43 Maps
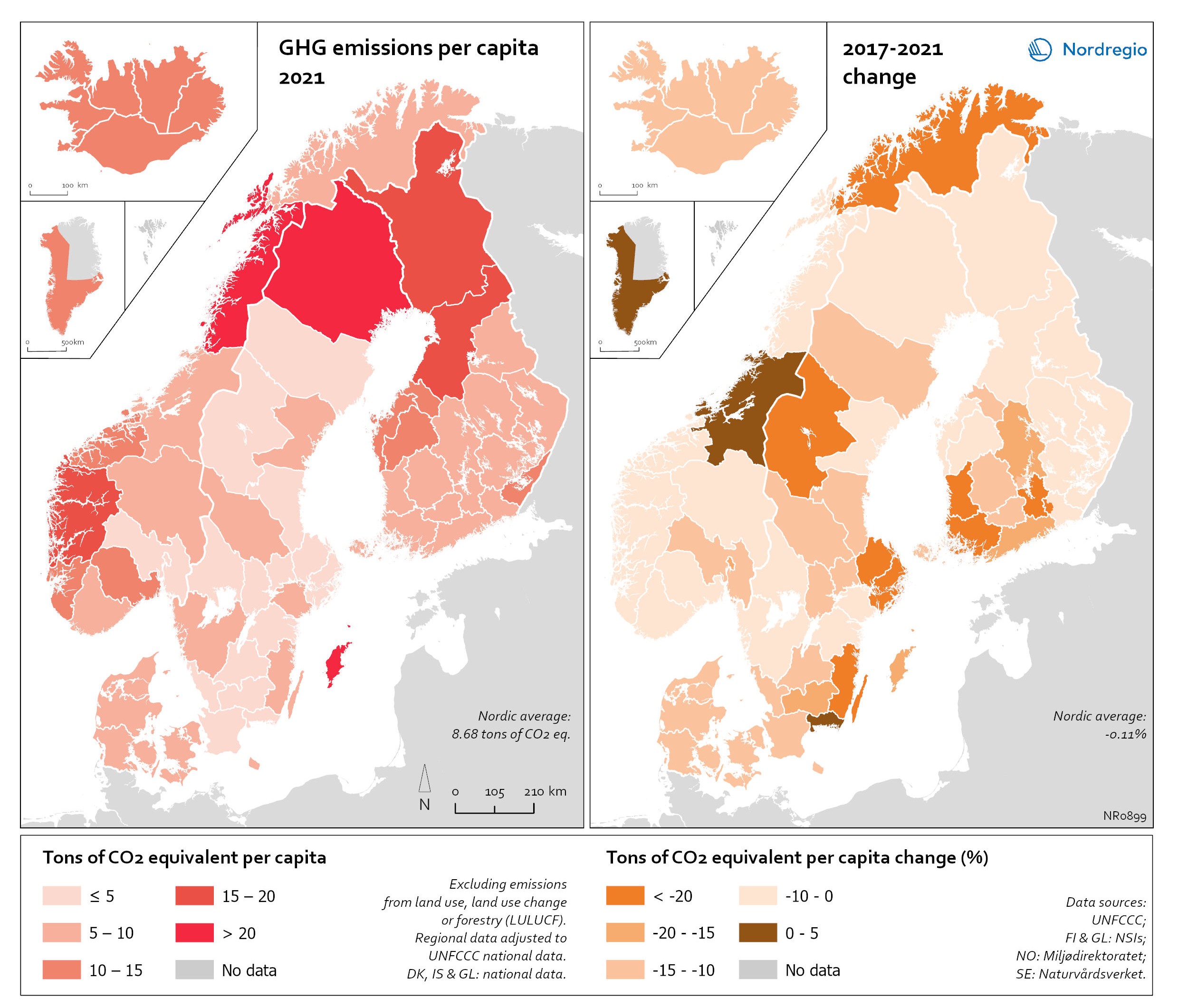
Regional GHG emissions per capita in 2021 and change 2017-2021 on a territorial basis
The data excludes emissions from land use, land use change or forestry (LULUCF). The regional data has been adjusted to UNFCCC national data. The data for Denmark, Iceland and Greenland is on national level. It should be noted that displaying emissions on a territorial basis may be skewed due to the inter-regional dynamics of energy processes, natural resource distributions and concentrations of industrial activities. From 2017 to 2021, the Nordic regions cut their per-capita GHG emissions by on average 11.3%, with an overall Nordic average fall of 8.7% over the same period. In regions historically reliant on fossil fuels for heat and power generation, emissions have continued to decline. This trend is evident in Denmark, as well as in Southern Sweden and Southern Finland – densely populated areas that have taken steps toward expanding district heating coverage and reducing carbon intensity. The largest decrease in GHG emissions per capita was found in Troms and Finnmark, with a 42.3% decrease, Satakunta with a 30.2% decrease and Päijät-Häme – Päijänne-Tavastland with a 29.2% decrease. Only three regions (Greenland, Trøndelag and Blekinge) saw an increase in GHG emissions per capita. At an aggregated level, industrial-related emissions decreased throughout the Nordic Region, but this trend does not hold true for regions in Norway with intensive offshore oil and gas operations. For instance, Nordland, Vestland, Møre og Romsdal, Vestfold and Telemark exhibited the highest per capita emissions in 2021. Between 2017 and 2021, emissions were increasing in many Norwegian regions with intensive offshore oil and gas activity, but also in Norrbotten in Sweden (21.2 tonnes of CO2 equivalent per capita) and Gotland (33.6 tonnes of CO2 equivalent per capita) due to intensive activity in the metal and cement industries, respectively, as well as in several Finnish regions. At the other end of the scale, the…
2025 April
- Environment
- Nordic Region
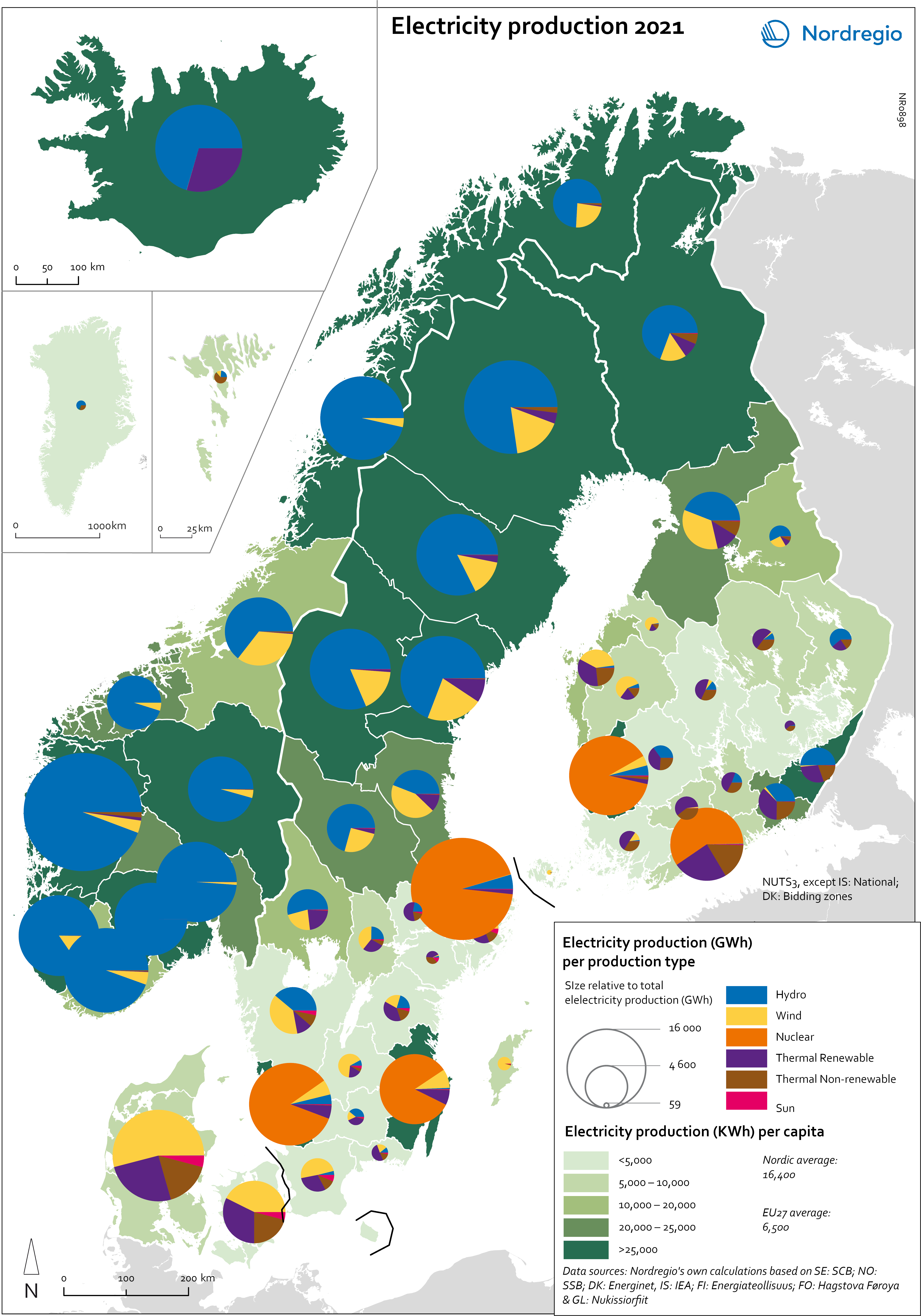
Electricity production 2021
This map shows the spatial distribution of Nordic electricity production per capita, by volume and source type in the Nordic Region in 2021. The data is presented at a regional level, except for Iceland (national level) and Denmark (bidding zones). The circles represent electricity production in GWh, while the green shades indicate electricity production per capita (kWh). Finally, the colour of the circles denotes the source of electricity. The Nordic Region overall has a high electricity production per capita; in fact, Iceland and Norway have the world’s highest electricity production per capita. The electricity mix in 2021 was 96% fossil-free – 73% from renewables (mainly hydropower) and 17% from nuclear power. In 2000 85% of the electricity production was fossile-free. Still there are clear spatial differences in the electricity production. Firstly, we see the high amount of electricity being produced for the five nuclear facilities in Sweden and Finland. Secondly, a substantial volume of hydro-electricity is produced in southern Norway, throughout Iceland, Northern Sweden and Northern Finland. As a result, over half of Nordic electricity is produced from hydropower. Wind power is the source of electricity that has been growing the most during the last two decades, from 1.2% in 2000 to 14% in 2021. The regions with the highest electricity production per capita are in Iceland, Northern Sweden, and Northern and Western Norway. Both Finland and Denmark are net importers of electricity, but both countries have rapidly transitioned away from fossil fuels. Cheap and fossil-free electricity is a prerequisite for the green transition and with growing industries within e.g. battery production, green steel and mining, the need for fossil-free electricity is expected to increase in the coming decades.
2025 April
- Environment
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
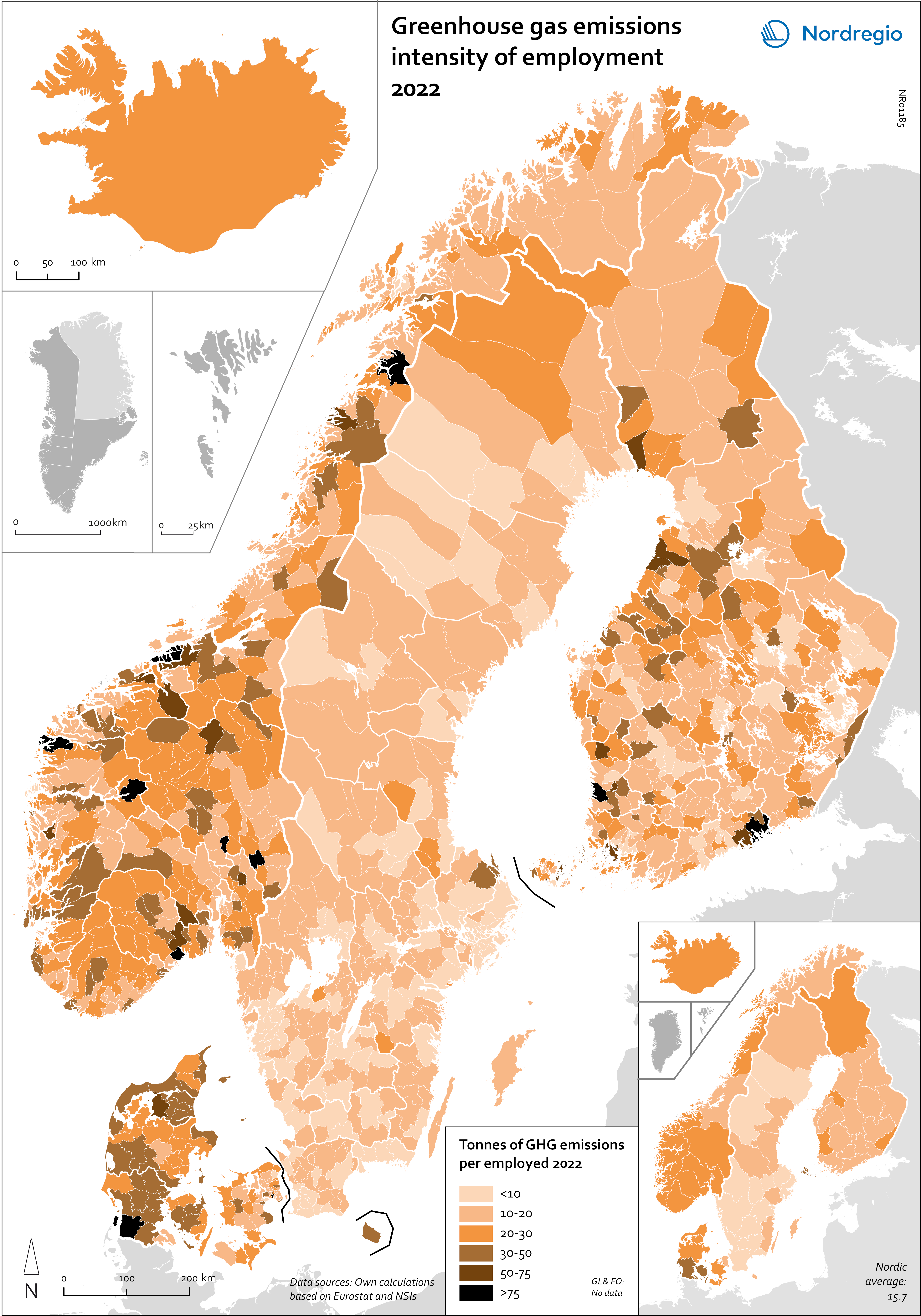
Greenhouse gas emissions intensity of employment in 2022
This map shows the tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions per person employed in Nordic municipalities (big map) and regions (small map) in 2022. The data for Iceland is presented at the national level, while no data was available for the Faroe Islands and Greenland. The map is based on data on emissions per sector and country from Eurostat and detailed employment by sector data from the Nordic statistical offices. By calculating the average emissions per person employed and per sector we could use municipal employment by sector data to assess the average emissions per person employed in each municipality. The results are an estimation based on the assumption that all jobs in the same sector have the same GHG emissions. In 2022, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions per person employed in the Nordic Region were 15.7 tonnes. This is higher than the EU average of 13.5 tonnes. There are also fairly big differences between the Nordic countries, with higher emissions per person employed in Iceland (28.6), Denmark (23.1) and Norway (20.5) and lower emissions in Finland (15.7) and Sweden (8). On the other hand, the emissions per person employed have decreased faster in the Nordic Region than for the EU as a whole. In the last decade, emissions per person employed fell by 24% in the Nordic Region compared to the EU average of 22%. The biggest decrease (32%) was in Finland. The sectors with the highest emissions per worker vary slightly between the countries. In Sweden and Norway, the sector with by far the highest emissions per worker was the manufacture of petroleum coke and refined petroleum products. However, it should be noted that the number of workers in this sector is small. In Denmark, the highest emissions by person employed could be found in water transport; in Finland, in…
2025 April
- Environment
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
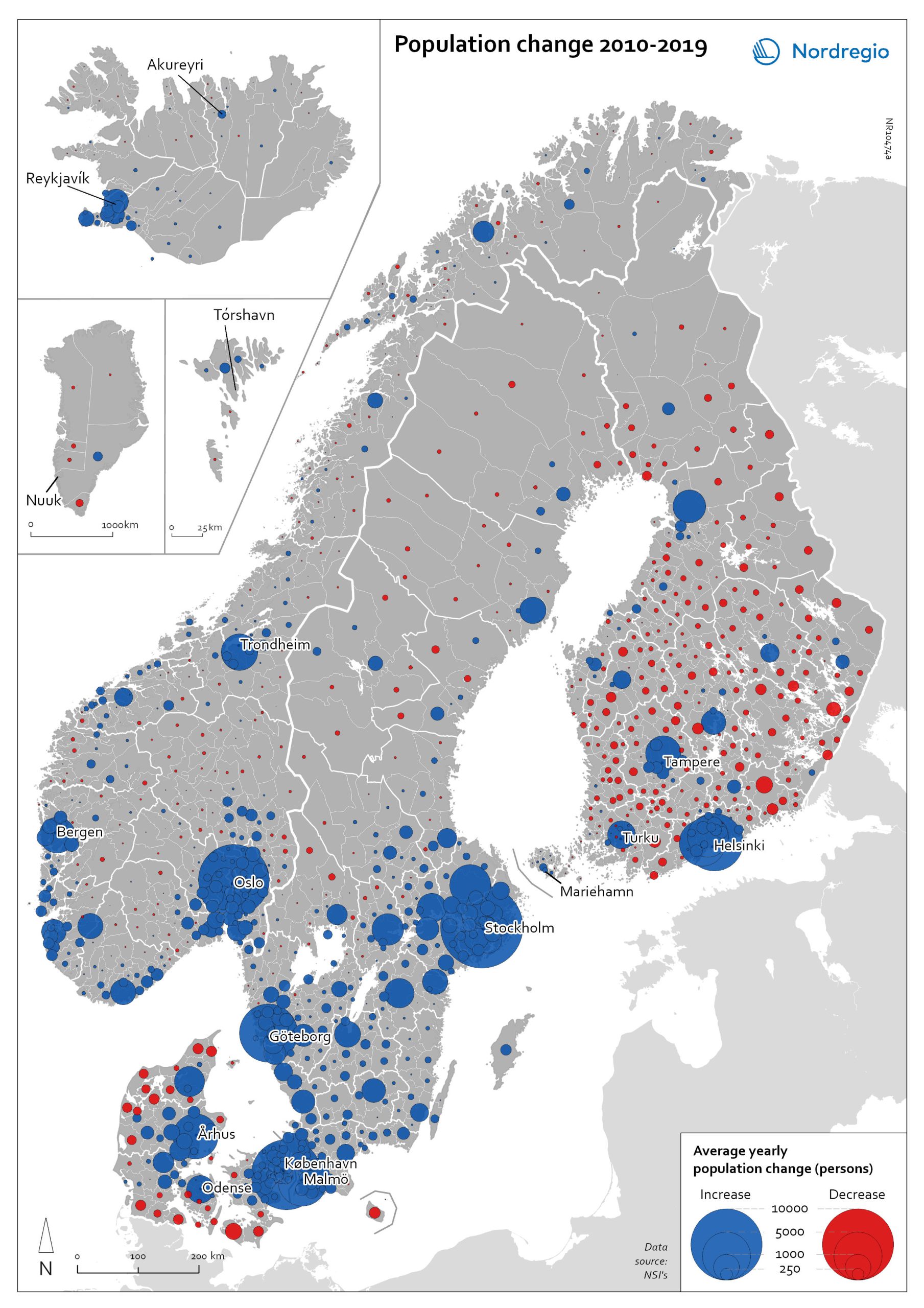
Population change 2010-2019
The map shows the type (positive or negative) and size of population change from 2010 to 2019 in all nordic municipalities. In Finland, Denmark, and Greenland there is a clear pattern of population growth in and around the larger cities and population decline in rural areas. Geographical and administrative differences mean that a much larger number of rural municipalities in Finland are dealing with population decline. Sweden experienced substantial population growth between 2010 and 2019, primarily due to high levels of international immigration. As a result, many rural areas also experienced population growth, particularly in the south of Sweden. However, in the more sparsely populated municipalities in the north of Sweden, the pattern is somewhat similar to that observed in Denmark and Finland, albeit with population decline in lower absolute numbers. Both Iceland and the Faroe Islands experienced substantial growth of their tourism industries within the period. This enabled some rural areas to maintain or even grow their populations. Norway exhibits more balanced population development in general, with a mix of population growth and decline in rural areas throughout the country.
2022 May
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
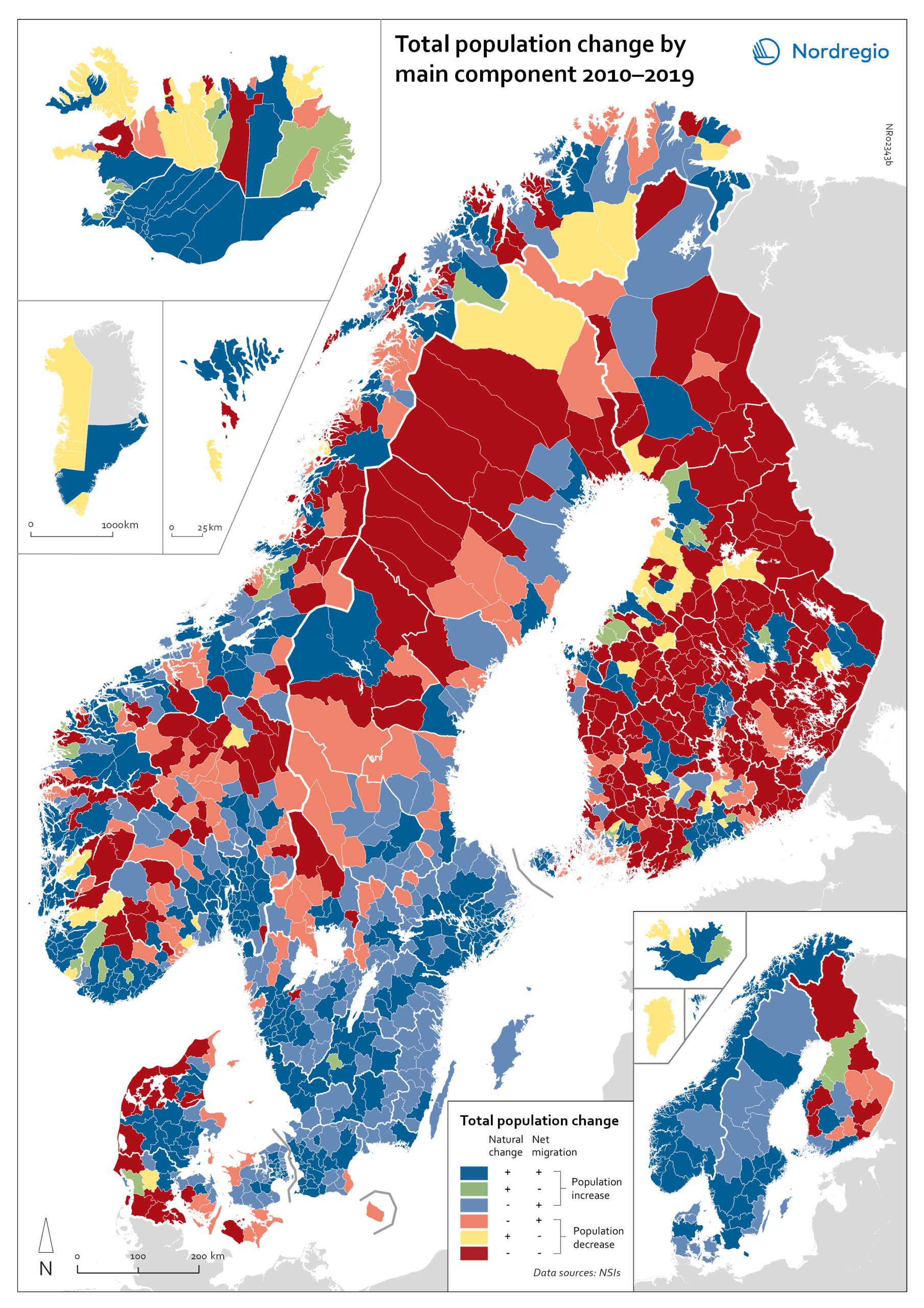
Population change by component 2010-2019
The map shows the population change by component 2010-2019. The map is related to the same map showing regional and municipal patterns in population change by component in 2020. Regions are divided into six classes of population change. Those in shades of blue or green are where the population has increased, and those in shades of red or yellow are where the population has declined. At the regional level (see small inset map), all in Denmark, all in the Faroes, most in southern Norway, southern Sweden, all but one in Iceland, all of Greenland, and a few around the capital in Helsinki had population increases in 2010-2019. Most regions in the north of Norway, Sweden, and Finland had population declines in 2010-2019. Many other regions in southern and eastern Finland also had population declines in 2010-2019, mainly because the country had more deaths than births, a trend that pre-dated the pandemic. In 2020, there were many more regions in red where populations were declining due to both natural decrease and net out-migration. At the municipal level, a more varied pattern emerges, with municipalities having quite different trends than the regions of which they form part. Many regions in western Denmark are declining because of negative natural change and outmigration. Many smaller municipalities in Norway and Sweden saw population decline from both negative natural increase and out-migration despite their regions increasing their populations. Many smaller municipalities in Finland outside the three big cities of Helsinki, Turku, and Tampere also saw population decline from both components. A similar pattern took place at the municipal level in 2020 of there being many more regions in red than in the previous decade.
2022 March
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
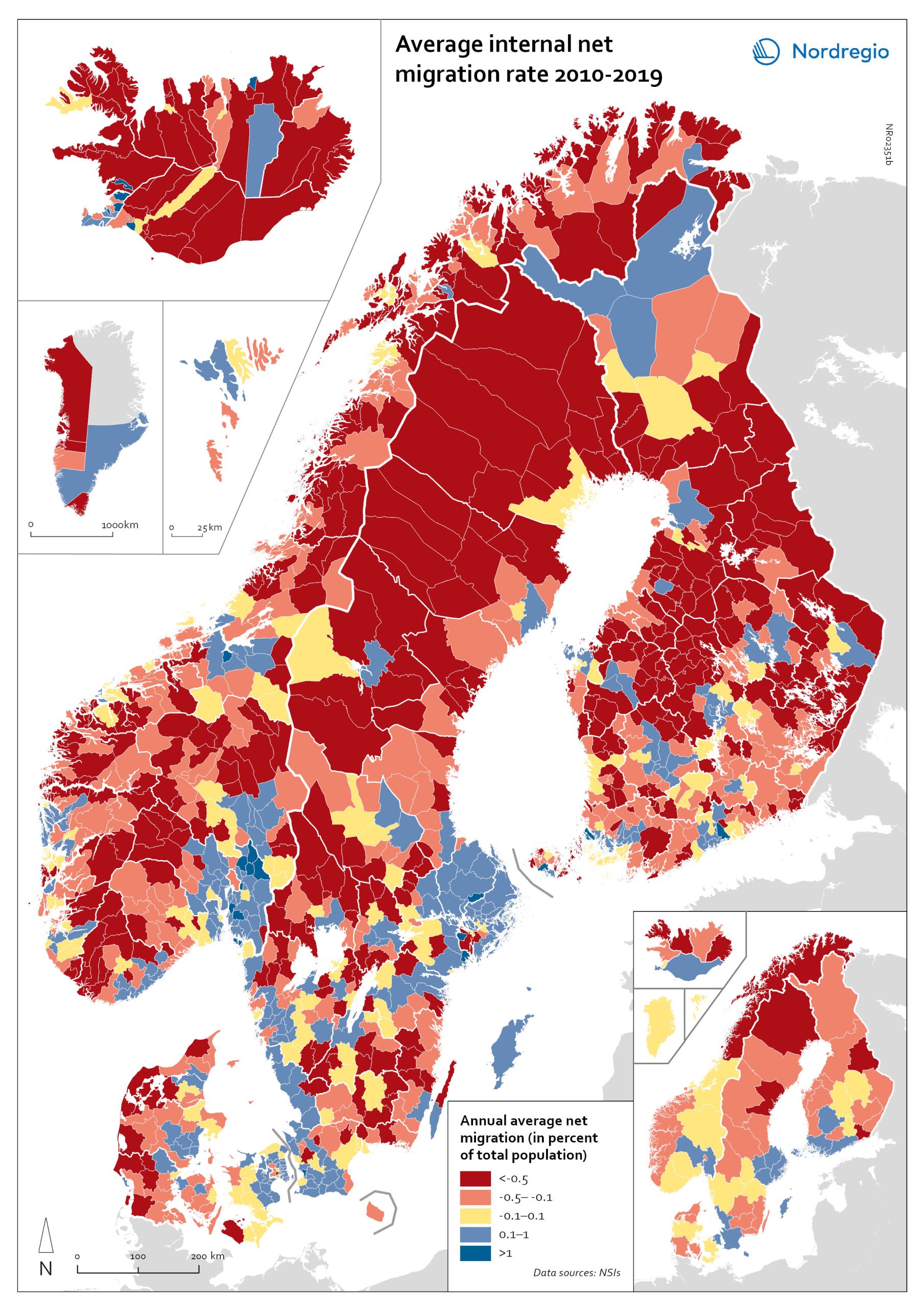
Net internal migration rate, 2010-2019
The map shows the annual average internal net migration in 2010-2019. The map is related to the same map showing net internal migration in 2020. The maps show several interesting patterns, suggesting that there may be an increasing trend towards urban-to-rural countermigration in all the five Nordic countries because of the pandemic. In other words, there are several rural municipalities – both in sparsely populated areas and areas close to major cities – that have experienced considerable increases in internal net migration. In Finland, for instance, there are several municipalities in Lapland that attracted return migrants to a considerable degree in 2020 (e.g., Kolari, Salla, and Savukoski). Swedish municipalities with increasing internal net migration include municipalities in both remote rural regions (e.g., Åre) and municipalities in the vicinity of major cities (e.g., Trosa, Upplands-Bro, Lekeberg, and Österåker). In Iceland, there are several remote municipalities that have experienced a rapid transformation from a strong outflow to an inflow of internal migration (e.g., Ásahreppur, Tálknafjarðarhreppurand, and Fljótsdalshreppur). In Denmark and Norway, there are also several rural municipalities with increasing internal net migration (e.g., Christiansø in Denmark), even if the patterns are somewhat more restrained compared to the other Nordic countries. Interestingly, several municipalities in capital regions are experiencing a steep decrease in internal migration (e.g., Helsinki, Espoo, Copenhagen and Stockholm). At regional level, such decreases are noted in the capital regions of Copenhagen, Reykjavík and Stockholm. At the same time, the rural regions of Jämtland, Kalmar, Sjælland, Nordjylland, Norðurland vestra, Norðurland eystra and Kainuu recorded increases in internal net migration. While some of the evolving patterns of counterurbanisation were noted before 2020 for the 30–40 age group, these trends seem to have been strengthened by the pandemic. In addition to return migration, there may be a larger share of young adults who…
2022 March
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
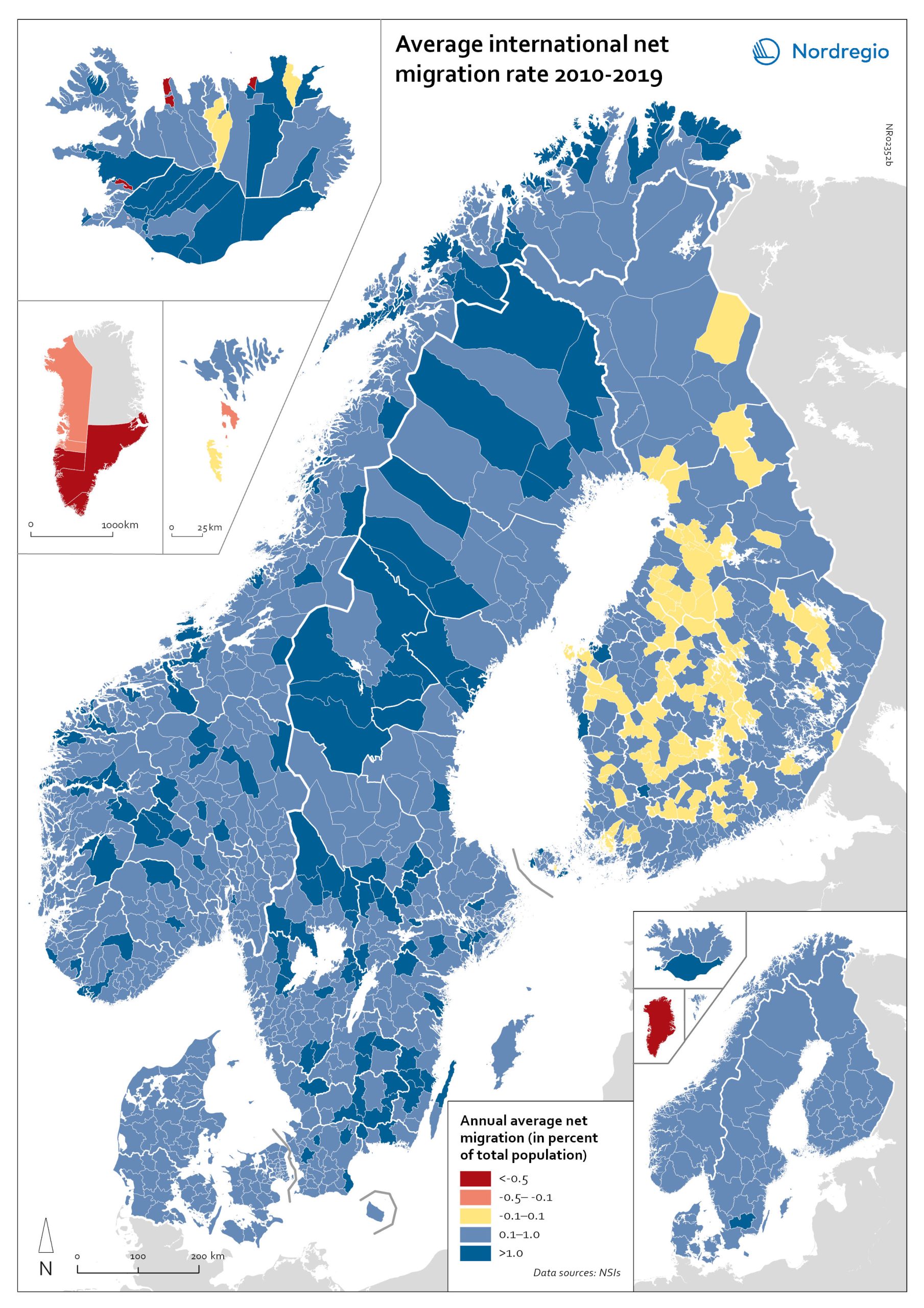
Net international migration rate, 2010–2019
The map shows the annual average international net migration from 2010 to 2019. The map is related to the same map showing net migration in 2020. At regional level, there are only minor changes between the net migration in 2010-2019 and 2020. All regions of Norway, all regions of Sweden except Gotland and Uppsala, and the regions of Österbotten in Finland, Midtjylland in Denmark and Norðurland eystra in Iceland experienced a slight decrease in international net migration I 2020 compared to 2010-2019. There is a more marked increase in net migration in the Faroe Islands, Greenland and the region of Norðurland vestra in Iceland, and a slight increase in the region of Austurland in Iceland. At municipal level, the maps show more changing patterns. In Denmark, Norway and Sweden, several municipalities – both in the capital, intermediate, and rural regions – had lower levels of international net migration in 2020 compared to 2010-2019. In Iceland and Finland, the picture is more balanced, with some municipalities showing a decrease, others an increase. In the Faroe Islands and Greenland, several municipalities/regions had an increase in international net migration.
2022 March
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
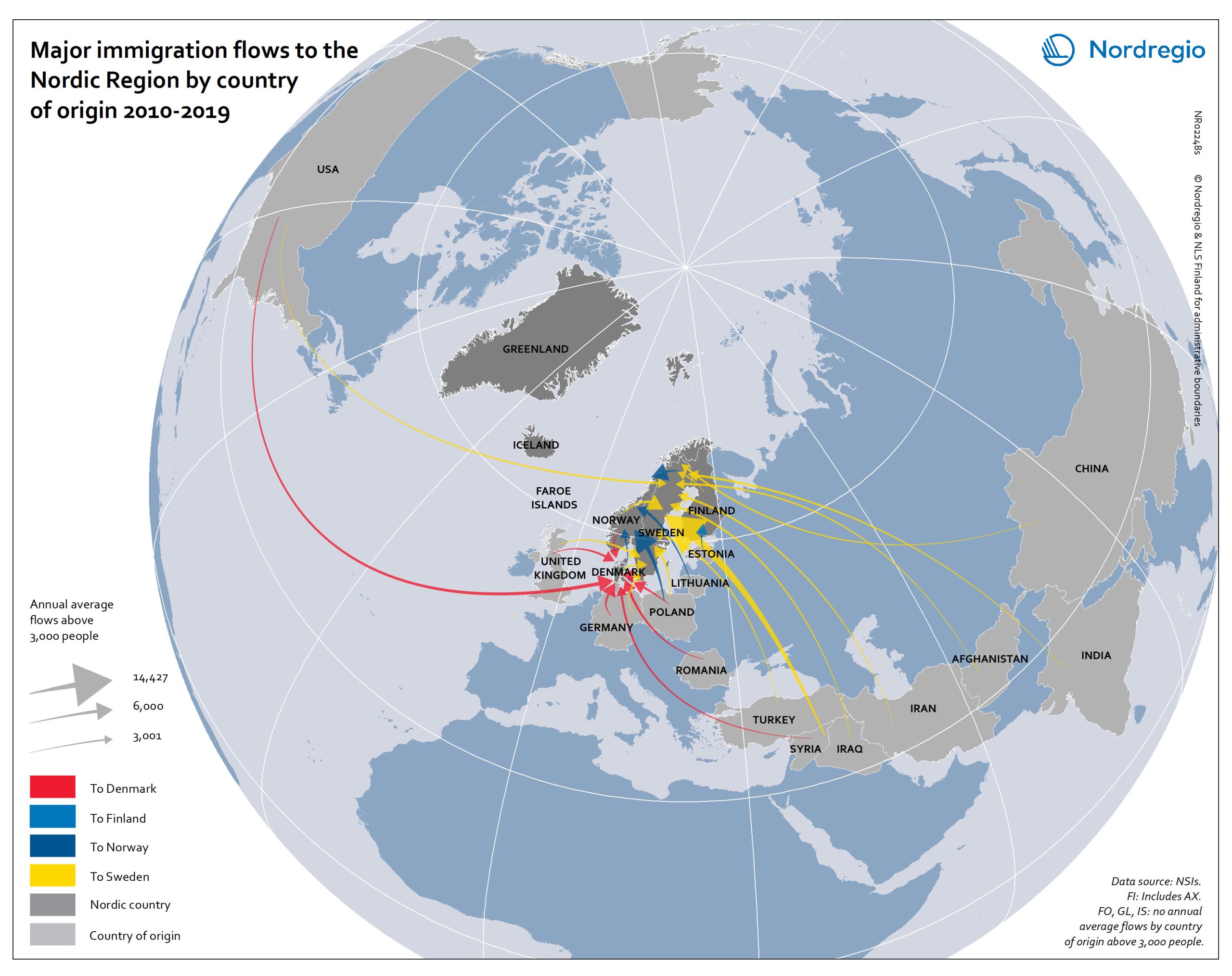
Major immigration flows to the Nordic Region from 2010 to 2019
The map shows annual average immigration flows above 3,000 people, and the growing diversity in their countries of origin Sweden and Denmark, in particular, experienced large inflows from non-Nordic countries during the period 2010-2019, with Sweden standing out as the Nordic country with by far the largest immigrant in-flows. A large portion of these arrivals were from war-torn Syria (an annual average of almost 15,000), followed by Poland (approximately 4,500), United Kingdom, Iraq, India and Iran (around 4,000 each). Denmark experienced a smaller number of inflows above 3,000 people, compared to Sweden. The largest non-Nordic inflows to Denmark were around 5,000 people (per sending country) and included migrants from the U.S., Germany, Romania and Poland. For Norway, large non-Nordic in-flows were limited to Lithuania and Poland. Similarly, Finland had only one major inflow, from Estonia.
2021 December
- Migration
- Nordic Region
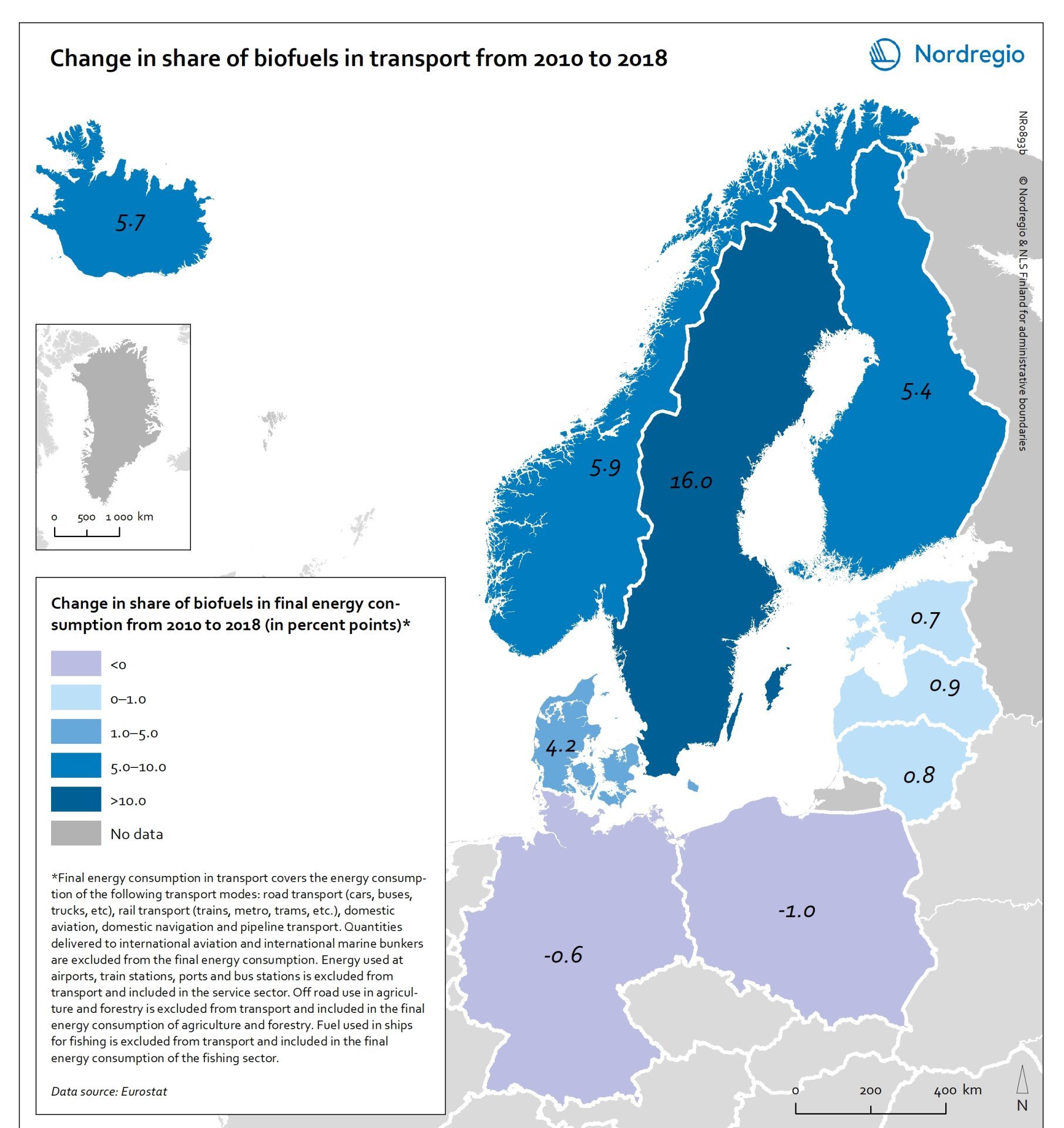
Change in share of biofuels in transport from 2010 to 2018
This map shows change in share of biofuels in final energy consumption in transport in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea Region from 2010 to 2018. Even though a target for greater use of biofuels has been EU policy since the Renewable Energy and Fuel Quality Directives of 2009, development has been slow. The darker shades of blue on the map represent higher increase, and the lighter shades of blue reflect lower increase. The lilac color represent decrease. The Baltic Sea represents a divide in the region, with countries to the north and west experiencing growth in the use of biofuels for transport in recent years. Sweden stands out (16 per cent growth), while the other Nordic countries has experienced more modest increase. In the southern and eastern parts of the region, the use of biofuels for transport has largely stagnated. Total biofuel consumption for transport has risen more than the figure indicates due to an increase in transport use over the period.
2021 December
- Arctic
- Baltic Sea Region
- Nordic Region
- Transport
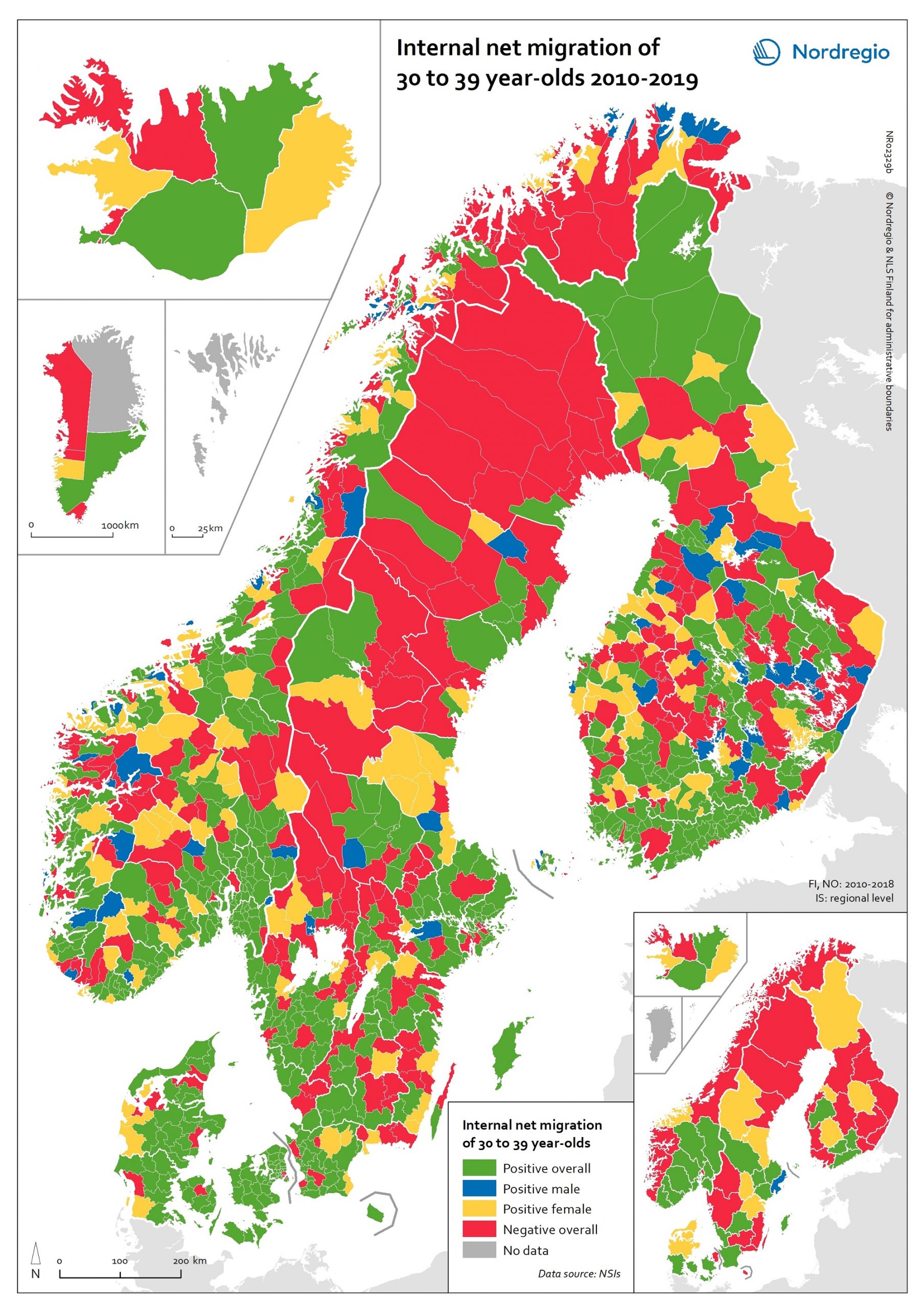
Internal net migration of 30 to 39 years-of-age, by gender, in 2010-2019
This map shows a typology that divides the Nordic municipalities and regions into four migration categories: positive net migration for both males and females (green on the map), positive male net migration (blue on the map), positive female net migration (yellow on the map), and negative net migration for both males and females (red on the map). These migration flows on 30 to 39-year-olds are of particular interest since it is often assumed that the future of rural regions is dependent upon their capability both to retain their populations and to attract newcomers, returning residents and second home owners. In this context, the map provides a rather positive picture, because a considerable proportion of rural municipalities have experienced positive net migration among females, males, or both sexes across all the Nordic countries. Even so, there is negative net migration among both females and males in many municipalities in northern Sweden, north-eastern Norway and eastern Finland, in addition to several inland municipalities within these countries. Interestingly, there is negative net migration among both sexes across all the capital city municipalities of the Nordic Region. According to the regional map, the capital city regions of Denmark, Iceland and Norway all experienced negative net migration of young people aged 30-39 years between 2010 and 2019. The capital city region of Sweden experienced positive net migration of males and negative net migration of females while the capital city region of Finland experienced positive net migration overall. Despite the majority of peripheral regions experiencing negative net migration of 30 to 39-year-olds during the time period studied, there are also several interesting examples of rural regions which experienced positive female net migration, for example Nordjylland (Denmark), Pohjois-Savo (Finland), Austurland (Iceland), Møre og Romsdal (Norway), and Jämtland (Sweden).
2020 October
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
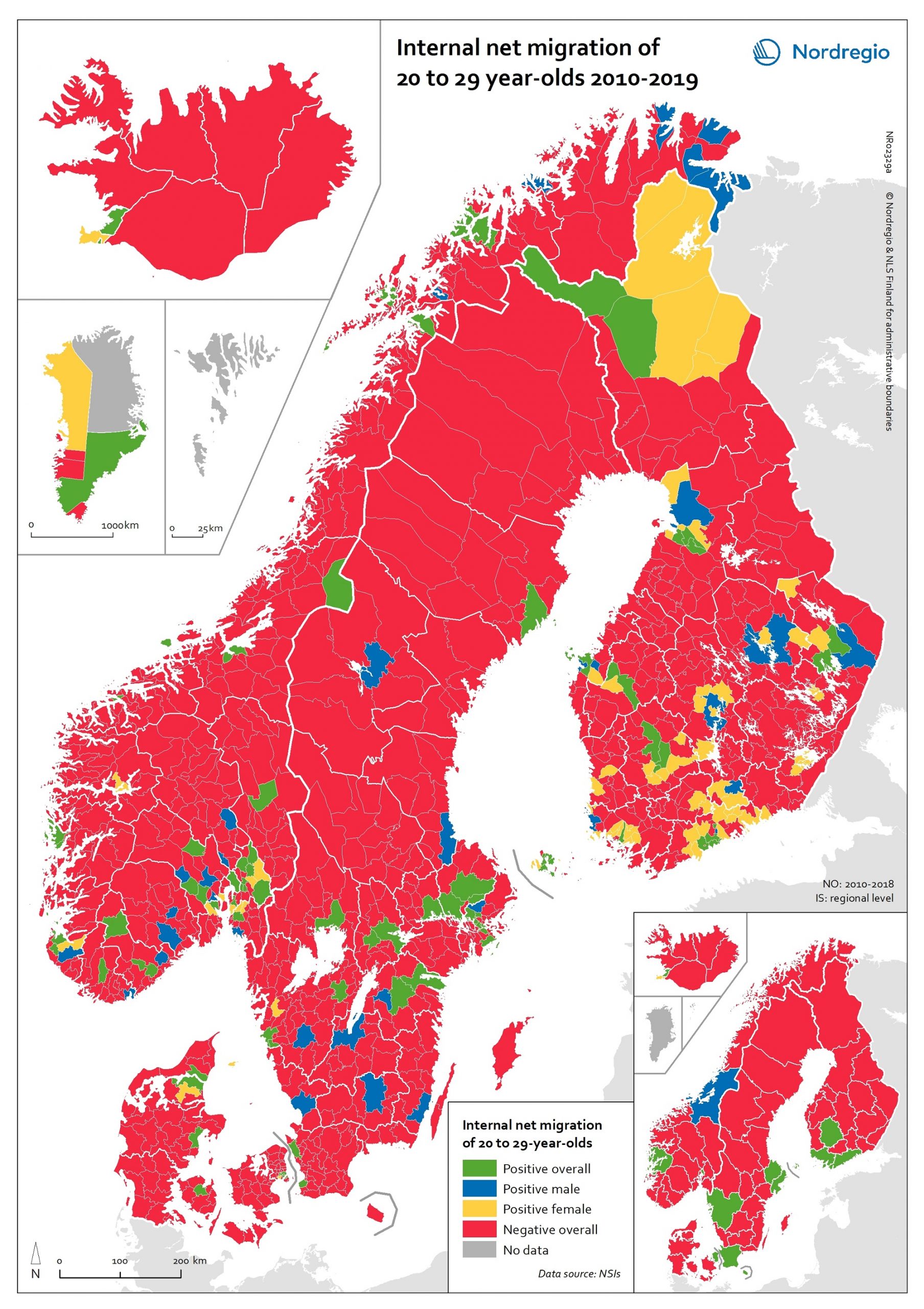
Internal net migration of 20 to 29 years-of-age, by gender, in 2010-2019
This map shows a typology that divides the Nordic municipalities and regions into four migration categories: positive net migration for both males and females (green on the map), positive male net migration (blue on the map), positive female net migration (yellow on the map), and negative net migration for both males and females (red on the map). These migration flows of 20 to 29-year-olds are of interest since there is a particularly high level of internal migration among young adults across the Nordic countries compared to other EU countries. While the map shows that the great majority of municipalities experience negative net migration of young adults in favour of a few functional urban areas and some larger towns, it is possible to observe a number of exceptions to this general rule. The rural municipalities of Utsira, Moskenes, Valle, Smøla, Ballangen and Lierne in Norway have the highest positive net migration rates both for men and women. There are also positive net migration rates for males and females in the peripheral municipalities of Jomala, Kittilä, Lemland and Finström in Finland and Åland. There is positive male net migration but negative female net migration in Gratangen, Loppa, Gamvik, Drangedal and a few other Norwegian rural municipalities, plus Mariehamn in Åland, while several municipalities in remote areas of Finland have positive female net migration but negative male net migration. Some of these patterns may be related to specialised local labour markets, such as fisheries in Loppa, or recreational tourism in Kittilä. In general, the pattern of net migration among young adults is more diverse in Finland (where 72.0% of all municipalities have negative net migration), compared with 84.6% in Norway, 88.9% in Denmark and 89.0% in Sweden. However, it is important to remember that Danish, Finnish and Norwegian municipalities are smaller in size…
2020 October
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
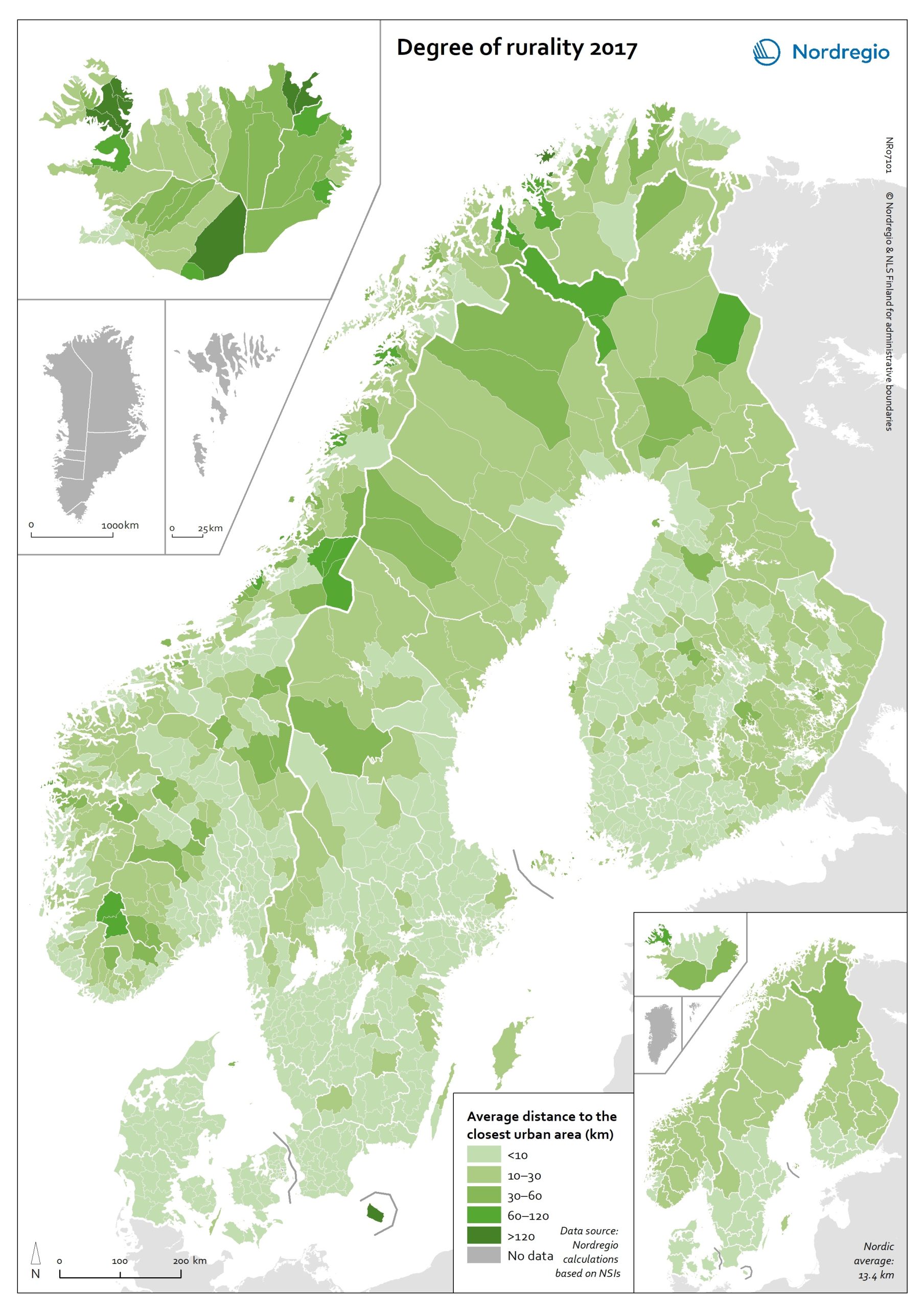
Degree of rurality at the municipal and regional level in 2017
This map shows the average distance to the edge of the closest urban area for the population living outside urban areas in the Nordic municipalities and regions. These figures are of particular interest in the analysis of urban-rural patterns and the Nordic populations’ access to local services in sparsely population areas. The darker shades on the map indicate longer average distances to the edge of the nearest urban area, and the lighter shades indicate shorter average distances. While almost all Danish municipalities have an average distance of below 10 km from rural grid cells to the nearest urban area, a large share of the municipal populations of the remaining Nordic countries need to contend with longer average distances to local services. The largest distances can be found in several municipalities of Iceland and Norway (Árneshreppur 230 km, Hasvik 154 km), whereas the largest average distances for Finnish and Swedish municipalities are considerably shorter (Enontekiö 103 km, Storuman 52 km). Regarding within-country variation, shorter average distances can generally be found in southwestern Finland and southern Sweden, in comparison with the more remote parts of these countries. Both Norway and Iceland provide a rather more mixed picture, since there are municipalities with shorter average distances scattered across different parts of each country. Method used to calculate the degree of rurality In order to take into account access to services such as grocery stores, pharmacies, schools, community centres and public transport, the European definition of urban grid cells was used to create this map, i.e. a population density threshold of 300 inhabitants per km2 applied to grid cells of 1 km2. The closest distance was calculated from each rural grid cell centroid to the nearest urban grid cell centroid along the existing road network traversable by car, including car ferries, based on population…
2020 October
- Environment
- Nordic Region
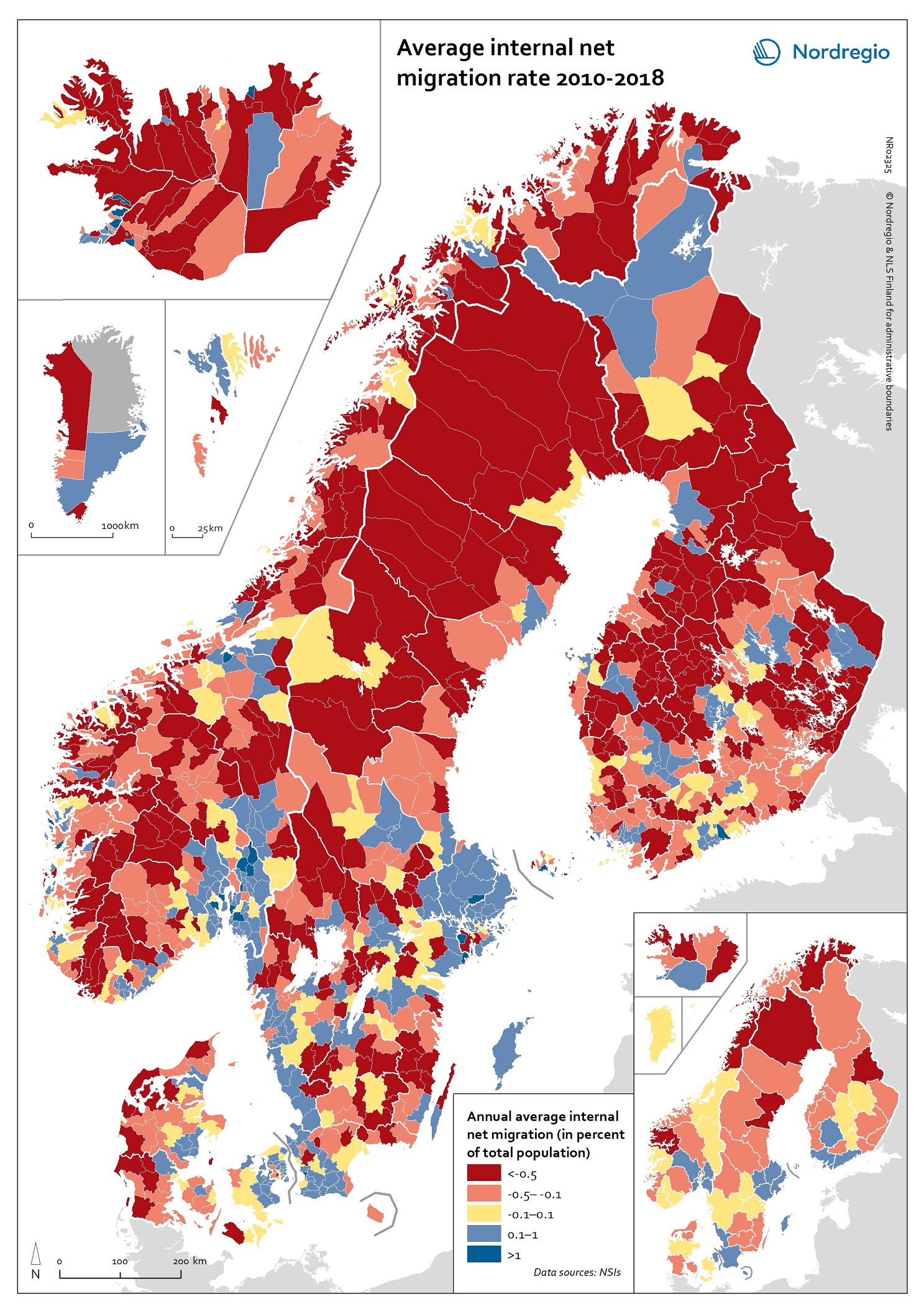
Internal net migration as percentage of population 2010–2018
This map shows annual average internal net migration rate at the municipal and regional level in 2010-2018. The map shows the percentage change from internal migration for the period 2010 to 2018. Internal or domestic migration refers to migration between municipalities and regions within the same country. The blue areas on the map show municipalities/regions with positive internal net migration (i.e. more people arriving than departing), the red areas show municipalities/regions with negative internal net migration (i.e. more people departing than arriving) and the yellow areas show municipalities/regions with balanced internal net migration rates (i.e. comparable numbers of people arriving and departing). The trend revealed is that internal migration movements are directed towards larger city regions, with many rural periphery regions losing people. The loss of people in some of these regions is felt especially acutely because of the age selectivity of migration, with young people leaving in large numbers, accelerating the ageing of the population structure in regions with high out-migration. Read the digital publication here.
2020 February
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
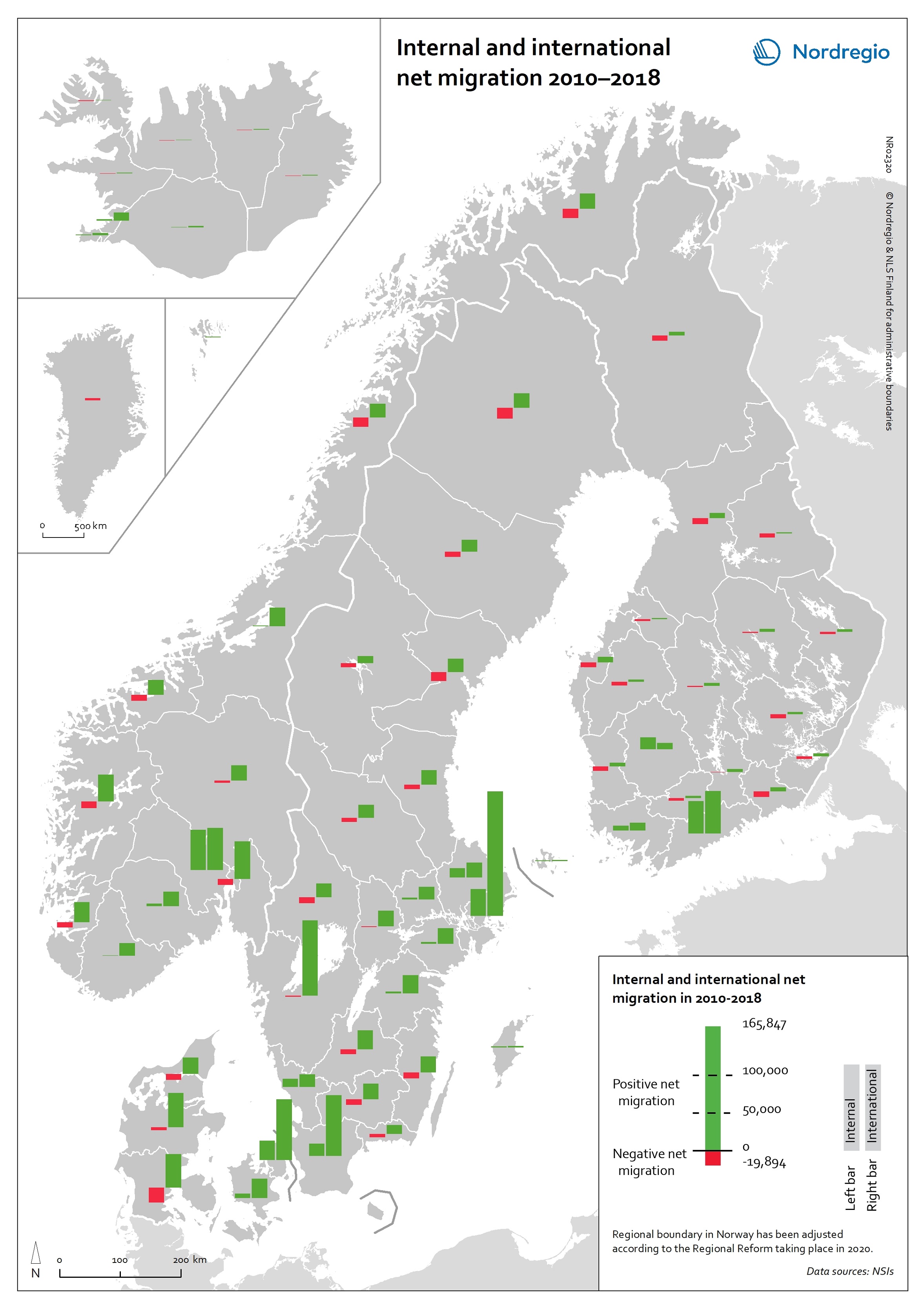
Internal and international net migration 2010-2018
This map shows internal and international net migration in 2010-2018. The map shows the combination of domestic migration (left-hand bar) and international migration (right-hand bar), with red indicating net out-migration and green indicating net in-migration, for the 66 regions within the Nordic Region in the period 2010 to 2018. The size of the bar indicates the size of the net flows. All regions have had positive international migration since 2010, which is not surprising given the size of the international migration flows into the Nordic Region in recent years. Overall in the Nordic Region, there were either domestic migration losses and international migration gains or gains from people moving both from elsewhere in the country and from abroad. The gains from international migration far exceeded those of internal migration in almost all regions that experienced net gains from both streams. Due to these different patterns of internal and international migration, nearly all regions are becoming much more diverse in terms of the size of foreign-born populations. Read the digital publication here.
2020 February
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
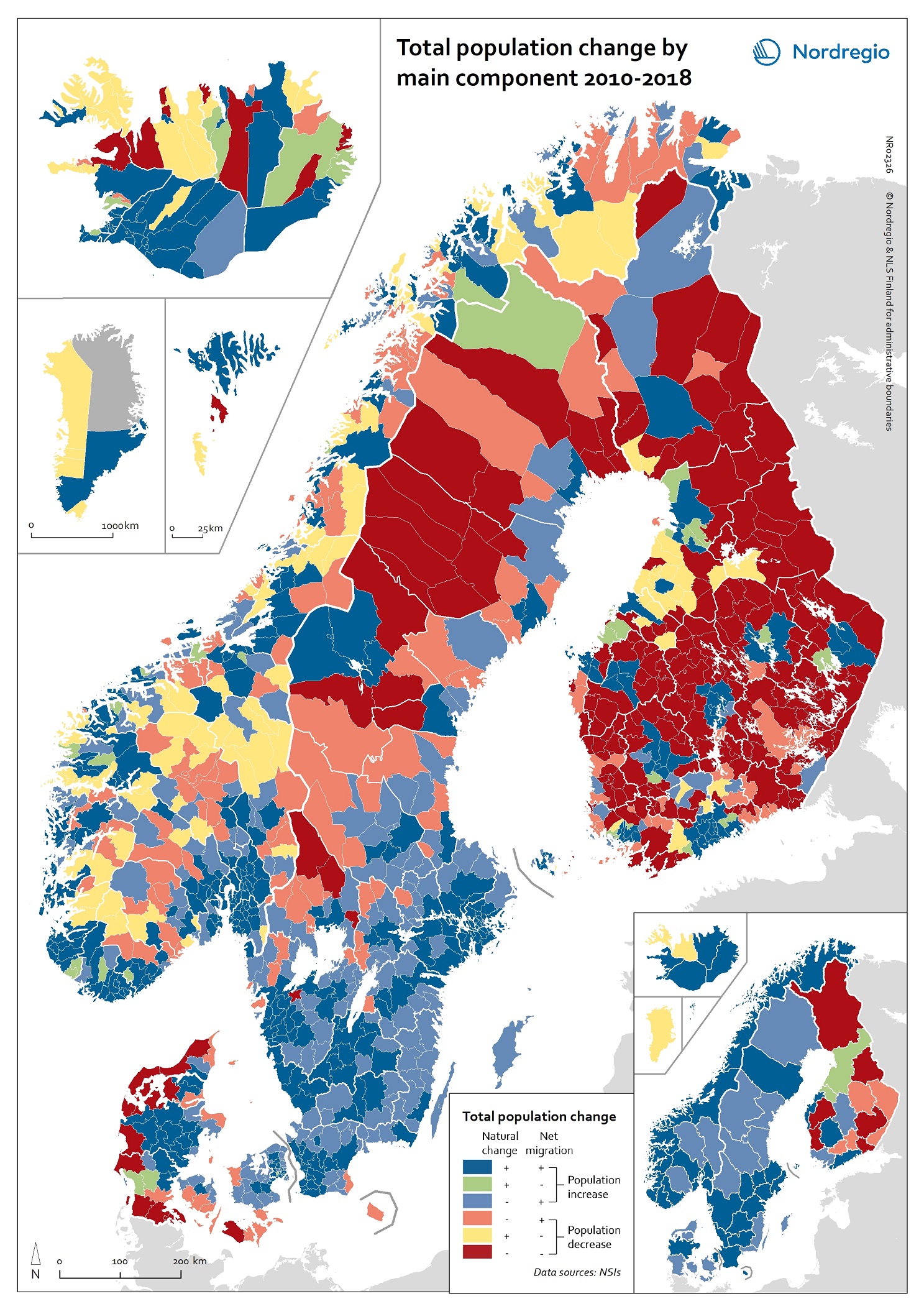
Total population change by main component 2010-2018
This map shows total population change by main component at the municipal and regional level in 2010-2018. The two components of population change are natural change and net migration. As the map shows, all regions in Denmark, Norway and Sweden experienced population increase due to either a combination of natural increase and net migration or through net migration alone between 2010-2018. In Iceland, all regions experienced both positive natural increase and positive net migration, except for Vestfirðir and Norðurland vestra, which experienced population decline despite experiencing more births than deaths over the period. The regional picture in Finland was more varied, with population decline most pronounced in the east and the north. At the municipal level, the highest overall population growth can be found mostly in the capital regions and bigger cities (e.g. Tampere and Turku in Finland), Central Jutland (Denmark), coastal areas of Norway, southern Iceland, southern Sweden, the northern municipalities of the Faroe Islands and Sermersooq Municipality (Greenland), which contains the capital of Nuuk. The highest overall population decline can be found mostly in the western and southern parts of Denmark, the majority of Finnish municipalities and most inland municipalities in northern Sweden. While the map shows a snapshot of population change for one decade, these trends of population increase in urban regions and municipalities and decline and ageing in periphery regions and municipalities have been underway for some time and are expected to continue into the foreseeable future. Read the digital publication here.
2020 February
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
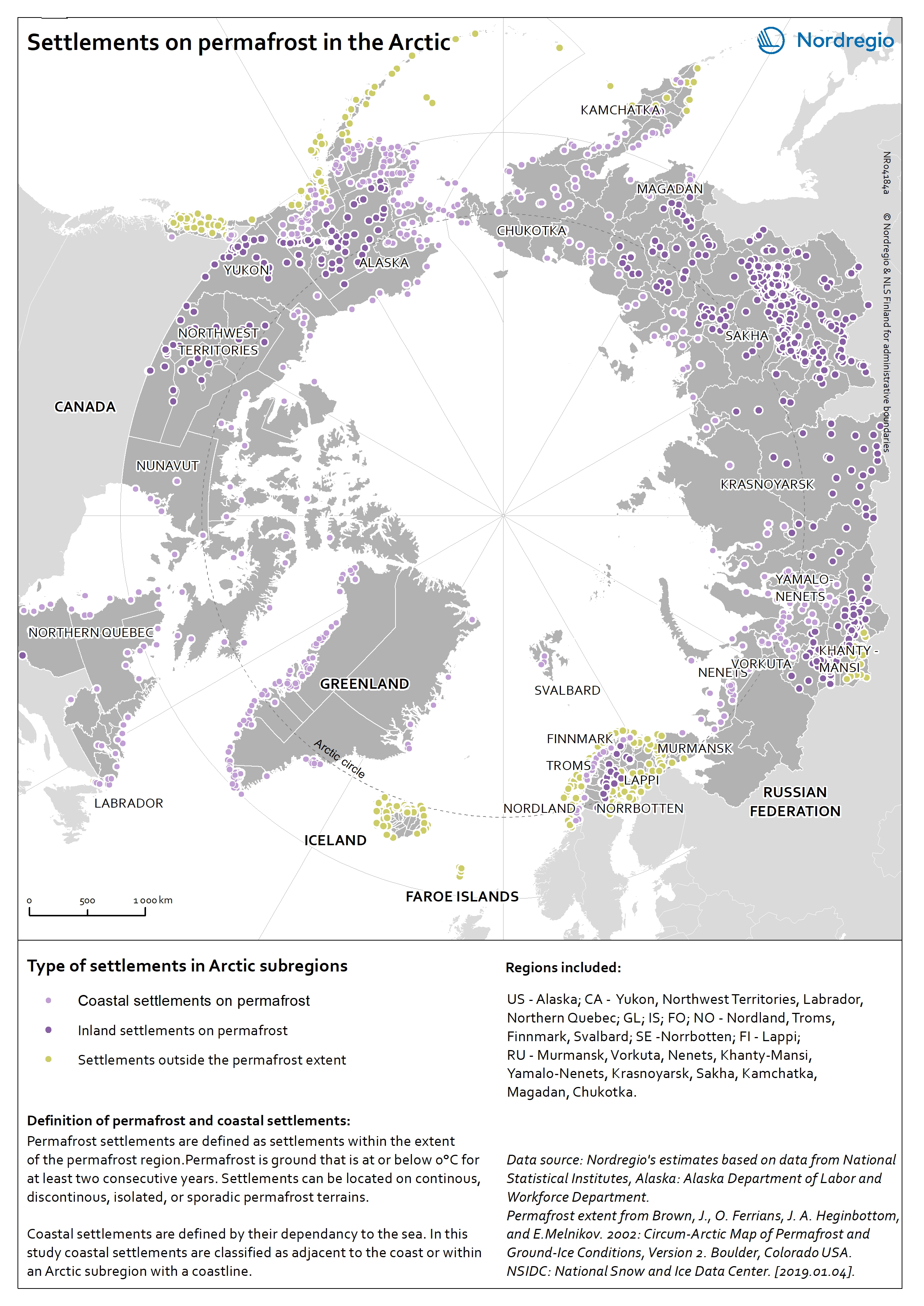
Settlements on permafrost in the Arctic
The map shows the distribution of coastal and inland settlements on permafrost in the Arctic in 2017. Permafrost is ground that is at or below 0°C for at least 2 consecutive years. The purple tones indicate settlements located on permafrost and distinguishes between coastal (light purple) and inland (dark purple) settlements. Settlements located outside the permafrost extent are in yellow. Among all Arctic settlements, 66,1% are located on permafrost. Settlements are classified as permafrost settlements if they are located within the permafrost extent, comprising zones of continuous, discontinuous, sporadic, or isolated permafrost. Among all permafrost settlements 46,0% are coastal. Coastal settlements are defined by their dependency to the sea. They are either adjacent to the coast, located inland along large rivers with a free connection to the open sea, or located within a short distance to the sea (0-200 km). In this map, coastal settlements comprise all settlements that are located within an Arctic subregion adjacent to the coast. Most of the settlements located outside the permafrost extent area are in the Nordic countries (Iceland, Norway, the Faroe Islands, Sweden, and Finland) as well as in the southern part of Alaska (USA) and the western part of the Russian Arctic. Almost all Arctic settlements in the Russian Federation and in Canada are located on permafrost. The increase in air surface temperature observed in the Arctic causes dramatic changes in the permafrost thermal regime leading to the destabilisation of infrastructure built on permafrost.
2019 March
- Arctic
- Demography
- Environment
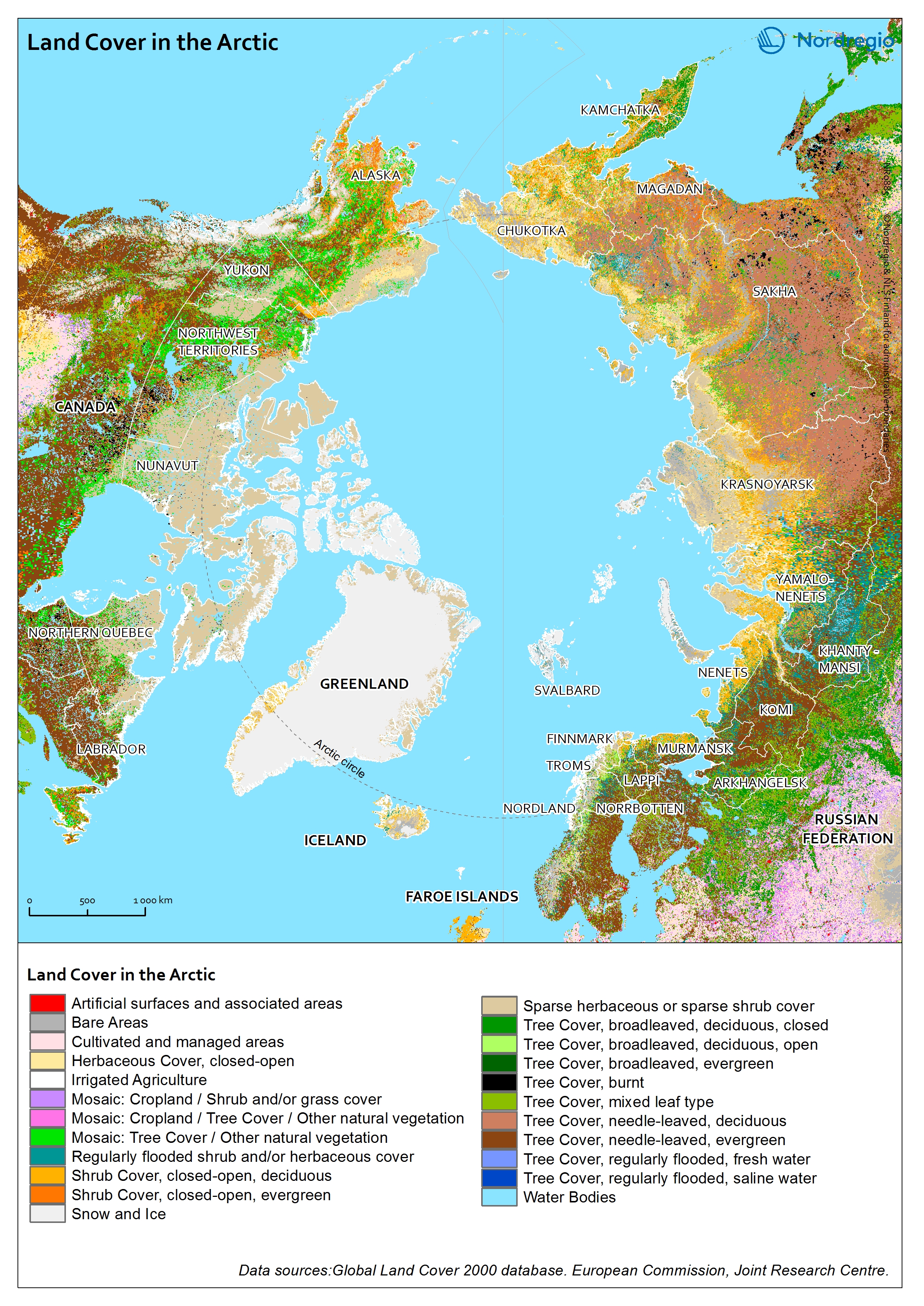
Land Cover in the Arctic
The terrestrial ecosystem of the Arctic is characterized by low tundra vegetation, composed of shrubs, herbaceous plants, mosses, and lichens. Arctic vegetation is becoming more productive due to increasing air temperature. One of the main trends shows an increase in tall shrub cover. On the contrary, the cover of lichen and moss has declined in response to regional warming.
2019 January
- Arctic
- Environment
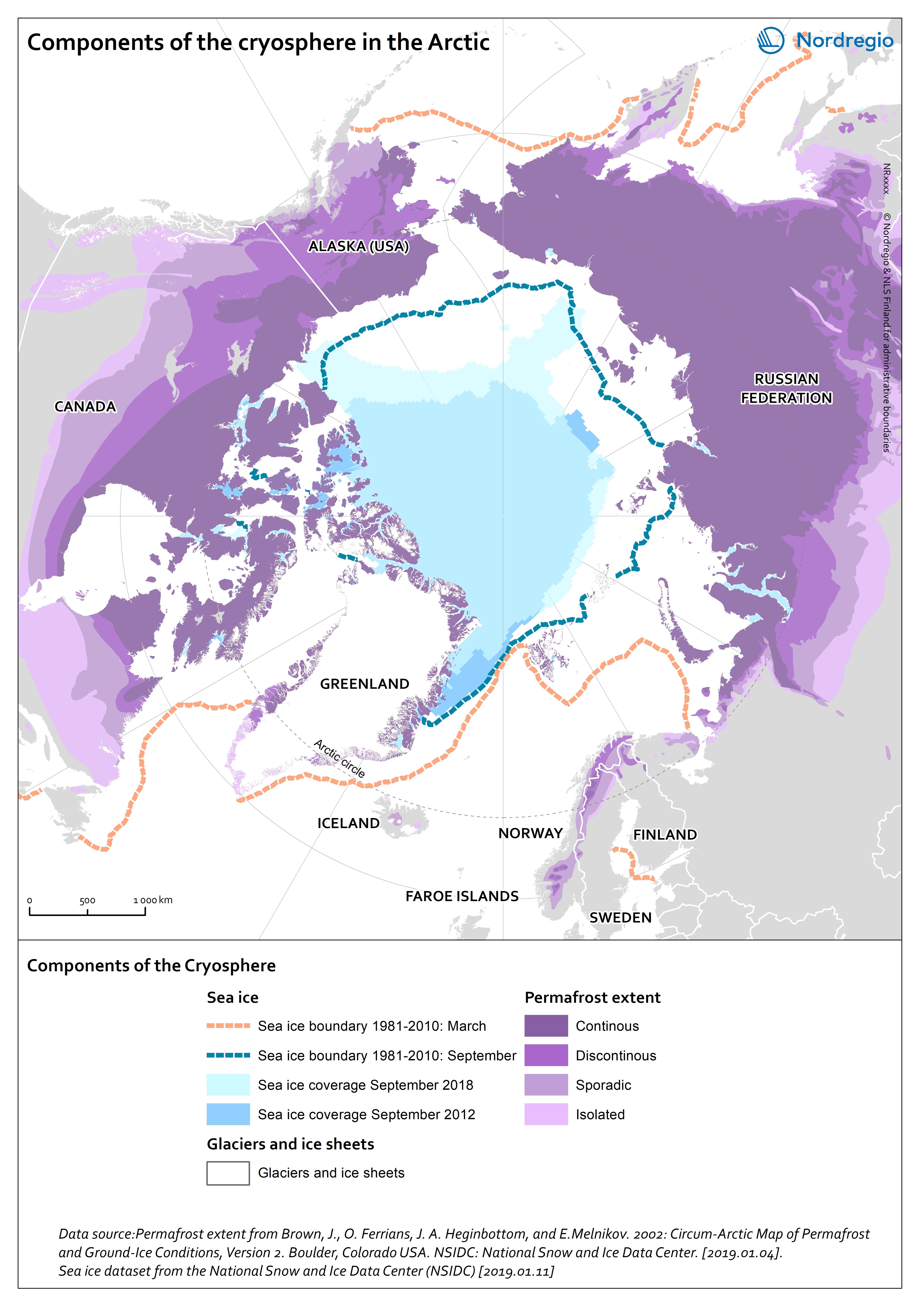
Components of the cryosphere in the Arctic
This map shows the main components of the cryosphere in the Arctic: sea-ice, permafrost, ice-sheets, and glaciers. Sea-ice covers most of the Arctic Ocean during winter. The sea-ice extent reaches its maximum in March, when it covers approximately 14-16 million km2. Since 1979, the Arctic ice extent in winter has decreased by 3% per decade relative to the 1981-2010 average, and this trend accelerates. Similarly, ice-sheets and glaciers, which cover globally over 15 million km2 are melting. In the Arctic, the main ice-sheet is the Greenlandic ice sheet. Most of the land surface in the Arctic is underlay by permafrost, ground that is at or below 0°C for at least 2 consecutive years. The purple tones on the map indicates the extent of the northern circumpolar permafrost. Permafrost can occur as continuous (dark purple, 90-100% coverage), discontinuous (purple, 50-90% coverage), sporadic (light purple, 10-50%), or isolated patches (magenta, 0-10% coverage). Permafrost is thawing due to increased air temperatures and precipitations in the Arctic. Permafrost temperature increased by 0.29 ± 0.12°C between 2007 and 2016.
2019 January
- Arctic
- Environment
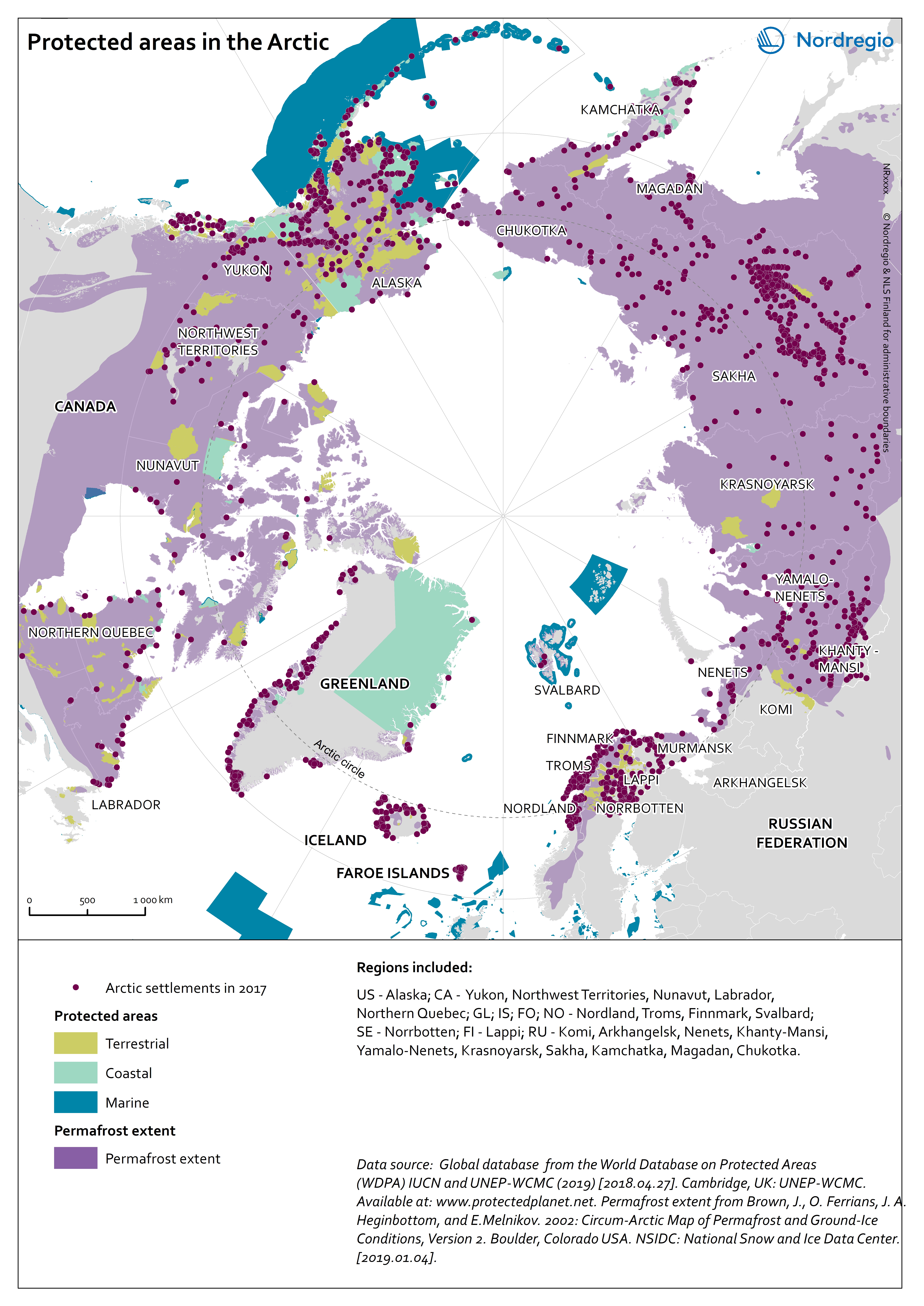
Protected areas in the Arctic
Within the northern circumpolar permafrost region, there are ca. 1300 protected areas. Most of these areas are terrestrial (1069), while 126 are coastal – defined as partially within the marine environment – and 62 are marine. The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA)[1] includes a wide range of protected areas, including national protected areas recognized by the government, areas designated under regional and international conventions, privately protected areas and indigenous peoples’ and community conserved territories and areas. Greenland is one of the countries with the largest protected terrestrial area (41,0%). [1] IUCN and UNEP-WCMC (2019), The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) [On-line], [January 2019]. Cambridge, UK: UNEP-WCMC. Available at: www.protectedplanet.net.
2019 January
- Arctic
- Environment