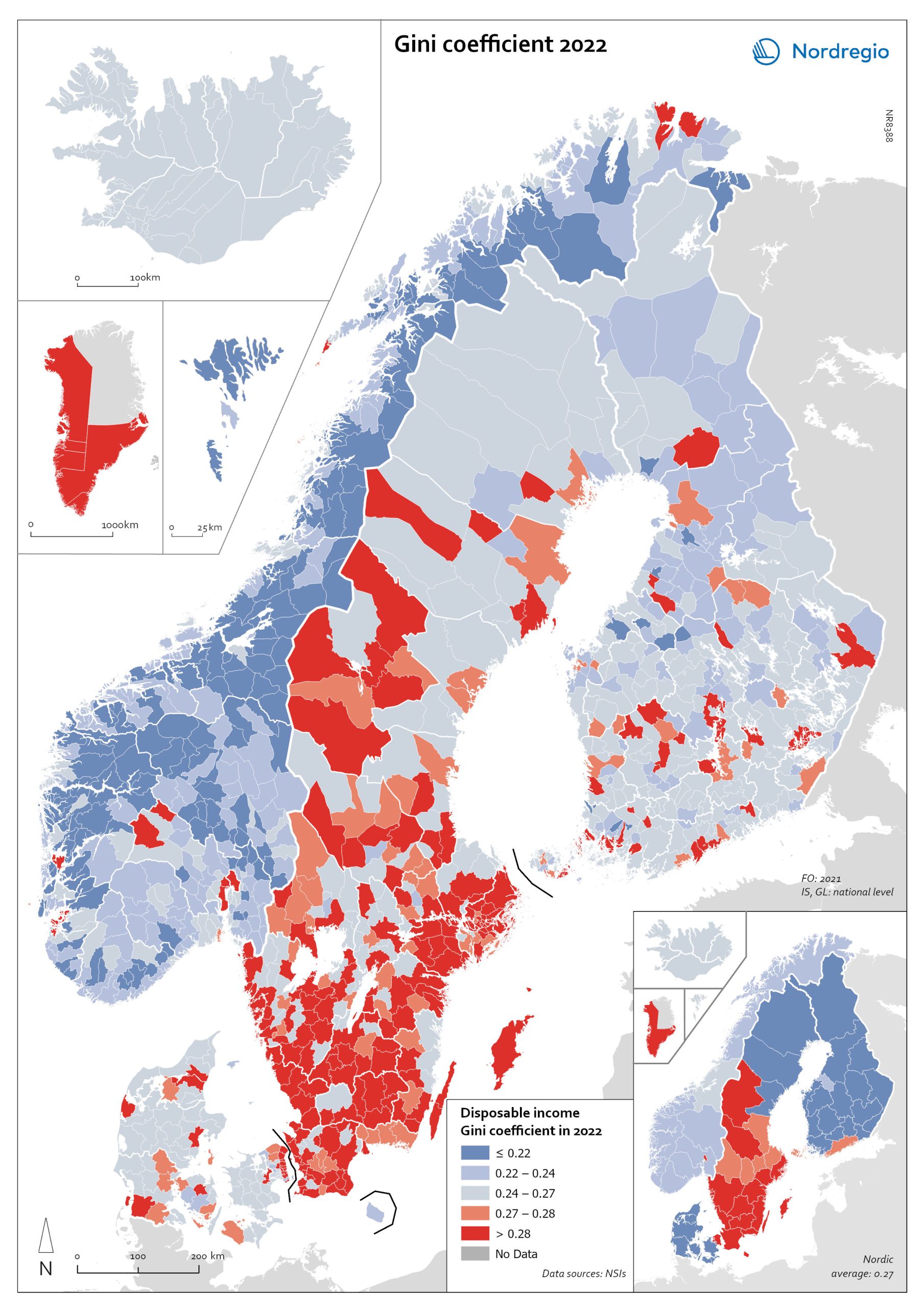
Gini coefficient for disposable income in 2022
This map shows the Gini coefficient in Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map) in 2022 (no data was available for Iceland). Blue shades indicate a Gini coefficient below the Nordic average. Red areas indicate a Gini coefficient above the Nordic average (0.27, excluding Greenland, as a statistical outlier). The data for the Faroe Islands is for 2021. The Gini coefficient index is one of the most widely used inequality measures. The index ranges from 0–1, where 0 indicates a society where everyone receives the same income, and 1 is the highest level of inequality, where one individual or group possesses all the resources in the society, and the rest of the population has nothing. In 2022, the highest municipality income disparities were observed in the capital city regions of Denmark, Finland and Sweden, each of which had Gini coefficients around 0.6. Danderyd (0.64), Lidingö (0.52), and Gentofte (0.51) had the highest Gini coefficients. These municipalities also have some of the highest incomes in their respective countries.
2025 April
- Economy
- Nordic Region
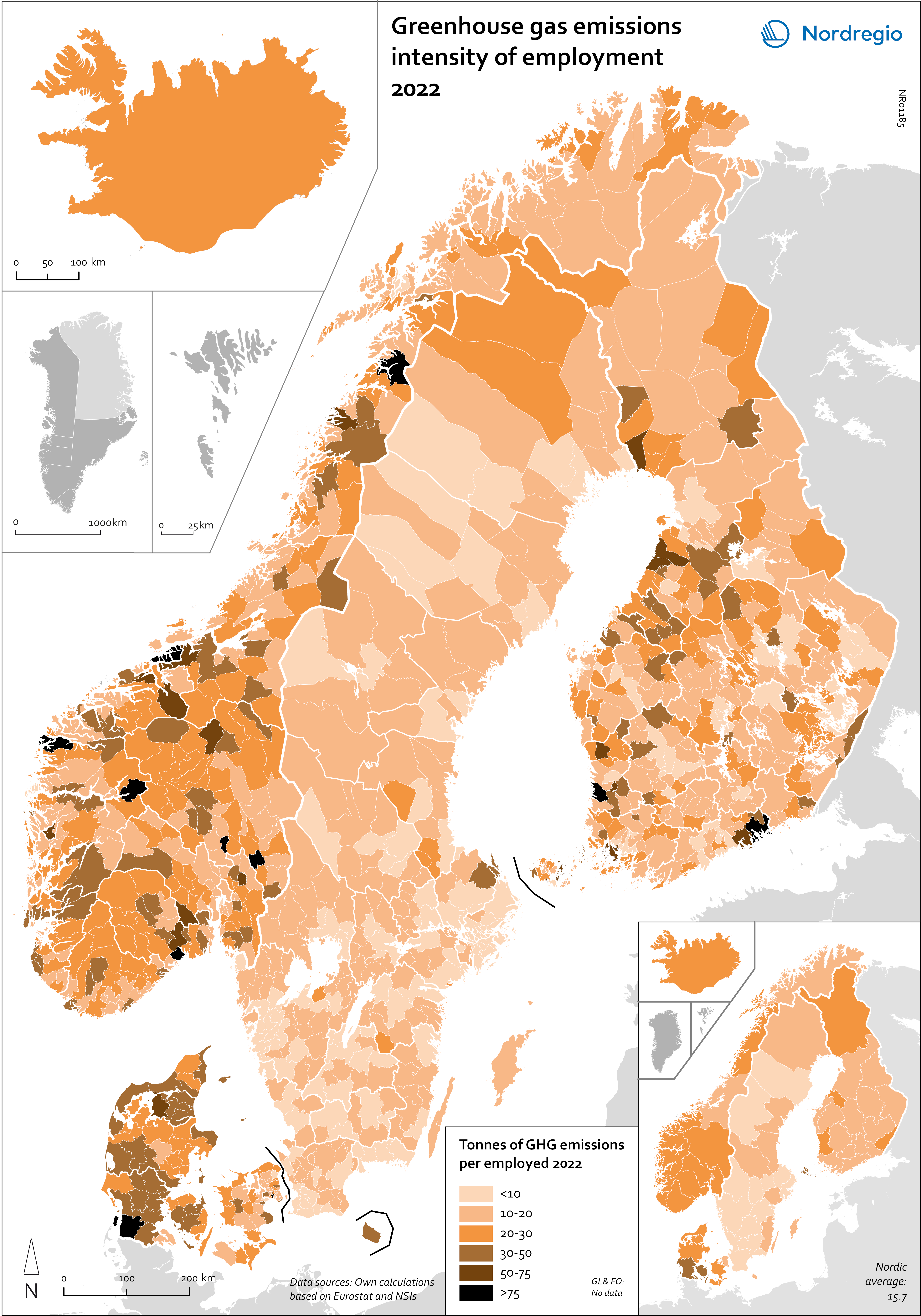
Greenhouse gas emissions intensity of employment in 2022
This map shows the tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions per person employed in Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map) in 2022. The data for Iceland is presented at the national level, while no data was available for the Faroe Islands and Greenland. The map is based on data on emissions per sector and country from Eurostat and detailed employment by sector data from the Nordic statistical offices. By calculating the average emissions per person employed and per sector we could use municipal employment by sector data to assess the average emissions per person employed in each municipality. The results are an estimation based on the assumption that all jobs in the same sector have the same GHG emissions. In 2022, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions per person employed in the Nordic Region were 15.7 tonnes. This is higher than the EU average of 13.5 tonnes. There are also fairly big differences between the Nordic countries, with higher emissions per person employed in Iceland (28.6), Denmark (23.1) and Norway (20.5) and lower emissions in Finland (15.7) and Sweden (8). On the other hand, the emissions per person employed have decreased faster in the Nordic Region than for the EU as a whole. In the last decade, emissions per person employed fell by 24% in the Nordic Region compared to the EU average of 22%. The biggest decrease (32%) was in Finland. The sectors with the highest emissions per worker vary slightly between the countries. In Sweden and Norway, the sector with by far the highest emissions per worker was the manufacture of petroleum coke and refined petroleum products. However, it should be noted that the number of workers in this sector is small. In Denmark, the highest emissions by person employed could be found in water transport; in Finland, in…
2025 April
- Environment
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
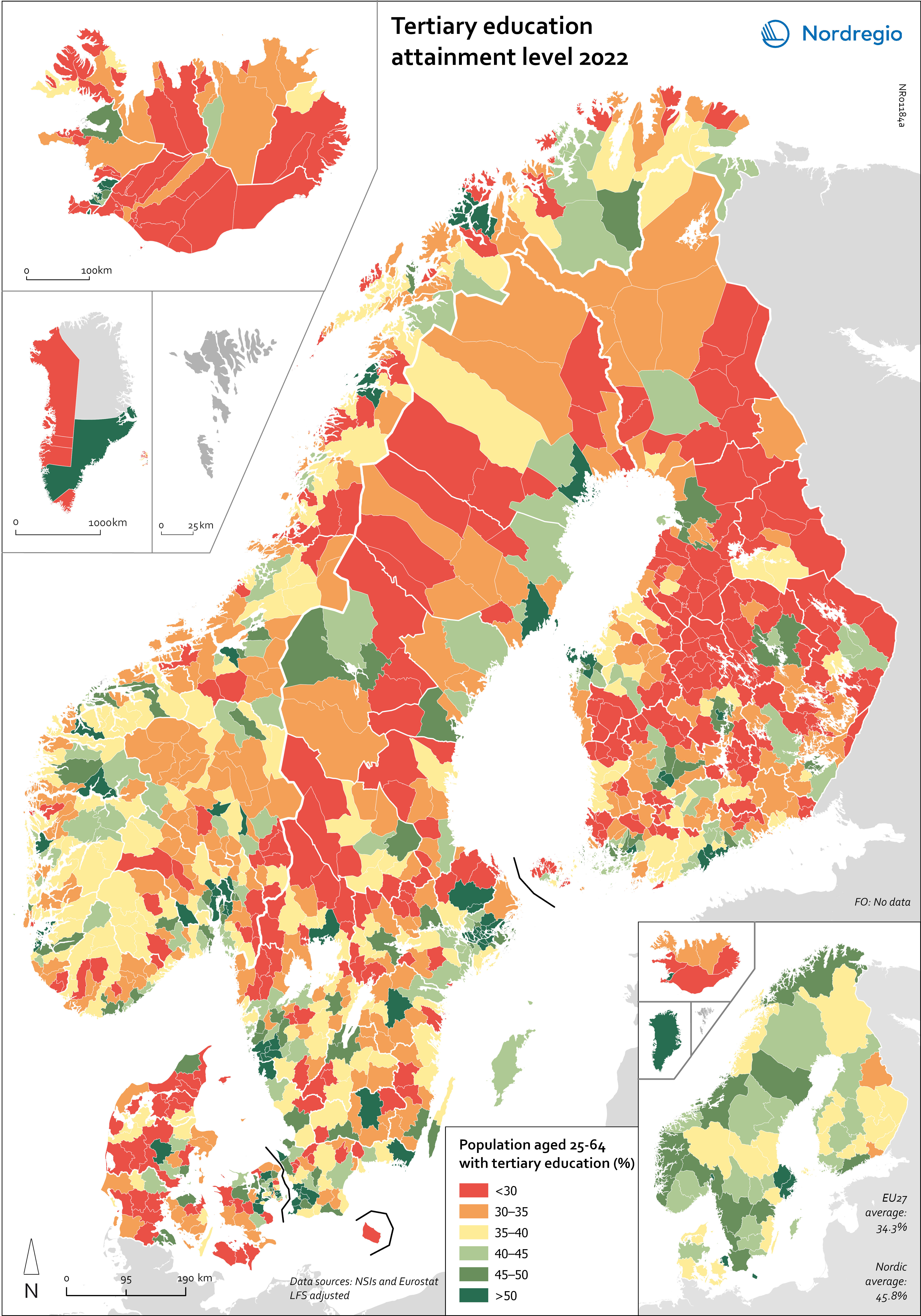
Tertiary education attainment level 2022
This map shows the share of people aged 25-64 years with a tertiary education in Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map) in 2022. All of the Nordic countries have a higher share of people who completed tertiary education than the EU average. The highest share is in Sweden (48.6%), followed by Norway (47.8%), Iceland (42.9%), Finland (42.7%) and Denmark (42.1%). There are, however, big differences within the countries with a considerable urban-rural divide in terms of tertiary education. The capital regions of Oslo (66%), Stockholm (58%), Copenhagen (Hovestaden) (51%), Reykjavik (51%) and Helsinki (Uusimaa) (49%) stand out with particular high share of tertiary educated population. Conversely, rural regions such as Iceland outside of Reykjavik (30%), Kymenlaakso (34%), Kainuu (34%), Etelä-Savo (35%), Satakunta (35%) in Finland and Syddanmark (35%), Midtjylland (36%) and Nordjylland (36%) in Denmark are among the regions with the lowest share of tertiary educated population. The successful implementation of the Bologna Process and the derived increase in educational levels of young people in the Nordic Region coincides with large numbers of the ‘baby boomer’ generation leaving the labour market. This generation has a significantly lower level of education than the current 24–35 age group – i.e. those who are now entering the labour market. This trend can be seen across the Nordic Region.
2025 April
- Labour force
- Nordic Region

Employment in high-skilled occupations 2022
This map displays the share of high-skilled workers as a share of the total number of workers in Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map). “High-skilled workers” is here defined as group 1-3 (Managers, Professionals and Techinicians/associated professionals) of the International Standard Classification of Occupations (ISCO). For Iceland national data is used. The EU average of high-skilled workers is 43%, and the Nordic countries are at the top of the rankings – 49.5% in Finland, 51.1% in Denmark, 54.2% in Norway, 54.5% in Iceland and 58.9% in Sweden. On a regional level, the highest share is in the capitals and bigger cities, such as Stockholm (72%), Oslo (71%), Hovedstaden (Copenhagen) (60%), Uppsala (60%) and Uusima (Helsinki) (59%). The lowest shares are in the Finnish regions of EteläPohjanmaa, Keski-Pohjanmaa, Satakunta and Etelä-Savo (less than 40%). However, this does not necessarily mean that employers will have a greater chance of successfully recruiting high-skilled workers in the future, partly because those in this group already have jobs and partly due to generally lower investments in education.
2025 April
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
- Research and innovation
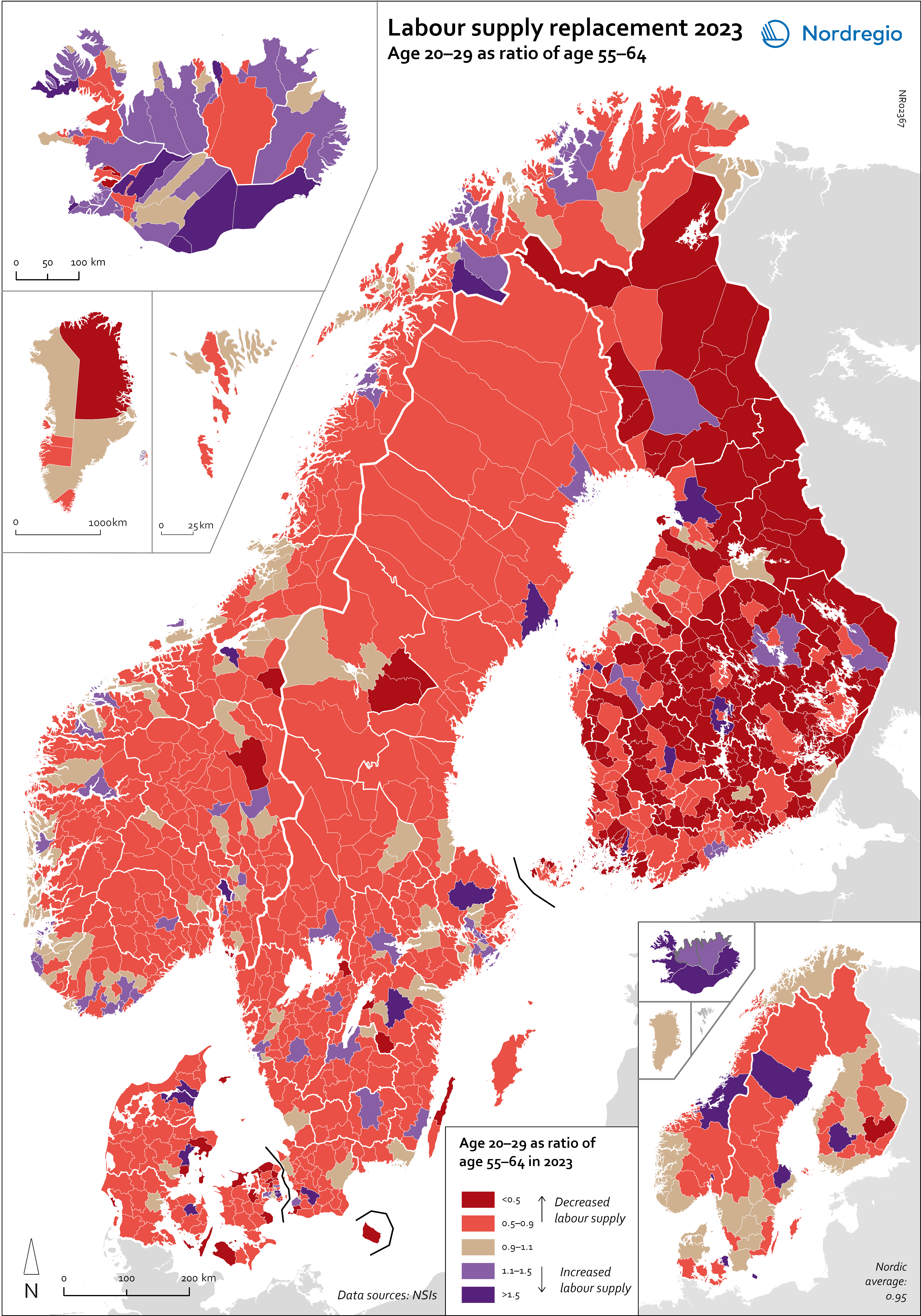
Labour supply replacement 2023
This map shows the ratio between the age groups 20–29 and 55–64 at the municipal level (big map) and regional level (small map). A ratio below 1 indicates that fewer individuals are entering the labor market than leaving it, while a ratio above 1 means more people are entering than exiting. For the Nordic Region as a whole, the ratio is 0.95, meaning that there are slightly fewer people in the age group 20–29 than 55–64. Iceland is the only country with a ratio above 1 (Iceland: 1.3; Greenland: 0.99; Denmark: 0.97; Norway: 0.95; Finland: 0.94; Sweden: 0.93; Faroe Islands: 0.88; Åland: 0.63). All of the Icelandic regions, as well as the capital regions of Norway, Denmark and Finland, have a ratio above 1. In Sweden, the highest ratios are in Uppsala (1.25), Västerbotten (1.14) and Östergötland (1.03), while the ratio in Stockholm is below 1 (0.95). The lowest ratios are found in Etelä-Savo (0.62) and Åland (0.63) in Finland, Sjælland (0.63) in Denmark, Västernorrland (0.74) in Sweden, and in Vestfold og Telemark (0.78) and Viken (0.77) in Norway. However alarming these trends and developments are, they are neither new nor undescribed. An analysis of the factors and policy strategies that are influencing these developments enables adjustments to be made to future trends.
2025 April
- Demography
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
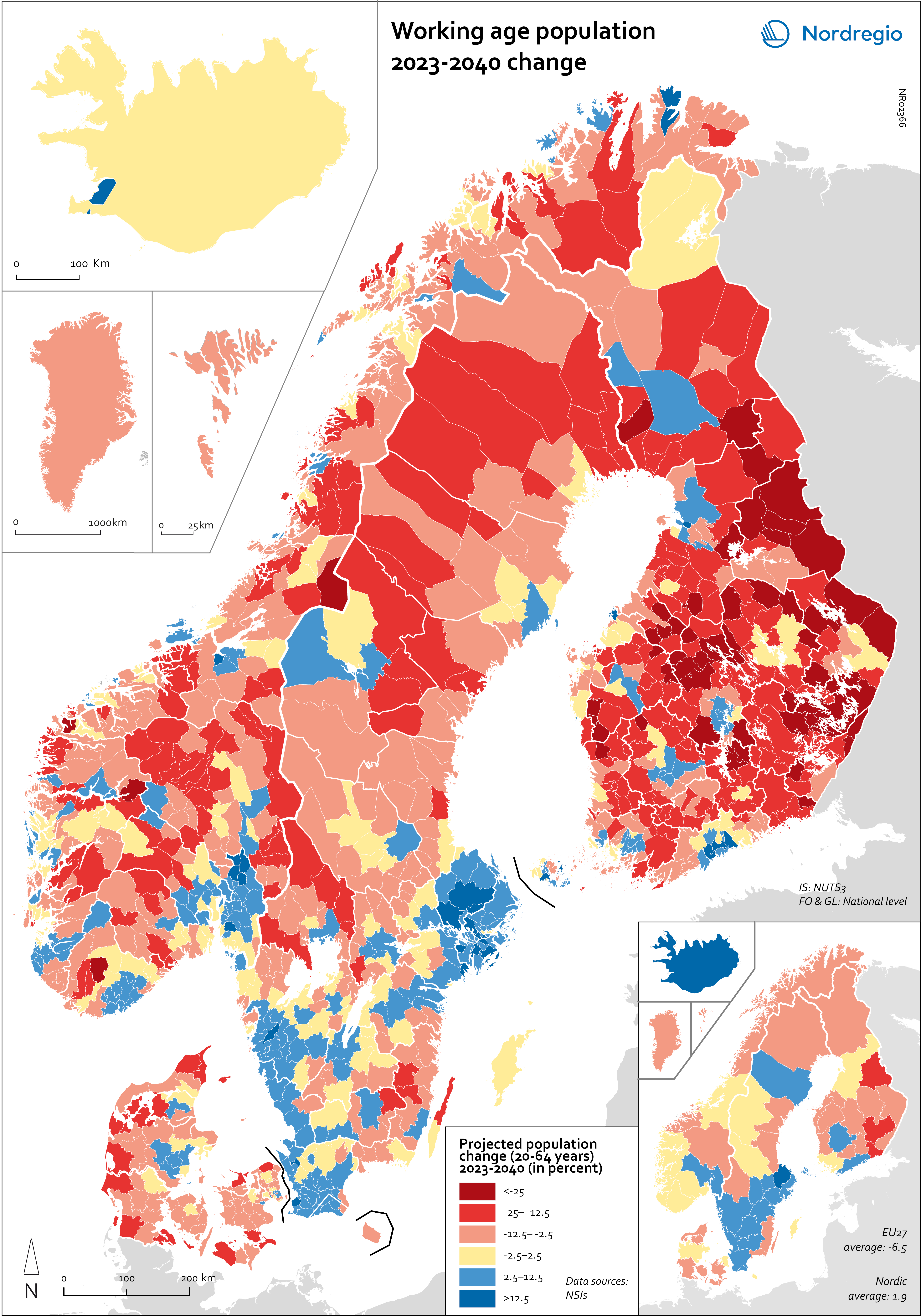
Working age population – 2023-2040 change
This map illustrates the projected change in the working-age population across Nordic municipalities (large map) and regions (small map) from 2023 to 2040. The working-age population is defined here as individuals aged 20 to 64. The blue areas on the maps represent municipalities and regions where the working-age population is expected to increase during this period. In contrast, the red areas indicate a projected decline in the working-age population. These projections are based on data from Nordic statistical institutes, though it’s important to note that the underlying assumptions may vary between Nordic countries. In most of the Western world, the working-age population is decreasing. In the EU, this age group is expected to decrease by 6.5% between 2023 and 2040. Only five EU countries – Malta, Luxembourg, Ireland, Sweden and Belgium – are expected to enjoy growth in the working-age population during this period. However, in the Nordic Region as a whole, the working-age population is expected to grow slightly, with an average increase of 1.9%. As the map shows, the distribution is quite varied, with considerable differences both between and within the countries. The biggest increase is expected in Iceland (28%), followed by Sweden (5.8%), Åland (3.9%) and Norway (0.6%). Decreases are expected in Finland (-0.5%), the Faroe Islands (-2.6%), Denmark (-3.2%) and Greenland (-11.4%). This development is in addition to the decreases already experienced by Finland since 2013. In general, the trend of growing populations in cities and decreasing populations in rural areas is expected to continue. The regions that are expected to have the highest working-age population growth include Höfuðborgarsvæðið in Iceland, Uppsala (+13%), Stockholm (+12%), Skåne (+9%), Halland (+7%) and Västra Götaland (+6%) in Sweden, Uusimaa (+8%) and Pirkanmaa (+5%) in Finland, and Oslo and Viken in Norway (+5%). In addition, Copenhagen municipality (+5%), Rødovre (+9%)…
2025 April
- Demography
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
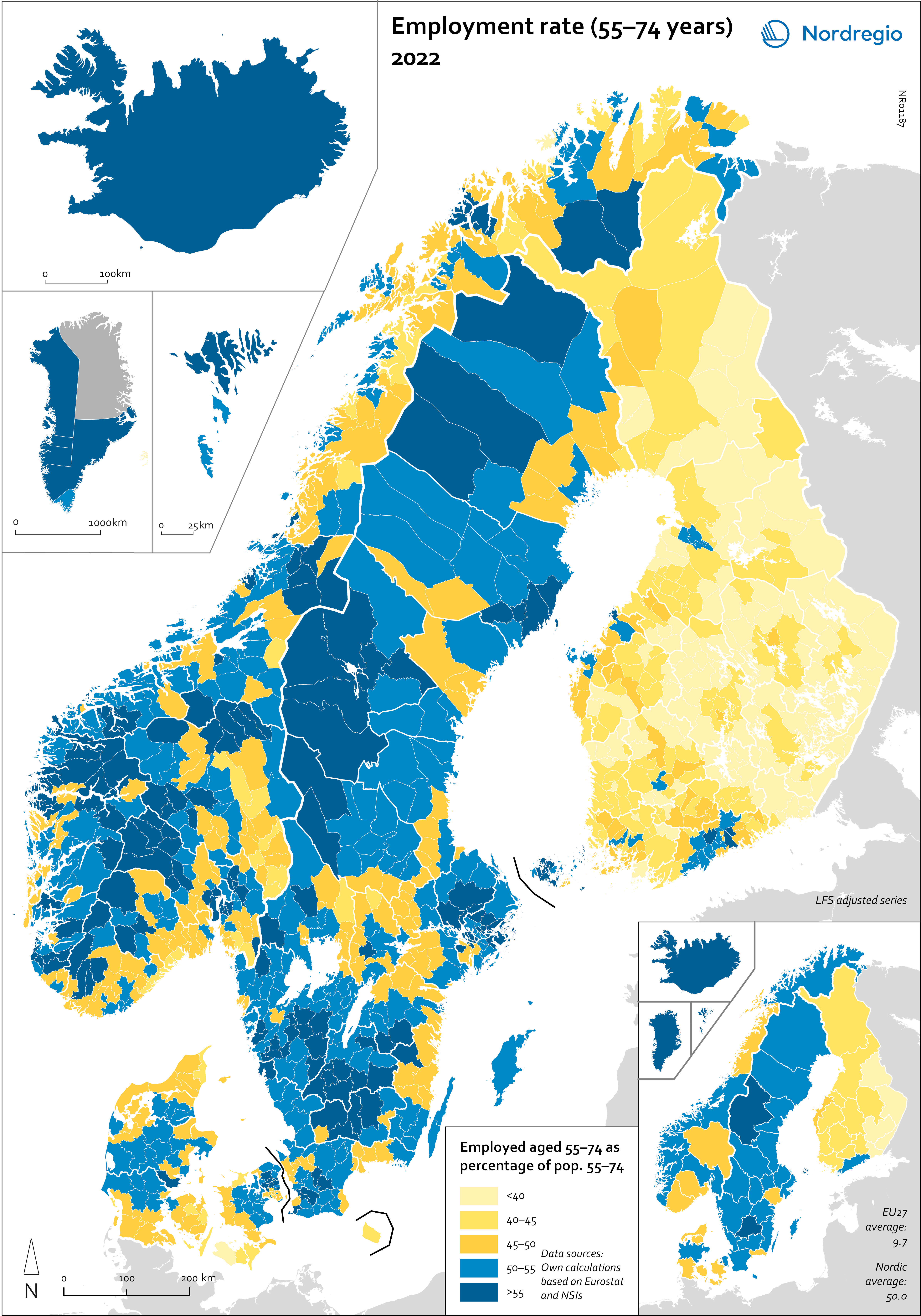
Employment rate (55-74 years) 2022
This map shows the employment rate for the age group 55-74 years in the Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map) in November 2022. Employment rate refers to the share of population in a particular age group that is in employment (LFS definition), in this map it is measured for the age group 55-74 years. Older adults (55+) were less affected by the pandemic. In general, this age group has a stronger attachment to the labour market, and a higher proportion work in occupations where remote work was possible. For quite some time, the Nordic Region has boasted a higher employment rate among older adult workers compared to the rest of Europe, although this gap has narrowed somewhat in recent years. In 2022, 75.5% of the Nordic population aged 55–64 were employed, whereas the EU average stood at 62.3%, representing a difference of 13 percentage points. In 2012, however, this difference was 21 percentage points, and in 2002, it was 29. The map shows variation between the Nordic countries, with Finland exhibiting a lower employment rate for this age group. The highest rates were observed in the Faroe Islands (62%), Greenland (61%), Åland (56%), and the Swedish regions of Jämtland-Härjedalen (55%) and Jönköping (54%). The Labour Force Survey (LFS) is the official source for labour market statistics and the only source that is comparable across countries. The data comes from a standardised survey that is conducted in the same way in all EU countries, as well as in many non-EU countries, including in Norway, Iceland and the Faroe Islands. The LFS is the main source for the map, however since it is not possible to break down at a municipal level, register data has been made to create estimates at a municipal level.
2025 April
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
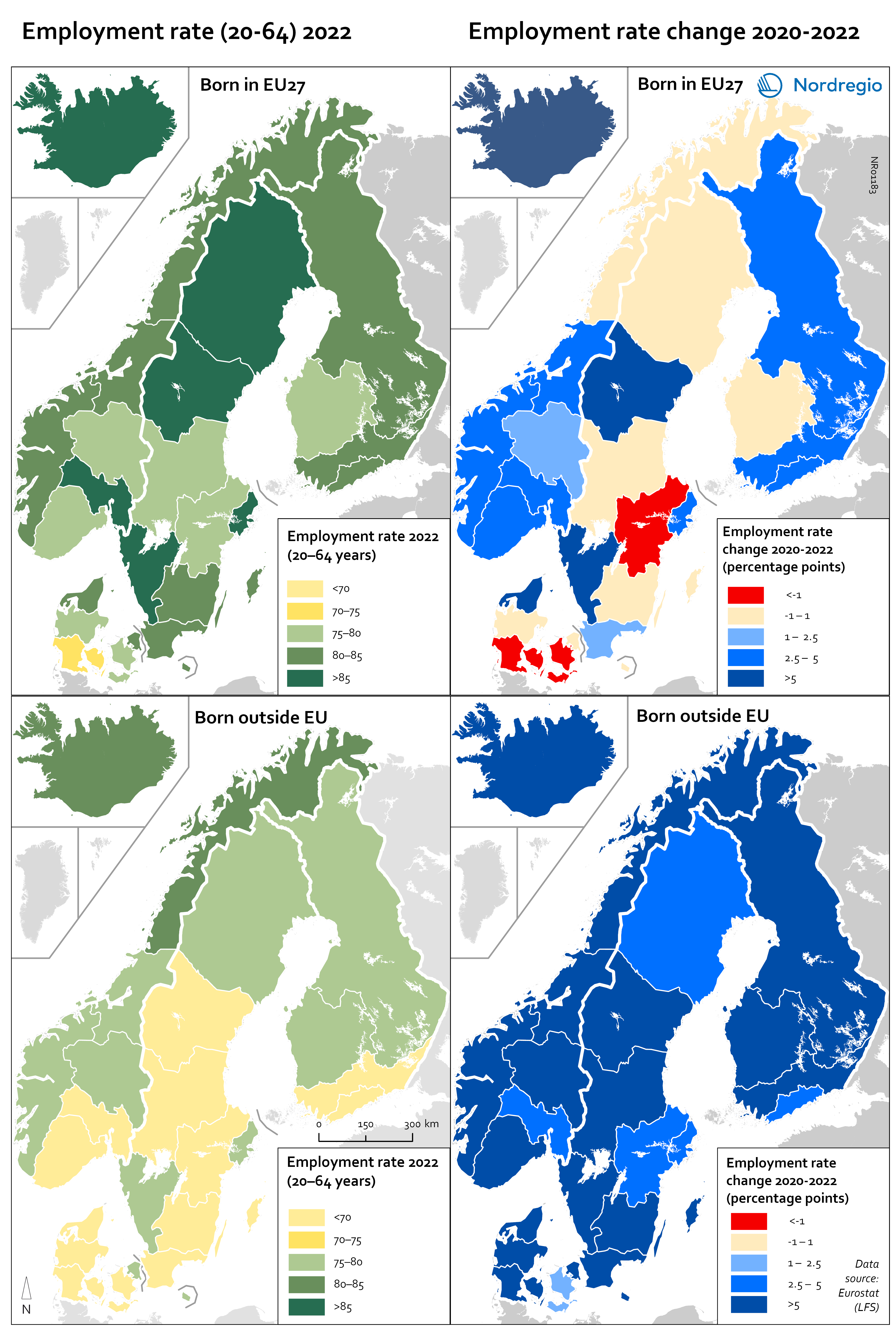
Employment rate 2022 and Employment rate change 2020-2022 among foreign-born
These maps shows the employment rate in 2022 for those born in a EU country (top left) and those born outside of the EU (bottom left), as well as the change in employment rate between 2020 and 2022 for those born in the EU (upper right) and outside the EU (lower right). The data is displayed at NUTS 2 level and comes from the labour force survey (LFS). The category ‘foreign-born’ is quite heterogeneous and consists of everything from labour migrants to refugees – two groups who face quite different conditions and have different connections to the labour market. The employment rate for people born in another EU country – a group that includes a large proportion of labour migrants – has been on par with the employment rate for native-born people for a long time. As can be seen in the top-left figure in the map, in 2022 all NUTS2 regions except Southern Denmark had an employment rate of 75% or more for this group. The highest employment rate was observed in the Swedish NUTS2 regions of Middle Norrland, Stockholm and Western Sweden, followed by Oslo in Norway and Iceland. The employment rate for people born outside of the EU (a group that largely consists of refugees) has been lower for a long time than that of native-born people and those born in the EU. While the employment rate for people born in non-EU countries is still lower than for natives (a 15 percentage point difference (pp) in Sweden, 11 pp in Norway, 7 pp in Denmark and Finland, and 2 pp in Iceland), this gap has been closing in the last couple of years since the pandemic. Between 2020 and 2022, the employment rate for those born outside of the EU rose almost eight percentage points in Denmark…
2025 April
- Labour force
- Nordic Region